Diseases of the retina and choroid can occur in acute and chronic forms. Chronic diseases include dystrophies and degenerations (central and peripheral), angioretinopathy of various natures, inactive and subactive phases of chorioretinitis.
Therapy for these diseases comes down to regular use of medications prescribed by an ophthalmologist. As a rule, it is recommended to take comprehensive courses twice a year, which include up to five types of drugs from several groups. Thus it turns out: 2 months of treatment, followed by a four-month break. It is better to combine one of the annual courses of therapy with local treatment - subconjunctival and parabulbar injections, and leave local instillations for the second annual course.
Drugs prescribed for annual courses of treatment are divided into the following groups: retinoprotectors, angioprotectors, anticoagulants, stimulants, absorbents, improve microcirculation, vasodilators, vitamins and drugs that activate tissue respiration. At the same time, one drug may have several specific properties and be in different groups. And drugs from the same group can have completely different effects on the body. For example, vasodilator drugs sometimes lower blood pressure, do not change it in any way, and in some cases they increase it. In this regard, the schemes of therapeutic courses are built taking into account the individual characteristics of a particular patient. To avoid polypharmacy, it is always better to choose 2 or 3 drugs that are completely suitable for the patient and will have the necessary complex effect on his body.
How to improve cerebral circulation?
December 12, 2022
1803
5
Content
- Why is it important to maintain normal blood circulation in the brain?
- Cerebrovascular accident and stroke
- Why does cerebrovascular accident occur?
- What should you do to prevent stroke?
- What medications are there to prevent stroke?
- Drugs for stroke prevention
- Warfarin
- Dilakor
- Cinnarizine
Our brain is, in fact, the center that controls the entire body. The brain regulates the functioning of muscles, organs and systems, and is responsible for memory, thinking, attention and speech. Unfortunately, cerebral circulation can deteriorate with age, due to certain diseases or due to stress. In this article we will talk about the causes of cerebrovascular accidents and stroke prevention.
Read also: Top 10 best blood thinners Blood thinners
Why is it important to maintain normal blood circulation in the brain?
Our ability to perform any action, eat, move, breathe, think, learn depends on the proper functioning of the brain. And it is very important that cerebral circulation is in order.
The blood that flows through the vessels of the brain supplies the nerve tissue with nutrients, glucose and oxygen. All of them are necessary for the proper operation of this “biological computer” even at rest, not to mention active mental or physical activity.
If blood circulation is impaired, the brain does not receive enough necessary substances, oxygen starvation occurs, metabolic processes suffer, and intoxication develops. What does this mean?
- If blood circulation to the brain is constantly impaired, cognitive abilities deteriorate. A person’s learning is worse, memory and attention deteriorate. Both mental and physical performance decreases.
- Poor blood circulation in the brain leads to problems with the autonomic system: dizziness, headaches, loss of balance, increased weather sensitivity, etc.
- Mental disorders are also often the result of impaired blood circulation in the brain. The person becomes depressed, irritable, and experiences frequent mood swings.
Factors that increase the risk of cerebral circulatory disorders
Read also Drugs to improve memory: neurologists recommend Drugs to improve cerebral blood circulation and memory.
Why does cerebrovascular accident occur?
There are many factors that provoke cerebrovascular accidents. Among them:
- hypertension;
- heart diseases;
- atherosclerosis;
- increased blood density (usually blood viscosity is increased in diabetes mellitus, heart and respiratory failure, autoimmune problems, etc.);
- cervical osteochondrosis (being deformed, the vertebrae compress the arteries through which blood flows to the brain);
- excess weight (obesity is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases);
- unhealthy diet (if the diet contains a lot of animal fats, the level of cholesterol in the blood increases - this leads to atherosclerosis);
- bad habits (alcohol and smoking). Smoking, for example, disrupts vascular tone, which increases the risk of atherosclerosis;
- taking certain medications that thicken the blood (primarily hormonal birth control pills);
- overwork and frequent stress.
Most often, symptoms of circulatory disorders are noticed by older people. This is because with age the number of chronic diseases increases (atherosclerosis, for example, is present in 100% of older people). With age, the walls of blood vessels lose their elasticity and become thicker - the blood supply to all organs, including the brain, is disrupted.
Therefore, the issue of improving blood circulation in the brain in old, middle and even young age is very relevant (after all, many diseases today have become “younger”).
Angioprotectors
These are substances that help normalize the permeability of vascular walls, reduce swelling of vascular tissue, and accelerate metabolic processes in the vascular wall. The angioprotective effect is fully possessed by: vitamin P, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, as well as the following medications.
Doxium, the main substance of which is a special form of calcium dobesylate, necessary for strengthening the walls of blood vessels. This drug is needed to increase capillary resistance, improve blood microcirculation, and stimulate drainage function in lymphatic vessels. It thins the blood and slightly reduces platelet aggregation, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the retinal tissue. Does not have any effect on microaneurysms and does not significantly penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
The tablet form of the drug is prescribed at the rate of 0.75-1.0 g per day, which is 3-4 tablets, which are drunk after meals. The course of treatment is quite long and can last a year or a year and a half.
Among the negative aspects of taking the drug, experts note dyspepsia and allergic skin rashes. This is a reason to reduce the dose or completely cancel it. Not prescribed during pregnancy.
Ascorbic acid is a drug for normalizing the permeability of the capillary wall, improving redox reactions, and regulating carbohydrate metabolism. In addition, ascorbic acid helps reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, accelerate tissue regeneration, and stimulate the production of steroid hormones. This property of the drug is very important if a course of steroid therapy is necessary.
Prescribed in injections or tablets. Dosage for tablets: 0.05-0.1 g up to 5 times daily, with intramuscular administration of a 5% solution - 2.0 ml No. 20-30. Intravenous injections in the same dose are also possible, although it must be taken into account that in the case of thrombosis, thrombophlebitis or increased blood clotting, they are contraindicated.
Flavonoid Rutin is a drug that reduces capillary fragility and permeability (especially in combination with ascorbic acid). Together with it, it is a participant in redox reactions and slows down the action of hyaluronidase.
The daily dose of Rutin is usually 0.1 g, prescribed in combination with ascorbic acid. Ascorutin tablets are mass produced, including rutin with ascorbic acid and glucose. The therapeutic course involves taking them 4 pieces per day. It has no contraindications or side effects.
Troxevasin (venoruton) is a drug with an action close to rutin. Regulates capillary permeability, fights swelling and tissue inflammation. In capsules, prescribed one at a time with meals, for a course of 2-4 weeks.
Divascan is a hemostatic drug that reduces microvascular permeability. Available in tablets, which are prescribed one three times a day. Patients with diabetic retinopathy or intraocular hemorrhages are recommended to take without interruption for at least two years.
Dicynone (etamsylate) is a substance that increases the content of high molecular weight mucopolysaccharides in the capillary wall, which increases their stability and normalizes permeability. The drug has the property of improving microcirculation, normalizing platelet adhesion, and has a hemostatic effect without promoting the formation of blood clots.
Prescribed orally or intramuscularly. The daily dose in tablets is 1.5-2.0 g, duration of administration is 2-3 months. IM injections are prescribed for 10-14 days; they can be combined with subcutaneous administration of this drug at a dose of 0.5 ml.
To prevent bleeding during surgical interventions, Dicynon is administered intramuscularly before and after surgery if there is a risk of postoperative bleeding.
The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with thrombosis and embolism. There are no side effects.
Prodectin (parmidin) is an angioprotector drug whose action is aimed at restoring microcirculation. It helps reduce platelet aggregation, activates fibrinogenesis, and improves the condition of the vascular endothelium. Prodectin has a pronounced anti-sclerotic effect and accelerates the disappearance of signs of intoxication.
Its intake is 4 tablets daily (1.0 g), for a course of up to 6 months.
Side effects include nausea, occasionally allergic skin rashes, and headache. When the dosage is reduced or the drug is discontinued, all phenomena disappear. Contraindications for use are liver disease.
Emoxipine helps reduce blood viscosity, reduce the permeability of vessel walls, and resolve hemorrhages. It is a retinoprotector and antioxidant, protects the retina from the negative effects of bright light (laser coagulation, sunburn). It is prescribed for hemorrhages, retinopathy, complicated myopia, retinal dystrophies, thrombosis of its veins, light or radiation burns of the eyes, and glaucoma. It is also a component of complex treatment for laser coagulation.
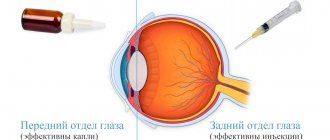
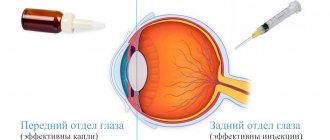
Prescribe one injection into the eye (subconjunctival, retrobulbar, parabulbar) of a 1% solution in a dosage of 0.5 ml every day for 10-15 days. If necessary, the course of treatment is extended to 30 days and repeated several times a year. Sometimes the drug is used in the form of eye drops.
Its side effects may include: itching, burning, pain, related to allergic reactions. They are relieved by using corticosteroids. Sometimes during injections, compaction of the orbital tissue is observed, which subsequently resolves on its own.
What should you do to prevent stroke?
The most important thing to prevent cerebrovascular accidents and stroke is to control blood pressure. Studies are also needed to show the condition of the blood vessels:
- fundus examination;
- pressure measurements throughout the day;
- ECG;
- general blood test and biochemistry;
- coagulogram (diagnosis of blood clotting);
- control of all chronic diseases that increase the risk of stroke (heart disease, diabetes, carotid artery stenosis).
Stroke Prevention
What medications are there to prevent stroke?
There are many drugs on the market today with different effects that improve cerebral circulation. Such treatment can only be selected by a doctor after a thorough examination. Types of drugs for stroke prevention:
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents.
Such medications are prescribed to prevent thrombosis. They thin the blood, help it flow faster, and prevent blood clots from attaching to the walls of blood vessels. Among such drugs: “Cardiomagnyl”, “Curantil”, “Warfarin”, “Trental”, “Thrombo ACC”. - Vasodilators.
These drugs improve blood circulation in the brain, dilating blood vessels and reducing blood pressure. Thanks to this, the blood better nourishes the tissues. Brain hypoxia passes, and it begins to receive all the necessary nutrients. Among such drugs: “Enalapril”, “Isoptin”, “Phenigidine”, “Verapamil”, “Dilacor”. - Nootropics.
Such drugs improve metabolic processes in tissues, improve blood circulation in the brain, and help brain cells function properly during oxygen starvation. Typically, such drugs are prescribed in complex therapy for the treatment of chronic or acute cerebrovascular accidents. Among such drugs: Phezam, Piracetam, Cinnarizine, Cerebrolysin.
Anticoagulants
Heparin , as an active substance, has a multicomponent effect: absorbable, lipotropic, anticoagulant. It is prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections according to the following scheme: the first 4 days, 4 daily injections, the next 4 days, 3 injections, then 4 days, 2 injections and another 4 days, 1 injection.
The dosage is up to 5000 units. The drug is not used in large doses as complications are possible.
Iodine preparations are prescribed to increase the fibrinolytic activity of the blood. In addition, they reduce the content of b-lipids and cholesterol. Prescribed orally 5-10 drops in milk twice or thrice a day, or in the form of pills with a dosage of 0.0005 g. The course of treatment is at least one month, carried out intermittently for many years.
Warfarin
"Warfarin" is prescribed to prevent blood clots; this vasodilator slows down blood clotting, being an anticoagulant. This remedy has been used successfully in many countries for a long time. The dosage of Warfarin is determined by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the individual patient. Often this medicine needs to be taken for a long time, in some cases for life. "Warfarin" is indicated for patients for the prevention of thromboembolic complications in atrial fibrillation, for patients with lesions of the heart valves or with prosthetic heart valves, for the treatment and prevention of strokes and transient ischemic attacks, for the prevention of thrombus formation after operations.
Warfarin
OZON, Russia
Treatment and prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, transient ischemic attacks and ischemic stroke.
Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction and prevention of thromboembolic complications after myocardial infarction. Prevention of thromboembolic complications in patients with atrial fibrillation, heart valve disease or prosthetic heart valves. from 45
627
- Like
- Write a review
Dilakor
The active substance of this cardiotonic drug is digoxin, extracted from woolly foxglove. This plant is a natural cardiac glycoside that improves the contractile function of the heart. "Dilacor" prolongs systole and normalizes myocardial function. Also increases minute and stroke volume. The drug reduces the need for oxygen in the heart muscle and stabilizes its size. You can buy Dilacor in tablets, in the form of an oral solution and in injections. Dilacor is prescribed for decompensated valvular heart defects, atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, cardiac overload due to hypertension, paroxysmal supraventricular arrhythmia.
Dilakor
Hello, Slovenia
This pharmaceutical drug belongs to the group of cardiac glycosides-cardiotonics used systemically. Digoxin, extracted from woolly foxglove, is the main active ingredient. It is a natural cardiac glycoside that has a positive inotropic effect associated with an inhibitory effect on certain types of cardiomycytic membrane. As a result, there is an increase in the number of sodium ions in the cells, and a decrease in the number of potassium ions in them. As a result of these processes, the amount of calcium in the cells increases, which enhances the contractility of the heart muscle. Systole lengthens, myocardial function improves. Also, these processes contribute to an increase in stroke and minute volume.
9
- Like
- Write a review
Tissue respiration stimulants
For this purpose, the enzyme preparation Cytochrome C , which is produced from the heart muscle of cows. The active substance is a participant in the act of tissue respiration and can accelerate oxidative reactions. Known as one of the components of Katachrom drops.
The drug is prescribed as an intramuscular injection of 5 ml. Before starting the course, a test is performed, the frequency of daily injections is 1 or 2. The duration of treatment is up to 20 days.
A test is required before each treatment course. With its help, the individual sensitivity of the patient is determined. As a test, 0.1 ml of Cytochrome C is injected into the skin and observed for half an hour. If redness, itching or allergic rashes occur, individual intolerance is indicated and the appointment is cancelled.
Cinnarizine
This nootropic drug affects the smooth muscles of blood vessels, reducing their response to adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine, angiotensin, and vasopressin. Cinnarizine dilates blood vessels in the brain without affecting blood pressure. The drug is effective both in the initial stages of cerebral circulatory disorders and in chronic cases. The product improves the nutrition of tissues and organs (including the heart muscle). "Cinnarizine" reduces blood viscosity and increases muscle resistance to oxygen starvation. The drug is prescribed for ischemic stroke, after traumatic brain injury, for migraines, diabetic angiopathy, thrombophlebitis, etc.
Cinnarizine
Antiplatelet agents
Curantil is a drug that slows platelet aggregation, which prevents the formation of blood clots in blood vessels. It has a vasodilating effect, slightly lowers blood pressure, reduces peripheral resistance, and improves cerebral circulation.
Prescribed as an antiplatelet agent to prevent the occurrence of thrombosis after operations and for blood clots in the central retinal vein. The antiaggregation activity of Curantil is close to that of acetylsalicylic acid. However, this drug is better tolerated and does not have ulcerogenic properties.
Curantil is prescribed orally at a dose of 25 mg three times a day for a long period.
There are side effects of taking the drug, although they are very rare. These include: redness of the face due to a vasodilator effect (short-term), increased heart rate, allergic rash. Not prescribed for widespread atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
Acetylsalicylic acid is an anti-inflammatory drug with antithrombotic action and the ability to inhibit platelet aggregation. The drug is used for thrombosis of retinal vessels to prevent the formation of clots.
Prescribed orally 0.125 g or 1/4 tablet after meals once a day. Can be used for a long time.
Tiklid (ticlopedine) has the ability to suppress the aggregation of erythrocytes and platelets, activates the synthesis of prostacyclin and prostaglandins E1 and D2, and improves microcirculation. It is used for retinopathy - diabetic and post-thrombotic.
Tiklid is taken orally 0.25 g with food twice a day for a long time (up to 6 months or longer) under the control of blood composition and liver function.
When taken, diarrhea and epigastric pain may occur. Phenomena of hemorrhages, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis are also possible.
The drug is not prescribed simultaneously with anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents. It is contraindicated in cases of increased risk of bleeding, stroke, exacerbation of stomach ulcers, liver disease, pregnancy and lactation.