The most common urological pathology for which men over 45 years of age consult a urologist at the Yusupov Hospital is prostate adenoma. The presence of this pathology significantly worsens the quality of life of men. One of the most dangerous possible consequences of the pathological process is the degeneration of benign prostatic hyperplasia into a malignant tumor.
To combat prostate adenoma, surgical and drug treatment methods are used. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital select the most effective medications or surgical methods taking into account the stage of the disease, the general condition and age of the patient, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. The surgery clinic has created comfortable conditions for treating patients.
Causes of development of prostate adenoma
The occurrence of adenoma is most often associated with age-related changes in the prostate, namely, changes in its structure and increase in size.
As a result of such changes, the urethra, which is located in the thickness of the prostate gland, is gradually compressed and disturbances in the urination process appear. Prostate adenoma in men develops as a result of hormonal changes in the body associated with age-related changes. The level of testosterone (male hormone) gradually decreases with age, while the concentration of the female sex hormone (estrogen), on the contrary, increases. This phenomenon is called male menopause.
The development of prostate adenoma may be due to the following risk factors:
- The age of the patient - an enlarged prostate gland is extremely rarely found in men under forty years of age, and after sixty years of age it is diagnosed in almost every second one;
- Hereditary predisposition - if prostate adenoma was diagnosed in close blood relatives of a man, he has a huge risk of inheriting this disease in adulthood;
- Diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases - a benign tumor (adenoma) of the prostate can arise not only as a result of these diseases themselves, but also the harmful effects of medications for their treatment (for example, beta blockers);
- Improper lifestyle – the risk of developing prostate adenoma is increased in men with obesity and insufficient physical activity.
Make an appointment
Why can the prostate become enlarged? What is the probability of getting sick?
Throughout life, the activity of organs is regulated by 2 systems: nervous and humoral. The latter includes hormonal regulation. It's no secret that the balance of hormones changes with age. In men, the amount of estrogen gradually increases, which leads to an increase in the activity of 5-alpha reductase. Under the influence of the enzyme, reactions occur:
- testosterone in prostate tissue is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT);
- DHT promotes increased division of prostate cells;
- hyperplasia leads to the formation of nodes from the paraurethral glands;
- as a result, the prostate tissue is pushed to the periphery.
Prostate adenoma develops under the influence of 2 main mechanisms:
- Enlargement of the prostate gland. This process leads to a gradual narrowing of the lumen of the urethra and, accordingly, urinary retention.
- Increased tone of smooth muscle fibers. The tense stroma of the prostate and posterior urethra leads to an even greater narrowing of the canal, aggravating the existing problem.
All cells of the organ participate in the enlargement of the prostate gland and the formation of nodes. “Adenoma” is more of a historical term, since it does not fully reflect the essence of the pathophysiological process in the organ. The term “benign prostatic hyperplasia” is able to more accurately reflect the essence of the pathology, since the formation of nodes occurs not only due to glandular tissue, but also the stroma.
In most modern documents, the abbreviation “BPH” is fixed, but “benign prostate adenoma” also remains common in colloquial speech.
Symptoms of prostate adenoma
Prostate adenoma in men can be suspected when a man develops the following symptoms, the most typical for this disease:
- increased urge to urinate;
- the need to tense the abdominal muscles to urinate;
- the presence of painful sensations, burning, sluggish stream of urine;
- discomfort and insufficient emptying of the bladder;
- increasing the duration of the urination process.
Prostate adenoma leads not only to a decrease in a man’s quality of life, but also to acute urinary retention, which requires the use of surgical treatment methods.
To avoid surgery, many patients use special medications to treat prostate adenoma, eliminating symptoms and restoring normal prostate function. However, only a qualified specialist can suggest the best remedy for prostatitis and prostate adenoma. You should contact him when the first symptoms of the disease appear. Treatment of prostate adenoma is individual for each patient. Drugs for the treatment of prostate adenoma, their dosage and duration of use are prescribed by the attending physician. Taking medications for prostatitis and prostate adenoma on your own can be not only ineffective, but also dangerous. Due to the presence of some “personal” chronic diseases in older men, drugs for the treatment of prostate adenoma in older people should be selected taking into account concomitant pathologies.
Can an adenoma transform into prostate cancer? Malignant neoplasm?
Prostate adenoma is a benign tumor. Its cells are well differentiated and perform their functions fully. Health problems develop precisely due to the increase in size of the organ. Adenoma cells cannot metastasize and grow into neighboring structures.
Previously, there was an opinion that the lack of treatment for prostate adenoma leads to the development of an oncological process. However, most modern studies deny this pattern. Most benign tumors in the human body are incapable of malignant transformation.
How does prostate adenoma develop?
Prostate adenoma is characterized by gradual development, which can be divided into three stages.
- The first stage of the disease occurs with minimal urination disturbances. There may be a slight increase in frequency, especially at night, and a sluggish stream of urine. The first stage can last from one year to 12 years or more.
- The second stage of prostate adenoma is characterized by more pronounced urination disorders: intermittent urine stream, the need to strain when urinating and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Residual urine, which is retained in the bladder and urinary tract, causes an inflammatory process, which is accompanied by pain, a burning sensation when urinating, pain in the lumbar region and above the pubis.
- The third stage is characterized by periodic or constant involuntary leakage of urine, which forces the patient to use a urinal.
Why is acute urinary retention dangerous?
Acute urinary retention is an insidious disease in which an enlarged prostate gland leads to obstruction of the urethra. If measures are not taken to force the outflow of urine (installation of a tube into the bladder through the anterior abdominal wall), then the following may develop:
- uremic coma;
- ascending pyelonephritis;
- urethritis;
- prostatitis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- hematuria;
- erectile disfunction;
- mental disorders (due to intoxication of the body);
- uncontrolled urination.
Lack of treatment leads to rapid deterioration of the patient's condition.
Complications of prostatitis
In some men, prostate adenoma does not impair the quality of life and proceeds without complications. However, in some cases, the disease can cause the following negative consequences:
- Acute urinary retention - it is characterized by a sudden inability to empty the bladder and pain in the suprapubic region. In such a condition, the patient requires emergency medical care with catheterization or minor surgery;
- The occurrence of infections in the urinary tract - stagnation of urine, which creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogens, leading to the development of cystitis and pyelonephritis;
- The formation of stones in the bladder is also a consequence of stagnation of urine;
- Damage to the bladder - when the bladder is not emptied regularly, it stretches and formation of protrusions (pockets) in the walls of the organ in which urine stagnates;
- Kidney damage – increased pressure in the ureters and bladder has a direct damaging effect on the kidneys, resulting in renal failure.
Prostate adenoma and potency
Prostate adenoma and potency are closely interrelated. Adenoma disrupts the structure of the gland tissue, which, in turn, leads to damage to another, no less important organ - the testicles, which are responsible for the production of androgens. Thus, prostate adenoma can cause impotence, requiring long-term and complex therapy.
Classification of benign prostatic hyperplasia
There are several main classifications of prostate adenoma that are currently used.
For example, there is a classification according to the stages of clinical manifestations. The main criterion in this classification: the amount of residual urine after urination:
- Stage: up to 40 ml of fluid remains in the bladder.
- Stage: the amount of residual urine varies from 40 to 100 ml.
- Stage: up to 1.5 liters of fluid remains in the bladder.
As a result, this leads to the formation of paradoxical ischuria. In this condition, there is constant leakage of urine. The bladder is distended, its muscle tone is reduced. As a result, the sphincters are open and cannot retain fluid in the bladder.
Another common classification of prostate adenoma (according to Guyon):
- Compensated stage. There is no residual urine in the bladder. In this case, minor urinary disorders are observed.
- Subcompensated. There is residual urine in the bladder. Complications begin to develop.
- Decompensated. An extreme form of the disease. With it, paradoxical ischuria is observed, and chronic renal failure also develops. Also, in the decompensated stage, ureterohydronephrosis may develop. In this condition, the ureters and pelvic system of the kidneys dilate.
The Guyon classification is outdated, but its use is considered acceptable in many countries around the world.
Diagnosis of the prostate gland in men
A simple and effective way to establish a preliminary diagnosis is for the patient to keep a diary of urination, recording quantitative and qualitative parameters: volumes of urine excreted, characteristics of fluid consumed, imperative urges, night urges. The main physical examination method for suspected prostate adenoma is a digital rectal examination of the prostate to detect its enlargement and exclude some other pathologies. Diagnosis of prostate adenoma at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using the following laboratory and instrumental methods:
- General blood and urine tests;
- Biochemical blood test for markers of kidney condition, urea and creatinine levels;
- PSA level analysis (to rule out prostate cancer);
- Transrectal ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- Uroflowmetry (to determine the speed of urine flow);
- Determination of residual urine volume (using ultrasound);
- Electromyography of the pelvic floor;
- Urethrocystoscopy;
- Excretory urography.
Surgical intervention
Surgical methods for treating prostate adenoma are varied. This can be a strip operation involving complete removal of the gland, intervention through punctures through the urethra.
Minimally invasive methods are also possible: excision of overgrown prostate tissue using laser therapy, radio waves, cryodestruction. These methods are quite effective and are less likely to cause complications. But they can be used in the first and second stages of the disease.
The key to success in treating and preventing the development of prostate adenoma is timely diagnosis of the disease in the initial stage. IMMA clinics have created comfortable conditions for conducting preventive examinations. An individual approach, attentive attitude to each client, and the professionalism of doctors make it possible to identify prostate adenoma in the early stages and prescribe effective treatment. The guarantee of the quality of medical services is the use of the latest methods of diagnosis and treatment of urological diseases.
Treatment of prostatitis - the most effective methods
Treatment of prostate adenoma is aimed at relieving symptoms of the lower urinary tract, improving the patient’s quality of life and preventing the development of complications of the disease. Patients with mild symptoms that do not impair the quality of life are often prescribed dynamic monitoring with regular examinations by a urologist, who monitors the course of the disease and gives recommendations on how to stop the growth of prostate adenoma. During this period, attention is focused on non-drug therapy. The methods described above can be an addition to conservative treatment, which consists of taking the following medications:
- Alpha blockers (Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin);
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Finasteride);
- Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (Sildenafil);
- Combinations of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and alpha blockers;
- Muscarinic receptor blockers or M-anticholinergics.
For patients with advanced stage prostate adenoma, surgical treatment is recommended, which can be performed by several methods: transurethral excision, transurethral resection and removal of the prostate.
There are certain indications for the use of surgical treatment:
- Recurrent urinary retention;
- Renal failure caused by prostate adenoma;
- Bladder stones;
- Recurrent urinary tract infections;
- Recurrent hematuria.
In addition, surgical intervention is necessary for patients in the absence of effectiveness of drug treatment.
During conservative therapy or in the postoperative period, patients require constant medical supervision with standard studies (determination of urine flow rate, ultrasound, analysis of PSA levels).
Make an appointment
Other tests
- Intravenous urography.
The urinary system (kidneys, urinary tract, bladder, urethra) can be examined using intravenous urography. The patient is given an injection of a contrast agent, then an x-ray of the abdominal cavity is taken. - Endoscopic examination
. Lower urinary tract endoscopy is also not a routine test. The test involves inserting a small device with a small camera at the end through the urethra and into the bladder. The image transmitted by the camera appears on the screen, allowing the doctor to assess the condition of the lower urinary tract. The method is also suitable for histological sampling if a malignant process is suspected.
Drugs for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma
There is a certain scheme according to which specific drugs are prescribed for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma.
High effectiveness of treatment is achieved through the use of drugs from the group of alpha-reductase inhibitors and alpha-blockers. These drugs for the treatment of prostate adenoma in men help eliminate the main symptoms of the disease, as well as restore sufficient urination. What are the most effective and widely used tablets for prostate adenoma? The list is topped by alpha1-adrenergic receptor blockers. In addition, this list includes 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, vitamins and minerals.
The complex of drug therapy includes not only drugs. For prostate adenoma, conservative treatment can be supplemented with biologically active additives - dietary supplements, which enhance the therapeutic effect of drugs and ensure a speedy recovery. Some of them contain zinc. This macroelement is directly involved in spermatogenesis and testosterone synthesis. Plant phytosterols normalize urination.
Treatment with drugs from the group of alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists
These drugs for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma provide relaxation of the smooth muscles of the urinary system and improve the process of urine discharge.
Tamsulosin, with the same name as the active substance, which is included in other drugs (Alfuzosin, Omnic, Silodosin, Urorek, etc.), is a highly selective drug that has a selective effect on alpha1-adrenergic receptors of the muscles of the prostate gland, prostatic urethra and bladder. Due to the decrease in muscle tone, the outflow and excretion of urine is facilitated. Tamsulosin, like all selective drugs, has minimal side effects, does not affect vascular tone and can be prescribed to patients with chronic hypertension. Alpha-adrenergic antagonists must be used continuously, thereby achieving a gradual reduction in irritation and obstruction in prostate adenoma. The drug Omnic in the treatment of prostate adenoma occupies a well-deserved priority in the prescriptions of urologists. It is produced by the Japanese company Astellas Pharma in the form of capsules and tablets (Omnic Okas). How long can you take Omnic without interruption? This directly depends on the stage of the disease. It is strongly recommended that for the risk of exceeding the dosage, consult your doctor about taking the drug and its dosage limits.
The tablet form of the drug is considered more progressive, since thanks to the controlled release of tamsulosin, the active substance is in the body in a constant concentration. The medicine enters the bloodstream evenly, thereby reducing the likelihood of developing the main side effect of drugs from the adrenergic blocking group - a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
An equally effective drug with the active ingredient tamsulosin is Urorek. Taking this drug is not accompanied by the following undesirable effects: orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, increased frequency of angina attacks in patients with coronary heart disease, so it can be prescribed to men with cardiac pathologies. Properly selected dosage and compliance with all rules for the use of drugs from the alpha-blocker group make it possible to achieve a good therapeutic effect with an almost complete absence of side effects.
Medicines from the group of reductase inhibitors (blockers)
Drugs of this pharmacological group (Finasteride, Penester, Alfinal, Dutasteride, Avodart) help facilitate the outflow of urine, and, therefore, eliminate the main symptoms of the disease.
A stable therapeutic effect occurs within two to three weeks after the start of the course. All symptoms disappear completely after three months. According to the results of clinical studies, maximum effectiveness is achieved after six months of therapy with these drugs. Finasteride and Dutasteride are specific inhibitors of type 2 5-alpha reductase (the cellular enzyme responsible for the transformation of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone). The growth of the prostate gland in prostate adenoma is directly related to a similar transformation of testosterone. Thanks to 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, the production of intraprostatic dihydrotestosterone is blocked and its concentration in the blood is significantly reduced.
Finasteride and Dutasteride are used for the following purposes:
- Treatment and control of prostatic hyperplasia;
- Improving the outflow of urine and eliminating the symptoms of prostate adenoma;
- Reducing the risk of developing acute urinary retention and the need for surgical intervention.
Finasteride and Dutasteride have a pronounced antiandrogenic effect, i.e. help reduce the level of male hormones in the blood. In addition, these drugs have a teratogenic effect, so they should be taken with caution. With the help of modern medications, it is possible to stop the growth of the prostate and prevent the need for surgical treatment.
Prostate adenoma in men, or BPH: what is the point?
The prostate gland is located in the pelvic area downward from the bladder. It affects the ejaculatory ducts and urethra, has an elastic consistency and consists of glandular and muscle cells. The important functions of this gland are the production of secretion to ensure the life of sperm, the creation of normal hormonal levels, and blocking the elements of the bladder at the time of ejaculation.
With the development of prostatic hyperplasia, benign tumor-like formations form in the prostate, which, as they grow, increasingly put pressure on the urethra, making it difficult for the normal passage of urine.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) also disrupts a man’s sexual function - the time of sexual intercourse is reduced, and a feeling of discomfort and pain appears during ejaculation.
With prostate adenoma, the gland stops secreting. It is filled with fibromuscular tissue. This is a type of connective tissue that has relatively high tensile strength. It consists of collagen and elastic fibers.
One of the main factors in the development of the disease is age. Often, prostate adenoma affects men whose age exceeds 40 years.
How do the symptoms manifest and what are the signs of prostate adenoma?
The manifestation of signs of prostate adenoma in men occurs in stages. The development of the disease is quite slow, and if the fibrous neoplasm is localized far from the urethra, its first stages develop asymptomatically. Further, as it develops, it will no longer be possible to ignore the disease.
Symptoms of prostate adenoma, or prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men are:
- Significant increase in the number of urges to urinate at night (up to 8 times).
- Urgent and sudden urge to urinate during the day.
- Difficulty passing urine.
- Low-intensity stream of urine.
- When the bladder is full, urine is released drop by drop.
- After urinating, there is no feeling of emptying the bladder, the desire to go to the toilet still remains.
- Problems with erection.
- Pain in the groin, radiating to the testicular area.
A man should seek medical help when he detects the first, even mild, signs of prostate adenoma.
Causes of prostate adenoma in men
The main cause and factor provoking the occurrence of prostate adenoma is age. According to research, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) occurs in approximately 50% of men after forty years of age. At the same time, of course, it cannot be said that pathology occurs in absolutely all men after this age. There are other causes of this disease, which together affect men’s health:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Inflammatory processes of the genital organs of a chronic form. Inflammations of an acute form can progress to the chronic stage, for which the necessary treatment was not prescribed (or the patient himself did not pay attention to his health, did not consult a doctor).
- Incorrect, unbalanced diet.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Excess body weight.
- Passive lifestyle, inactivity.
Causes of prostate adenoma can also be a man’s bad habits – alcoholism, smoking.
As can be seen from such a long list of reasons, some of them do not depend on the man (for example, heredity). But some risk factors can be prevented by monitoring your health, diet and lifestyle.
Types and stages of development
Prostatic hyperplasia is divided into types in diagnosis:
- Glandular – in the structure of the prostate the number of glandular elements increases.
- Fibrous - formed from connective and glandular tissue. It takes a lot of time to grow. Despite its benign quality, if left untreated for a long time, it can develop into cancer.
- Muscular – formed as a result of the growth of smooth muscle tissue of the prostate gland.
- Mixed.
According to the type of localization, the disease is divided into forms:
- Intravesical - the tumor partially extends into the cavity of the bladder.
- Prevesical - the lateral parts of the prostate adjacent to the bladder expand.
- Subvesical - the tumor is directed towards the intestine.
The disease develops gradually, slowly moving from one stage to another.
1st degree . The disease has mild symptoms and is expressed in a slight change in the dynamics of urine outflow, frequent urination at night, and a somewhat prolonged outflow of urine during the day. Perhaps the pathology will affect erectile function, but many men tend to attribute this symptom to fatigue and stress rather than to problems with their health. Often, first-degree prostate adenoma can be confused with similar diseases, such as cystitis and nephritis.
2nd degree . A man wakes up at night with the urge to urinate, but cannot easily empty his bladder (there is always residual urine in it). The desire to urinate does not disappear.
3rd degree . At this stage, in addition to all the symptoms described above, pain is added, which appears both during urination and during ejaculation. Pain in the abdominal area can bother a man even at rest. It becomes very difficult to empty your bladder. Always filled, it stretches, its walls lose sensitivity, and the muscles stop contracting. Constant discomfort makes a man irritable, his sleep and appetite are disturbed, weakness and chronic thirst appear. In other words, normal life activity and performance are almost completely disrupted.
Consequences and complications of prostate adenoma in men
The consequences of an untreated adenoma are as follows::
- Kidney dysfunction.
- Inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract.
- Urolithiasis (or urolithiasis).
- Varicose veins of the bladder neck.
- Impotence.
The complications mentioned above leave no doubt as to whether prostate adenoma is dangerous for men. Definitely yes.
Diagnosis of prostate adenoma: what procedures does a doctor prescribe to examine a man’s prostate gland?
Diagnosis of BPH begins with palpation of the prostate gland, which allows the doctor to draw conclusions about the size of the prostate itself and the approximate volume of benign hyperplasia. Next, to diagnose prostate adenoma, ultrasound or TPUS (or both procedures) is prescribed. TPUS is a more informative examination and is performed transrectally.
In case of prostate adenoma, the patient is also prescribed a referral for a blood test, which will show the number of antigens present in it.
In order to make sure that it is a benign tumor and not cancer, the patient is prescribed a biopsy of adenoma (hyperplasia nodes) of the prostate gland. Next, the biological material is transferred to the laboratory for microscopic examination for the presence of atypical cells.
These diagnostic procedures can be performed at any stage of development of prostate adenoma.
Antispasmodics and painkillers for exacerbation of the disease
The main purpose of antispasmodic and analgesic drugs during exacerbation of prostate adenoma is to alleviate the general condition of the patient and eliminate pain.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen) have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. They help fight not only the pain that occurs during urination, but also the constant pain in the groin and perineum. Thanks to the action of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the inflammatory process is reduced, swelling of the prostate gland is reduced, body temperature is normalized, and unpleasant symptoms are eliminated. Non-opioid analgesics, available in the form of tablets or suppositories, help relieve pain during exacerbation of prostate adenoma. The most accessible of them is Analgin. However, this drug is intended rather for one-time use, since it can only affect mild pain. In addition, analgesics with lidocaine, benzocaine, anesthesin and novocaine (Ichthyol, Anestezol, Procto-Glivenol) are effective.
Forms of BPH
Nodular form of prostate adenoma
- indicates that changes in prostate tissue are presented in the form of nodes.
Diffuse form
- implies that the process is evenly distributed throughout the prostate gland.
Focal prostatic hyperplasia
- may mean that the process is localized in a certain area,
Hyperplasia of the transition zones of the prostate
- indicates a shift in emphasis to the transitional areas of different lobes to the area of the upper urethra.
Vitamin E 400
Tocopherol acetate or vitamin E is often included in the complex treatment of prostate adenoma as an antioxidant, radioprotective agent and an indispensable link in reproductive processes.
Vitamin E in a dosage of 400 mg is prescribed by urologists to patients with disorders of erectile function and spermatogenesis associated with prostate adenoma. Treatment of such a serious chronic disease as prostate adenoma should be prescribed and monitored by a urologist. Taking certain medications on your own, without prior consultation with your doctor, is strictly prohibited, since self-medication in this case may not only be ineffective, but also dangerous for men’s health. Only a qualified specialist can tell you which tablets for prostate adenoma are the most effective in each specific case, and which of them can cause negative consequences.
Structure and functions of the prostate gland
The prostate is an organ that synthesizes and secretes a complex secretion that is part of the seminal fluid of men. It contains:
- acid phosphatase;
- lemon acid;
- fibrinolysin;
- prostate-specific antigen;
- protein complexes.
It is thanks to the secretion of the prostate that sperm become more mobile, which increases the possibility of fertilization. This fluid is released into the urethra during ejaculation.
Another important feature of prostate secretion is the ability to change the pH of the partner’s vagina. This results in sperm being able to survive for a longer period of time, which also increases the likelihood of conception.
The prostate gland is capable of growth throughout a person's life. This feature is associated with a thin capsule of the organ, which is well nourished by blood vessels. Significant enlargement of the prostate gland leads to pain and discomfort due to pressure on neighboring organs and systems. Therefore, men require complex treatment.
Operations
Urologists at the Yusupov Hospital masterfully perform classical and minimally invasive surgical interventions and use innovative methods of surgical treatment of prostate adenoma.
Each patient is selected for the operation that suits him best. The generally accepted standard in the surgical treatment of prostate adenoma is transurethral resection of the prostate. The operation is highly effective. After the intervention, patients get rid of bladder outlet obstruction (narrowing of the urethra) and associated symptoms. The rehabilitation period is short. During or after surgery, bleeding and “water intoxication” syndrome may develop in the body.
Alternative methods of treating prostate adenoma include the following surgical interventions:
- Stenting;
- Balloon dilatation;
- Hyperthermia;
- Thermotherapy;
- Ultrasound, laser and needle ablation;
- Interstitial coagulation.
After them, complications occur less frequently, but these techniques are inferior to transurethral resection in terms of effectiveness, both clinically and economically.
Laparoscopic removal of prostate adenoma is used when the tumor has grown significantly, and removing it using transurethral resection is problematic. This operation is more complicated and is performed under anesthesia. Through small incisions, the surgeon inserts special instruments into the body cavity, which are used to remove the prostate adenoma. The operation is carried out using images from video cameras, which are displayed on the screen. The main advantages of the intervention are minimal blood loss and low likelihood of complications. After the operation, the patient does not need long-term rehabilitation.
When there are signs of prostate adenoma in men, doctors use a high-tech method of treating adenoma - laser enucleation. The intervention is carried out when the tumor is large. Excess tissue is removed using a laser. The operation is performed through the urethra. The tumor is separated, divided into small parts, and then removed. The method is considered minimally invasive. It has a number of significant advantages: it does not violate the integrity of cavities and does not cause unnecessary damage.
Laser vaporization involves destroying the adenoma by laser evaporation. The urologist inserts a special device through the urethra, brings it to the tumor and precisely targets it with a strong green laser. The depth of penetration of the laser and the accuracy of its impact make it possible to avoid damage to neighboring areas. The method is minimally invasive, bloodless, fast and effective. Its only drawback is the inability to take tumor tissue for histological examination.
In some situations, the inevitable method of treating prostate adenoma is abdominal surgery - adenomectomy. It is performed when other methods cannot help the patient. During surgery, the surgeon uses a scalpel to access the prostate gland and manually, using surgical instruments, removes the adenoma. As a result of the operation, significant blood loss and complications may develop. After surgery, the patient needs long-term rehabilitation.
Removal of prostate adenoma using transvesical (transvesical) adenomectomy involves radical excision of hyperplastic prostate tissue through a longitudinal incision in the anterior abdominal wall and bladder. The operation is performed in advanced stages of the disease, when the tumor reaches a large size, the bladder is overstretched due to its overflow with accumulated urine, and renal failure develops.
The bladder is pre-catheterized and filled with a sterile solution of furatsilin or another substance. Then it is isolated and taken in two places on special holders, for which the wall of the organ is lifted. The surgeon cuts through the resulting fold and opens the bladder.
Along the inner end of the installed urinary catheter, the area of the bladder neck is determined and around the urethral opening that appears in the field of view, stepping back from it by 0.5-1 cm, an incision is made in the mucous membrane. After this, the operating urologist penetrates the thickness of the prostate with his finger, enters it between the tumor capsule and adenomatous nodes, and removes the latter. At the same time, with the finger of the other hand, which is first inserted into the patient’s rectum, the doctor moves the gland towards the anterior abdominal wall. It becomes more accessible to manipulation. Thanks to this technique, the operation time is reduced and blood loss is reduced.
Then the surgeon performs hemostasis (stopping bleeding) of the bed of the removed adenoma and suturing the bladder, leaving a thin drainage in the wound. It is designed to wash its cavity from formed blood clots. The urinary catheter inserted before the operation is not removed for 7-10 days. A new section of the urethra is formed around it instead of the prostatic part of the urethra excised during the operation.
Transvesical adenomectomy is one of the most traumatic of all techniques used for prostate adenoma. It is accompanied by the risk of developing the following complications:
- Bleeding from the tumor bed;
- Congestive pneumonia;
- Violation of the motor-evacuation function of the intestines, manifested by constipation.
To avoid complications, after surgery at the Yusupov Hospital, the patient undergoes early activation. The following undesirable consequences of surgery to remove prostate adenoma may occur:
- Insufficient drainage of the bladder;
- Narrowing of his neck;
- Urinary infiltration of peri-vesical tissue;
- Formation of a “pre-bladder” (residual cavity in the place where the prostate adenoma was removed);
- Formation of narrowing of the lumen of the urethra;
- Urinary incontinence.
This negatively affects the quality of life of patients and prolongs the time required to restore adequate urination.
The consequences of the operation are less pronounced when the intervention is performed using a laparoscope. Laparoscopic surgery to remove prostate adenoma is one of the less invasive options for surgical interventions on the prostate gland. Urologists at the Yusupov Hospital use this technique if the patient has a sufficiently large prostate adenoma.
If the size of the prostate gland of a patient with adenoma does not exceed 120 cm3, transurethral resection of the prostate adenoma is recommended. But for 10% of patients who need surgical intervention, this option is not suitable, since the gland reaches a size of more than 120 cm3. Laparoscopic surgery to remove prostate adenoma is not performed for urolithiasis, inguinal hernia, bladder diverticula, or ankylosis of the joints of the lower extremities. In this case, the decision on the possibility of performing an operation is made collectively by a urologist, andrologist, abdominal surgeon and other specialists at the Yusupov Hospital.
With laparoscopic access, general anesthesia is used. Laparoscopic removal of prostate adenoma is carried out using specialized equipment. The surgeon uses trocars through which he passes laparoscopic instruments to the prostate gland. The trocar is equipped with a small video camera that transmits the image to the screen. This way, surgeons have the opportunity to perform all actions as accurately as possible.
Laparoscopic surgery to remove prostate adenoma has the following advantages over open adenomectomy:
- During the operation, bleeding and complications occur much less frequently;
- The pain syndrome is less pronounced, the patient does not need a large amount of analgesics;
- Bladder catheterization does not last long;
- Physical activity is restored faster, the next day after the operation the patient can walk without difficulty.
- Hospitalization after laparoscopic adenomectomy takes much less time. The patient quickly returns to normal life. He has no cosmetic problems. The length of scars after surgery does not exceed one centimeter.
After laparoscopic removal of prostate adenoma, the need for repeated surgery is minimized, since a significant part of the prostate tissue is removed.
Embolization of prostate arteries is one of the most modern methods of treating adenoma. It is used more often abroad. The operation involves blocking the blood vessels supplying the prostate adenoma. An endovascular surgeon for large blood vessels brings a microcatheter to the source of blood supply to the tumor and injects a special composition that blocks the blood flow. As a result, the tumor does not receive oxygen and nutrients, and it decreases in size. Contraindications to the use of this method are malignant tumors, allergies to contrast and embolic agents, cardiovascular pathology, some chronic diseases of internal organs, and acute diseases.
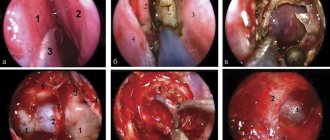
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a method of removing prostate adenoma without external incisions. The intervention is performed using a special instrument (resectoscope). The urologist inserts it into the patient’s bladder through the urethra. After examining the urethra, bladder and the actual area where the prostate adenoma is located (the border of the urethra and bladder), the surgeon removes the prostate adenoma using a special device - a loop. Transurethral resection of the prostate requires good visibility. It is ensured by a constant flow of fluid through one of the resectoscope channels and outflow through the other channel. Visibility may be impaired due to bleeding from blood vessels. During the operation, the surgeon stops the bleeding in order not to lose orientation in the tissues.
Transurethral resection of the prostate is used if the size of the prostate gland does not exceed 80 cm3. The adenoma is removed until the tissue of the gland itself is visible. After the prostate adenoma is removed, the tissue is washed from the bladder using a special instrument, and a control examination of the surgical site and the bladder is carried out. If necessary, additionally stop bleeding from blood vessels. After this, the surgeon removes the operating instrument (resectoscope). A special Foley catheter is passed through the urethra into the bladder. An inflating balloon is located at the bladder end of the catheter. After the catheter is inserted into the bladder, the balloon is filled with fluid. It takes the place of the removed adenoma, which helps stop bleeding from small vessels and prevents the catheter from falling out of the bladder. In this case, minimal consequences are observed after removal of the prostate adenoma. Patient reviews of the operation are excellent. Recovery after removal of prostate adenoma occurs quickly.
Transurethral resection of the prostate is one of the most complex and precious operations in the entire spectrum of endoscopic urological surgery. Urologists at the Yusupov Hospital have undergone special training. Surgeons are fluent in the technique of this surgical intervention.
Transurethral electrovaporization combines the advantages of standard transurethral resection (the possibility of immediate removal of tumor tissue, optical control of the intervention, clinical and economic efficiency) with a significant reduction in blood loss during and after surgery, preventing “water intoxication” of the body. Electrovaporization of the prostate also has disadvantages. “Roller vaporization” is technically simple, there is good endoscopic visibility, there is no bleeding, but, compared to monopolar transurethral resection, it has a lesser ability to remove hyperplastic tissue. Roller vaporization is used as monotherapy for prostate adenoma with a volume of no more than 40 cm3. Vaporizing resection is not inferior in efficiency and speed to standard transurethral resection. It is just as difficult to master, since the hemostatic effect of the vaporizing loop is not as pronounced as the “roller vaportrode”, and the technique of cutting and removing prostate adenoma requires considerable experience of the surgeon.
New methods of transurethral endoscopic treatment of prostate adenoma include rotoresection. The technique combines electrovaporization, coagulation and mechanical removal of the prostate tumor with a rotating electrode. Due to sufficient depth of coagulation, good bleeding control is ensured during surgery, and the simultaneous mechanical removal of dehydrated and carbonized tissue with a rapidly rotating rotoelectrode allows the urologist to continue effective ablation by evaporation. Patients of the Yusupov Hospital have the opportunity to receive all complex methods of treating prostate adenoma at partner clinics.
What is the prostate
The content of the article
The prostate is a unique organ located in the male pelvis between the bladder and rectum at the beginning of the penis. The organ surrounds the cervical part of the bladder and the initial part of the urethra. It consists of connective tissue, smooth muscle and glandular tissue.
The glands of the prostate produce secretions, which during ejaculation (the release of sperm during sexual intercourse) penetrate the urethra and mix with the secretion of the seminal vesicles. The role of the secretor is to ensure the viability and fertilization of sperm cells with the carbohydrates, enzymes, minerals and other ingredients it contains.
Prevention of the prostate gland in men
There are certain rules for the prevention of prostate adenoma, following which you can maintain the health of this important organ:
- Follow a diet - reduce consumption of red meat and fatty foods. A man's diet should be dominated by vegetables, fruits, and omega acids;
- Increase physical activity – physical exercise has a positive effect on prostate health;
- Control your body weight – this will significantly reduce the risk of developing prostate adenoma;
- Minimize stress – will improve hormonal levels and slow down the development of the disease;
- Have an active sex life;
- After 45-50 years, be systematically examined by a urologist and take an analysis of the dog’s blood level.
Prostate adenoma, detected in the early stages of development, can be corrected with medication and non-surgically without any problems.
Timely contacting a urologist and unquestioningly following all his instructions for treating the disease in almost all cases guarantees stopping the growth of the gland and preventing urinary disorders. Late stages of the disease with symptoms that significantly reduce a man’s quality of life will require the use of surgical treatment methods. Therefore, early diagnosis of prostate adenoma is of great importance, which can be done in the modern medical center of Moscow - the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic’s high-tech diagnostic equipment ensures the most accurate research results, thanks to which Yusupov Hospital specialists select an effective individual treatment regimen for each patient, whenever possible, giving preference to non-surgical, gentle treatment methods.
Make an appointment
Causes of the disease
Despite the widespread prevalence of the disease, the exact causes of the disease have not been identified. There was a connection between the disease and the age of the patients. This phenomenon is associated with hormonal changes: a decrease in male sex hormones and an increase in female ones. Estrogen promotes the growth of glandular tissue.
The following reasons aggravate the situation:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excess body weight;
- heredity, the presence of the disease in close relatives.
Recent studies have shown that such phenomena as promiscuous sexual relations, their absence, the presence of bad habits, and infections do not provoke the development of adenoma.
Prostate adenoma should not be confused with prostatitis - these are two different diseases. The first is characterized by tissue growth, the second by the development of an inflammatory or infectious process.
Scientists have identified a connection between eating behavior and the risk of adenoma. Eating large amounts of fatty, smoked, and salty foods aggravates the development of the disease.
Interesting! There is a racial predisposition to the disease. For example, representatives of the Negroid race suffer from adenoma more often than others. Asians are least susceptible to the disease.
Surgery
The purpose of surgery in the late stages of prostate adenoma is to eliminate compression at the level of the prostatic urethra.
Indications for surgical treatment :
- severe compression of the urethra;
- ineffectiveness of taking medications;
- painful symptoms of adenoma (for example, frequent debilitating urge to urinate);
- complications of adenoma (renal failure, urinary stones, blood in the urine, chronic urinary retention).
Indications for emergency hospitalization in a urological hospital :
- Acute urinary retention - manifested by a complete cessation of urine flow from the urethra, bloating of the lower abdomen, and an increase in pain in the bladder area;
- The development of acute renal failure, which is clinically manifested by a sharp decrease in urination, an increase in edema, deterioration of the condition, up to loss of consciousness, an increase in the concentration of potassium, urea, and creatinine in the blood;
- Blood in the urine and the possibility of blockage of the bladder with clots.
Types of surgical interventions
Prostate TOUR
Transurethral resection of the prostate gland.
It is the “gold standard” for surgical treatment of BPH. TUR is the main type of surgical intervention for medium-sized prostate adenoma.
It is used for prostate volume from 30 to 80 cm3.
Performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia, it is a very gentle method of surgical treatment in terms of complications. It involves burning out the prostate tissue that has blocked the lumen of the urethra using a special device using an electric resectoscope.
The average operation time is up to 1 hour. Rehabilitation may require 4 to 6 weeks. In the postoperative period, discomfort may appear during urination, blood in the urine, signs of inflammation, and sexual activity may be delayed.
In the postoperative period, the patient takes tablets: adrenergic blockers and anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics.
Open adenomectomy
Removal of the prostate gland. The operation is performed through the bladder, but an operation through the perineum is also possible.
It was first performed more than 100 years ago, but is still used in patients with large prostate sizes greater than 80 cm3.
Open adenectomy is recommended as the standard of care for such adenomas by the European Association of Urology.
Prostate removal is performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. This type of operation is more traumatic, but the effect is more lasting and there are no relapses. The operation time is more than 1.5 hours, longer than with TUR, the recovery period is up to 3 months.
During the operation, a catheter is inserted into the abdomen to drain urine, which is removed after 2 weeks. Time spent in hospital is 2-3 weeks.
Laparoscopy
Gentle surgical techniques for large prostates are becoming increasingly popular - laparoscopic removal of the prostate gland using special instruments and several small holes in the abdomen. Such operations reduce the operation time and the likelihood of complications.
One of the options for laparoscopic surgery is robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) using the Da Vinci robot. RARP is actively “displacing” open prostatectomy in the treatment of large prostate adenoma throughout the world.
With RARP, compared with conventional adenomectomy, the volume of blood loss is significantly reduced, and there are advantages in assessing the restoration of urinary continence and erectile function.
Alternative treatments for prostate adenoma :
All these methods have a certain significance and can constitute a worthy alternative to surgical treatment of the prostate gland.
- Stenting of the prostatic part of the urethra with temporary and permanent devices - stents;
- Hyperthermic effects on the prostate gland with temperatures from 40 to 100 degrees;
- Laser technologies: vaporization (evaporation) of the prostate gland with a “green” laser beam,
- laser resection of the prostate,
- laser coagulation,
- holmium enucleation HoLAP - a variant of evaporation of the affected prostate gland with two different laser radiations, developed by New Zealand urologists;
Despite their good effectiveness, alternative methods of treating prostate adenoma are quite expensive, are not included in the compulsory medical insurance system, and there are few clinics performing these methods in Russia.
"Ethnoscience
Many patients with prostate adenoma use herbal preparations for therapy. Herbal preparations undoubtedly have some effect, but extensive clinical international studies have not been conducted on them! Therefore, the use of these drugs is of an auxiliary nature. In Russia, products isolated from African palm trees are widely used: Serenoa repens (Prostamol UNO, Permixon), Pigeum Africanum (Pidgeum), Hypoxisrooperi (Hypoxis).
Of the domestic traditional medicines, the following are most often used as additional restorative therapy for prostate adenoma:
- Beekeeping products (honey, bee bread, dead bees, propolis) - inside;
- A decoction of young aspen bark;
- Decoction of fireweed (angustifolia fireweed);
- Red root decoction (Altai endemic - forgotten kopeck) decoction;
- Pumpkin seeds (contain zinc, so necessary for the prostate) up to 50 pieces per day orally;
- Burdock root decoction.
In addition, in Russia, products from animal raw materials are actively used - the prostate of bulls, in suppositories and injections.
Such drugs as Vitaprost, Prostatilen, Prostakor and Samprost. There are only Russian studies on these drugs, and a certain effect occurs, especially with concomitant prostatitis, but, again, there have been no broad international research programs.
Hirudotherapy (leech treatment), which reduces inflammatory edema and improves blood circulation in the prostate area, is of some importance in terms of symptomatic treatment of prostate adenoma. However, such therapy is fraught with bleeding and should be carried out only by qualified specialists.
Important! It should be clearly understood that all of the above remedies have a rather uncertain effect, therefore, if symptoms of prostate adenoma develop, a visit to a urologist is mandatory!
Useless remedies and contraindications
The following have a completely incomprehensible effect: shock wave therapy, Sytin's moods, salt dressings, urine therapy, Thermex, magnetotherapy, microenemas, Vitafon, Almag, hydrogen sulfide baths, phonation, Chinese urological patch, radon baths, various dietary supplements, homeopathy, treatment salt according to the method of Professor Okulov, hydrogen peroxide according to Neumyvakin, beaver stream, indigal, adenorphine and other “exotic” agents.
Important! In case of prostate adenoma, are contraindicated , otherwise this can lead to progression of the disease and even the development of oncology.