What's happened
A stroke is a sudden disruption of the normal blood supply to the brain.
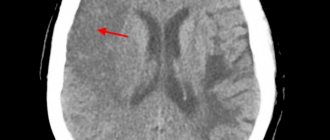
Based on the nature of the disorders, there are two main types of stroke: ischemic (often called cerebral infarction) and hemorrhagic (including subarachnoid hemorrhage). This article will talk about ischemic stroke, which is 4 times more common than hemorrhagic stroke. The word “ischemic” literally means that there is not enough blood flowing to one or another organ - with such a stroke, blood does not flow to the brain due to blockage or severe narrowing of the main arteries. As a result, brain tissue cells die.
Treatment
If an ischemic stroke is diagnosed, treatment should be started without delay. The main task is to normalize cerebral circulation. For this purpose, medications of different principles of action are prescribed. In addition, it is imperative to eliminate risk factors, including arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, and so on. Mandatory measures include nutritional correction and normalization of lifestyle.
IMPORTANT! Uncontrolled use of medications for ischemic stroke . All medications for ischemia should be prescribed only by the attending physician, because many drugs have a serious list of contraindications.
Causes and prevention of ischemic strokes
Most often, the cause of a cerebral infarction is the movement of a blood clot through an artery and clogging it in a narrow place. A thrombus is a blood clot that is primarily made up of platelets. With normal vascular patency, platelets are responsible for blood clotting, but with atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques form, narrowing the lumen of the artery, because of this, the usual blood flow is disrupted, side turbulence is formed, and platelets stick together into clots. Also, the cause of the formation of a blood clot can be an increased level of sugar in the blood: when it occurs, microtraumas form in the walls of the artery due to an increase in blood density, which also disrupts normal blood flow.
The cause of a cerebral infarction can also be a narrowing of the lumen of a large artery by more than half. You can read more about this using the example of carotid artery stenosis (note: link to article). When an artery narrows, the blood supply to the brain does not completely stop, so a person often experiences a so-called minor stroke. A minor stroke is similar in symptoms to a regular stroke. Although the degree of damage is much less, this condition requires immediate medical attention: further deterioration of the condition of the arteries can lead to a stroke with all its consequences.
A person cannot influence the movement of a blood clot through the vessels, but everyone can pay attention to a number of risk factors, eliminate them if possible, in order to prevent the formation of a blood clot and minimize the risk of ischemic stroke.
- It is important to undergo a course of treatment and periodically check your condition with a doctor if you have a chronic disease, such as diabetes mellitus, confirmed atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, or various disorders of the heart and blood vessels.
- Experts strongly recommend giving up tobacco and alcohol.
- It is advisable to maintain an active, mobile lifestyle.
- You need to monitor your diet and avoid a strong imbalance towards fats and fast carbohydrates.
The above points are effective measures to prevent not only stroke, but also many other diseases, proven through numerous studies.
But there are also risk factors that we cannot influence. Among them are old age (over 60 years old) and heredity (if immediate relatives suffered a stroke, or they were found to have serious vascular disorders).
Why it develops: the main causes of pathology
There are two main reasons that lead to cerebral ischemia . We are talking about atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension. People over 40 years of age are susceptible to the disease, because it is at this age that cholesterol begins to actively deposit on the vascular walls. Accordingly, the risk of getting sick increases. An unhealthy lifestyle is also a contributing factor.
There is another common cause of cerebral ischemia . We are talking about chronic heart failure. So, if the heart does not produce enough blood, the nutrition of the brain is automatically disrupted.
Other reasons that can lead to the development of the disease include:
- angiopathy of hereditary origin;
- renal pathologies;
- blood diseases;
- diabetes;
- impaired metabolism;
- endocrine system disorders;
- systemic vasculitis.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
Almost never a cerebral infarction is asymptomatic. You may have already come across actively distributed reminders on the timely recognition of a stroke: after all, it is very important to call an ambulance and provide medical assistance to the patient as early as possible - the earlier assistance is provided, the less brain damage.
The main symptoms of ischemic stroke are:
- dizziness,
- loss of orientation in space,
- vomit,
- convulsions,
- impaired coordination, speech, vision, writing, reading, swallowing,
- inability to move individual limbs and/or perform simple manipulations such as raising two arms at the same time, brushing teeth, or turning pages of a book.
The symptoms are extremely varied. They depend primarily on which particular part of the brain was deprived of blood supply - then exactly the function for which this part is responsible will be disrupted.
At the same time, all the symptoms do not appear; you may notice one or more - and this is a good reason to immediately call an ambulance.
Symptoms
If we are talking about an acute manifestation cerebral ischemia , then the symptoms of this condition are quite bright and distinct. The main thing is that treatment for ischemic stroke is started in a timely manner, then doctors give favorable prognoses. Symptoms directly depend on which area of the brain is affected.
Chronic cerebral ischemia can take years to develop. At the same time, brain activity noticeably deteriorates. The patient's psycho-emotional state also noticeably worsens and becomes depressed. Often the patient exhibits apathy, develops insomnia, hysteria, and depression. A characteristic symptom is difficulty concentrating, especially during mental stress. This condition is often accompanied by anxiety and fatigue. In this case, the symptoms may go unnoticed for a long time, but the disease progresses and develops every day.
Soon, without proper treatment , the symptoms described above are joined by terrible headaches and dizziness, and the patient often experiences nausea and even vomiting. Fainting occurs. When walking, coordination of movements is impaired.
Without treatment , dementia progresses, patients stop caring for themselves and are unable to work. To prevent dangerous conditions and complications of chronic brain , it is necessary to undergo diagnostic measures as soon as possible, during which the diagnosis will be accurately established, and to begin adequate therapy.
Diagnosis of stroke
Diagnosis of a stroke is quite complex, because to identify the cause and assess brain damage, and therefore the consequences of a stroke, the doctor will need a large amount of data.
To visualize the condition of the brain vessels, CT or MRI can be used, depending on the situation. A fairly informative study on the state of blood flow will be angiography - an X-ray examination using a contrast agent injected into the vessels.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe blood and urine tests; test for glucose and cholesterol levels; conduct an ultrasound examination.
Treatment in old age
If the patient is aged, the treatment ischemic stroke must take into account concomitant pathologies and the general condition of the patient’s body. sclerotic drugs, antihypertensive drugs, antiplatelet agents, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, membrane protectors, antidepressants, and so on are prescribed for ischemia
All medications are taken according to the schedule established by the attending physician. It is necessary to constantly ensure that the patient does not miss their appointment - this is extremely important and vital.
Motor rehabilitation
Passive gymnastics. Motor rehabilitation of patients who have suffered a stroke is an integral and one of the most important components of the recovery process. The basic method of motor rehabilitation is physical therapy, which begins as soon as the patient’s condition allows. The objectives of physical therapy include restoration (full or partial) of range of motion, strength and dexterity in the affected limbs, balance function, and self-care skills.
In the early period, immediately after a cerebrovascular accident occurs, passive gymnastics is performed. It allows not only to normalize the tone of the limbs, but also to prevent the formation of bedsores. Passive gymnastics is performed by exercise therapy specialists together with the patient’s relatives.
When performing gymnastics, passive movements of paretic limbs are performed at a slow pace, carefully, slowly, while trying not to cause pain or increase muscle tone. Such gymnastics is first performed on the healthy side and then on the sore side. It is important to start proximally, in isolation at each joint. In this case, 8–10 movements are performed in each joint.
Active gymnastics. The next stage of recovery is the beginning of active gymnastics, which begins with simple movements of the limbs and becomes more complex as the patient becomes more active. The patient is taught to sit up in bed, maintain balance and stand up, then walk, first accompanied or with support, and then independently.
Great importance is given to motor rehabilitation in the affected upper limb, in particular the restoration of fine motor skills, which is the key to full social and everyday readaptation. The patient learns simple self-care skills, in particular eating, personal hygiene, using the toilet and bathroom, as well as dressing independently, in stages.
The duration of the various stages of motor recovery depends, first of all, on the extent of the area of brain damage. An important part of rehabilitation, both motor and psychological, is the early involvement of patients in household work and the preparation of able-bodied patients to go to work.
Massotherapy
Along with physical therapy, positioning of the lying patient and therapeutic massage are important for the recovery of the patient. The purpose of these therapeutic measures is to prevent the development of muscle contractures and maintain normal joint function, prevent bedsores and pulmonary complications, primarily congestive (hypostatic) pneumonia. When conducting massage sessions, certain principles must be observed:
- the extensor muscles are usually massaged on the arm,
- on the leg - the flexor muscles of the leg and the dorsum of the foot.
Massage is carried out throughout the entire recovery period.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, acupressure, cryotherapy, and water procedures are widely used as additional methods that speed up the rehabilitation process.
Speech rehabilitation
Speech disorders after a stroke are observed in more than a third of patients who have suffered acute cerebrovascular accident. It is necessary to understand that the concept of “speech impairment” implies not only a violation of one’s own voluntary speech (motor aphasia), but also a violation of the understanding of the speech of others (sensory aphasia), forgetting of individual objects and actions (amnestic aphasia), and there are also combined manifestations of these conditions. Another common type of speech impairment after a stroke is dysarthria - a violation of the correct articulation of sounds while maintaining “inner speech”, understanding the speech of others, reading and writing.
The main factor for success in restoring speech functions is systematic long-term classes on the development of speech, reading and writing, which are conducted by a speech therapist-aphasiologist or under his direct supervision.
It is necessary to begin speech restoration classes in the acute period of a stroke, as soon as the level of consciousness allows. At this stage, classes are short - no more than 15-20 minutes. Subsequently, the duration increases to 30-45 minutes or more. In such a situation, speech isolation of the patient is very dangerous. Relatives and friends of the patient must understand that not only special classes, but also ordinary constant everyday speech contact with the patient and reading books in themselves contribute to the restoration of both his own speech and understanding of the speech of others. Consequently, the timing of the patient’s return to normal life after a stroke depends on the atmosphere created by the loved ones around him.
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Drug rehabilitation
Drug therapy in patients after a stroke is aimed at restoring the functions of the affected areas of the brain that were “inhibited” as a result of the cerebral catastrophe, improving cerebral blood flow, as well as preventing the development of postoperative complications.
Drug rehabilitation includes a range of metabolic drugs and biogenic stimulants. This group includes the following drugs:
- amino acids,
- adenosine triphosphate,
- B vitamins, etc.n
- nootropic drugs,
- Essentiale.
Biogenic stimulants include:
- ginseng tincture,
- aloe extract, etc.
Anticholinesterase drugs are prescribed according to indications, which include:
- oxazyl,
- prozerin,
- improving neuromuscular conduction.
If muscle spasticity is detected, muscle relaxants are used, such as:
- baclofen,
- isopropane,
- mydocalm.
In cases of increased plastic tone, cyclodol and other drugs are prescribed.
In the absence of contraindications, all patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke receive drugs that improve the rheological properties of the blood, in particular, aspirin and new generation antiplatelet agents (Plavix, Tiklid, etc.). Therapy is prescribed and carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
Classification
Ischemic stroke can be a consequence of one or another disease of the cardiovascular system. There are several pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke. The TOAST (Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment) classification, which is most widely used, distinguishes the following types of ischemic stroke:
- cardioembolic - ischemic stroke caused by arrhythmia, valvular heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- atherothrombotic - ischemic stroke that occurred due to atherosclerosis of the large arteries, which resulted in arterio-arterial embolism;
- lacunar - ischemic stroke caused by occlusion of small arteries;
- ischemic stroke associated with other, more rare causes: blood hypercoagulation, arterial wall dissection, non-atherosclerotic vasculopathies;
- ischemic stroke of unknown origin - a stroke with an unknown cause or with the presence of two or more possible causes, when it is not possible to establish an accurate diagnosis.
In addition, a minor stroke is distinguished when the existing symptoms regress during the first three weeks of the disease.
There are also several periods of ischemic stroke:
- The most acute period is the first 3 days. Of these, the first three hours were defined as a “therapeutic window”, when it is possible to use thrombolytic drugs for systemic administration. In case of regression of symptoms during the first day, a transient ischemic attack is diagnosed;
- acute period - up to 4 weeks;
- early recovery period - up to six months;
- late recovery period - up to 2 years;
- period of residual effects - after 2 years.
How many years do people live after a stroke?
Statistics answer the question of how many years people live after a stroke. As a rule, life expectancy is about 10 years, but in severe cases, death can occur immediately after the attack. Observations of specialists showed:
- some patients (30-35%) die in the first month after the attack;
- After the first year, only half of stroke victims are alive.
In addition, how long people live after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke also depends on the number of attacks.
Repeated cerebral circulatory disorders are extremely dangerous. So, if after the first attack the life expectancy is approximately 9 years, then the secondary attack reduces it to a period of 2 to 3 years. But what is the overall picture and how long will a person live after a repeated major, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke?
In such circumstances, only 5-15% survive the first year after an attack, and over the next 5 years - about 42% of men and 25% of women. There are many reasons for such sad statistics, but the main thing is that the factors that led to the blow do not disappear anywhere. That is, a predisposition to blood clots, vascular damage due to atherosclerosis, hypertension and heart problems still remain in the body.
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
The duration of life after an impact directly depends on such factors.
- The severity of the attack and the extent of damage to brain tissue. Sometimes the severity of the blow is excessive, which leads to death or a global reduction in the life expectancy of the victim.
- Consequences of vascular damage. A person with extensive paralysis is doomed to a lying position, which without proper care is fraught with bedsores and pneumonia.
- Immobility after an impact provokes the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities. Such blood clots, when they break off, often enter the lungs and provoke thromboembolism, which often leads to death.
- Ensuring the safety of a stroke victim. It is necessary to exclude falls caused by dizziness and weakness in the legs, since any fractures, especially the femoral neck, are quite difficult to treat in elderly patients.
- Age. This is an equally important factor, since young people are more likely to survive.
- General health.
Features of the rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after a stroke
After a vascular lesion of the brain, rehabilitation measures are mandatory, regardless of the severity of the lesions caused by the stroke. The entire recovery period can be divided into two stages: the first days after the attack within the walls of a medical institution and the rehabilitation period in special centers and at home.
Recovery stage in the first month after the attack
As a rule, doctors insist that the victim stay in a specialized department for 2 to 4 weeks. At this point, specialists of various profiles can reduce the entire therapeutic process to a specific system and further recovery. Disturbances in the blood supply to the brain lead to the formation of a focus of dead cells, and nearby cells often exhibit rather weak activity. To restore their normal activity, timely medical care is required.
It is better to remain under the supervision of specialists for some time after a stroke
First, patients are placed in the correct and comfortable position for them, and only then they begin physical therapy. Thanks to regular exercise and medication, brain cells begin to function more actively, which stimulates the restoration of damaged areas of the organ. But positive changes can only be achieved with a daily increase in loads. In the first 14 days, the victim is prescribed only a light massage with stroking and rubbing and procedures using electrical muscle stimulation. If the patient tolerated this stage well, then they begin to restore speech function.
- Life expectancy and consequences after left-sided ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation after discharge
Sometimes all the problems that arise can be eliminated in 2-4 weeks in the hospital, but if this does not happen, then the recovery stage is delayed. It is important for the victim to continue to systematically increase the load over the next two months.
The program of the therapeutic and gymnastic complex, carried out at home, is previously agreed upon with the local doctor. The neurologist develops an adaptation map, based on which all exercises and procedures must be performed. It should be noted that for older people (over the age of 70), a stroke is too severe a trauma, rehabilitation after which is almost impossible.
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Recovery in a boarding house
Rehabilitation of an elderly person after a stroke at home requires the full-time employment of one of the relatives for the next six months. While the patient is bedridden, he cannot be left at home alone for two reasons: he is helpless and it is necessary to deal with him several times a day. The volume of care is so large and multidirectional that soon the caregiver himself will need support and replacement.
In boarding houses for the elderly, professionals are involved in the rehabilitation of patients. Special equipment is used for treatment. An individual program is developed for each patient. Restoration methods that have been developed over the years produce positive results within a month.
Possible complications
If treatment for a long time or it is prescribed incorrectly, the brain will not receive enough oxygen. This, in turn, can lead to many disastrous consequences and dangerous conditions, including:
- ischemic cerebral stroke;
- necrotic changes in brain ;
- epileptic seizures;
- inflammatory processes in the veins of the lower extremities;
- development of thrombosis;
- vascular changes;
- paralysis.
Also, patients with ischemia treatment , their sensitivity is impaired, and severe pain becomes chronic and is felt constantly. Against this background, depressive syndromes often develop.
How can you increase your chances?
Each person is individual and their body copes with illness differently. Some stop walking and working, while others simply become less active. Anyone can recover, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and listen to your body.
The sooner you start rehabilitation, the faster your brain will recover. In the beginning, gymnastics and massage will help. The rehabilitation program includes exercise therapy and classes on robotic simulators.
Important! Stroke also affects the psyche. Often, the help of a psychiatrist is required.