Enzymes Indicators of lipid metabolism Indicators of protein metabolism Rheumatic tests Diagnostics of anemia Cardiac markers Indicators of residual nitrogen and purine metabolism Indicators of pigment metabolism Analysis for sugar Inorganic substances, macro and microelements Markers of osteoporosis
take a biochemical blood test for enzymes at the Health Laboratory CDC. We conduct research in a short time: in 2-3 days you can get the results. Thanks to the use of the latest equipment, we can guarantee the reliability of the results.
Biochemical blood test is one of the main methods of primary diagnosis of many diseases. It allows you to detect dysfunction of various organs and assess the deficiency of certain substances. The analysis determines the concentration and ratio of various enzymes. Depending on what disease the doctor suspects, a set of enzymes to be tested is selected. This profile is aimed at identifying pathologies of the liver, pancreas, and kidneys. Tests for these indicators can be taken at any office in our laboratory.
Before taking a biochemical blood test for enzymes, you must undergo preparation. The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, at least 8 hours must pass after the last meal. It is better to take tests in the morning, when enzyme levels are most objective. A few days before the procedure, you should avoid alcohol and fatty foods, high physical activity and severe stress. Following these measures will help you obtain the most reliable data possible.
A biochemical blood test for enzymes is highly informative. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can make a diagnosis, choose an appropriate treatment program or direction for further diagnostics.
Lipid metabolism indicators
Indications for laboratory testing of lipid metabolism are the diagnosis of the following diseases:
- atherosclerosis and its complications,
- IHD - coronary heart disease,
- myocardial infarction,
- stroke.
Increased concentrations of lipids in the blood significantly increase the risk of developing vascular complications in atherosclerosis. The level of substances largely depends on the quantities in which they are supplied with food. Therefore, to correct lipid status, a low-fat diet is often prescribed.
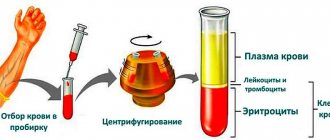
Analyzes allow you to determine the content of the main lipids - cholesterol and triglycerides. For transport in the blood, they bind to proteins - apoproteins. Such combinations are called lipoproteins. There are several types, differing in the level of triglycerides, cholesterol and apoproteins.
As part of a laboratory study of lipid metabolism, the concentration and ratio of all indicators of lipid status are determined:
- cholesterol,
- triglycerides,
- high and low density lipoproteins,
- apolipoproteins A1 and B.
A blood test is performed for diagnosis. Biomaterial is given on an empty stomach in the morning. Before the study, you must refrain from eating for 12 hours. In the morning you can only drink water. The blood collection procedure is painless and takes only a few minutes.
The study is carried out over 3 days. The results are available on our website after filling out a special form. You can also pick up the report in person or use a courier delivery service. The cost of the study is indicated on the website. Collection of biomaterial is paid separately.
Protein metabolism indicators
A biochemical blood test for protein includes the study of two main metabolic indicators:
- total protein,
- albumen.
The first allows you to evaluate the synthesis and breakdown of substances in the body as a whole. Its concentration may decrease due to:
- fasting,
- vegetarian diet,
- metabolic disorders,
- diseases of the digestive tract,
- neoplasms,
- significant blood loss,
- improper functioning of the liver and kidneys.
If a biochemical blood test shows a high concentration of total protein, this indicates:
- dehydration (for burns, gastrointestinal diseases),
- multiple myeloma.
Analysis for protein fractions
Albumin is one of the fractions of total protein. A biochemical blood test for this indicator is prescribed if kidney and liver pathology is suspected. The reasons for the increase and decrease in concentration are the same as for the main substance. Albumin levels may also be reduced in pregnant or breastfeeding women or young children.
To determine the level of other specific proteins, you need to take blood tests to compile a proteinogram. The biochemical test allows you to evaluate the concentration of alpha, beta and gamma globulin fractions, as well as their qualitative composition. The level of these substances in the blood increases significantly during inflammatory processes or exacerbations of chronic diseases. Malignant tumors also cause an increase in their plasma volume.
A biochemical blood test for total protein and its fractions is taken strictly on an empty stomach. The day before the test, it is necessary to exclude fatty and heavy foods from the diet. Compliance with these requirements guarantees the accuracy and information content of the test.
Rheumatic tests
A blood test for rheumatic tests is usually performed as part of a comprehensive examination of the immune system.
During the tests, the amount of specific proteins that are markers of systemic or autoimmune diseases is determined. Rheumatic tests include blood tests to determine the following protein compounds:
- C-reactive protein,
- rheumatoid factor,
- ASL-O.
The level of C-reactive protein increases if there is an inflammatory process in the body. This test is carried out in cases of suspected chronic infectious diseases with a latent course. Taking a blood test is not recommended for people who have recently undergone surgery or been injured, as protein levels also increase when tissue is damaged.
A blood test for rheumatoid factor is prescribed for the differential diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. During the rheumatic test, the quantitative content of protein compounds in the serum is determined. A significant excess of the norm indicates a severe course of arthritis. High rheumatic test scores can also be a sign of connective tissue inflammation or viral infections.
Antistreptolysin-O is a marker of streptococcal infections. This protein is found in the blood of patients with meningitis, scarlet fever, and myocarditis. Streptococcus also leads to exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis, so patients with this diagnosis should undergo this test regularly.
All blood tests for rheumatic tests are taken strictly on an empty stomach, after 8-12 hours of fasting. A few days before the test, you need to stop taking medications, give up alcohol and significant physical activity. The test will not be informative if you donate blood after an X-ray examination.
Causes of rheumatoid arthritis
Currently, there is no reliable data on the causes of the disease. There are several most likely versions supported by most of the medical community. The most popular of them is that RA is caused by several factors present in the patient’s medical history at the same time.
- Genetic predisposition to autoimmune disorders.
- Presence of MHC class II antigen (noted in most patients).
- Infectious agents: paramyxoviruses, hepatoviruses, retroviruses.
- The presence of antibody titers to the Epstein-Barr virus (found in 80% of patients).
Thus, the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis is higher in women aged 35 - 40 years and older. Increases the chances of having close relatives with a similar diagnosis, as well as previous diseases such as measles, hepatitis B, lichen, herpes, mumps.
Any changes in the immune system, which begin an attack on one’s own connective tissue, can activate the pathological process. Among the triggering factors are frequent hypothermia, hyperinsolation (sunstroke), prolonged intoxication, viral and bacterial infections. May be affected by medications, disruption of the endocrine glands, long-term stress and depression.
Diagnosis of anemia
CDC "Health Laboratory" diagnoses anemia using blood tests. On this page you will find a set of studies that you can take separately or together.
Anemia, or anemia, is a group of syndromes that have a common symptom: a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, usually with a simultaneous decrease in the number of red blood cells. Assessing the following indicators increases the accuracy of diagnosing anemia using blood tests:
- LVSS - ability of serum to bind iron; one of the main indicators used to diagnose anemia using a blood test ; changes with disturbances in microelement metabolism; in the case of iron deficiency anemia, the LVSS increases; if complex tests show a low level of serum iron, this indicates anemia, which is associated with chronic diseases, cancer, infections,
- vitamin B12 - important for the normal formation and maturation of red blood cells; The risk of cyanocobalamin deficiency is highest in vegetarians, since the vitamin comes with animal products, a decrease in concentration affects the decrease in the amount of folic acid,
- B9 - folic acid is also important for hematopoiesis: it stimulates the formation of erythro-, leukocytes and platelets, the compound enters the blood along with green vegetables, wholemeal bread and is partially formed by intestinal microflora, the reserve of acid in the liver is small, a month of stopping consumption is enough for a deficiency to occur source products, anemia develops after four months.
As part of the diagnosis, you can take a blood test for transferrin, ferritin, and erythropoietin. Choose tests according to the recommendations of your doctor. Only a specialist evaluates the results obtained. Diagnosing anemia using a blood test can be difficult, so the doctor evaluates clinical symptoms, comprehensive research data, and medical history.
Cardiac markers
Cardiac markers are specific protein compounds found in muscle tissue. In heart disease, cells are damaged and released enzymes enter the blood. A large number of amino acids in the blood may also indicate the destruction of skeletal muscles and hidden bleeding.
Tests for cardiac markers are prescribed:
- in preparation for surgery under general anesthesia,
- patients with complaints of heart pain,
- for differential diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases.
Patients admitted with suspected heart attack are tested for myoglobin, troponin I and creatine kinase. An increase in the concentration of these proteins in the blood begins within a few hours after damage to the heart muscle.
If systemic heart disease or destruction of the vascular wall is suspected, a blood test is performed for the cardiac marker homocysteine. An increase in amino acid concentration indicates damage to the vascular epithelium. Indicators below normal are a sign of a lack of folic acid and B vitamins in the body.
Patients with ischemia or acute coronary syndrome should be regularly tested for troponin I. This specific protein is present only in the heart muscle and is released when its cells are damaged at the slightest level. An increase in the concentration of a cardiac marker indicates the risk of developing myocardial infarction in the near future.
You can undergo any test in our laboratory without a doctor’s prescription. All you need to do is make an appointment by phone. Test results for cardiac markers will be ready in one to five business days, depending on the number of indicators. You can obtain the data at the office where the survey was conducted or by email.
What is rheumatoid factor
The name itself, “rheumatoid factor,” is associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
But it is not so. It was discovered while studying rheumatoid phenomena in the joints, hence the name. In fact, the results of the study are a reliable marker for identifying any autoimmune processes. Rheumatoid factor (rheumatoid factor) is specific proteins of the body (autoantibodies) that react with special protective proteins of the immune system - immunoglobulins. It turns out that the body's cells act as enemy agents for its own immune system. If they are produced, the immune system attacks its own proteins, which leads to the destruction of healthy cells. Normally, rheumatic factor is not detected in humans, or its amount does not exceed 14 IU/ml. This tiny amount can only be determined by highly sensitive quantitative analysis.
To determine the rheumatic factor, the following methods are used:
- latex agglutination, also known as latex test;
- Valera-Rose reaction;
- nephelometry;
- linked immunosorbent assay.
Typically, a latex test and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are used to identify rheumatic factor.
With the latex test, a rapid determination of the presence of these proteins is done (yes/no).
With enzyme immunoassay, quantitative indicators of rheumatic factor can be determined.
Result
The norm for biochemical analysis of residual nitrogen is from 14.3 to 28.6 mmol/l.
An increase in residual nitrogen may indicate:
- acute or chronic renal failure;
- renal dysfunction;
- heart failure;
- dehydration;
- obstruction of the urinary tract;
- bleeding from the upper digestive tract;
- severe bacterial infections;
- decreased adrenal function (Addison's disease).
A decrease in residual nitrogen levels may be a symptom of:
- liver failure;
- viral, toxic and autoimmune hepatitis;
- celiac disease.
Indications for testing
Rheumatoid tests or rheumatic tests are prescribed by a doctor to confirm autoimmune pathologies:
- arthritis;
- thyroiditis;
- polymyositis and autoimmune prostatitis (in men);
- multiple sclerosis;
- scleroderma.
Often, a rheumatoid test is prescribed to determine pathological changes in connective tissue (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, gout).
Indications for such a study are the following symptoms of disorders in soft tissues:
- swelling and pain in the joints;
- changes in body asymmetry;
- impaired mobility of joints and ligaments;
- pain in the lower back, and with weather changes - aches throughout the body;
- frequent headaches that do not respond to analgesics (a symptom of vasculitis);
- prolonged increase in body temperature without a clear reason.
Rheumatological examination for such symptoms allows one to assess the activity of the pathological process and predict the further course of the disease.
Preparation
A biochemical blood test requires special preparation.
- You need to take the test strictly on an empty stomach, after 8-12 hours of fasting, you can only drink still water.
- You should not change your diet for 3 days, but try to exclude fatty, spicy and fried foods.
- It is recommended to stop playing sports 3 days before the test.
- You should take a biochemical test in the morning, from 7 to 11 am.
- You should stop taking medications 3 days in advance; if this is not possible, notify your doctor.
- It is advisable to take tests in the same laboratory
Pigment metabolism indicators
A biochemical test for bilirubin allows you to determine the condition of the liver and biliary tract. It is carried out according to the following indications:
- liver diseases,
- cholestasis,
- hemolytic anemia,
- diagnosis of jaundice of various origins.
As part of a biochemical blood test, two indicators are assessed.
- Direct bilirubin is synthesized from free bilirubin due to binding with glucoronic acid. By its concentration one can judge the condition of the biliary tract and liver and identify the causes of jaundice. The enzyme content increases when there is a violation of the outflow of bile, hepatitis and other pathologies. A significant release of bilirubin into the blood causes yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes, and darkening of the urine.
- Total bilirubin is a breakdown product of myoglobin, hemoglobin and cytochromes. It is formed in the cells of the liver and spleen and is one of the main components of bile.
There is a normal value for bilirubin content: indirect - up to 17.1 µmol/l, direct - up to 4.3 µmol/l. Exceeding the concentration may indicate the following violations:
- vitamin B12 deficiency,
- liver cancer,
- hepatitis, primary cirrhosis,
- formation of gallstones,
- Gilbert's disease
- poisoning - medicinal, alcoholic or toxic.
To make an accurate diagnosis, additional tests are prescribed.
Before taking a bilirubin test, you should undergo simple preparation. The procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, at least 8 hours must pass after the last meal. The day before, give up alcohol and fatty foods, reduce physical activity and try to avoid stress. Following these recommendations allows you to obtain the most reliable data.
When a child needs a biochemical blood test:
* Yellowness of the skin and/or mucous membranes is a suspicion of hepatitis or stagnation of bile in the gallbladder.
* Colorless stools - possible hepatitis (sometimes occurs without jaundice) or a disease of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, pancreatitis).
* Vomiting and diarrhea - often associated with pancreatitis or viral hepatitis A.
* Strong thirst and hunger, rapid weight loss and fatigue, frequent urination - indicates diabetes.
* Poor appetite and weight gain . It is not necessary that the child is sick, but he needs a comprehensive examination.
* Nausea, abdominal pain, repeated indomitable vomiting and a pronounced odor of acetone from the mouth are signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (complications of diabetes mellitus - a life-threatening condition) or an acetonemic crisis in neuro-arthritic diathesis.
Read more about neuro-arthritic diathesis here
Sugar analysis
The laboratory of the CDC "Health Laboratory" offers
a blood test for sugar The main tests are collected in a special profile. You can choose individual tests or undergo a comprehensive study. Doctors recommend taking a blood and urine test for sugar in the following cases:
- diagnosis and control of diabetes mellitus types I and II,
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands,
- liver diseases,
- determination of tolerance to glucose (a component of sugar) when testing patients at risk,
- obesity,
- diabetes during pregnancy.
A blood test for glucose concentration is the main test for diagnosing diabetes mellitus. This is what you should take first when the following symptoms appear:
- excessive urination due to an increase in the osmotic pressure of urine caused by glucose dissolved in it (in a healthy person, the analysis shows the absence or minimal level of this substance),
- constant thirst associated with fluid loss,
- unexplained hunger and weight loss due to metabolic disorders.
These symptoms develop acutely and are most typical of type I diabetes. Secondary signs:
- itching,
- dry mouth,
- muscle weakness,
- skin inflammation,
- visual impairment.
A blood test for glycated hemoglobin is indicated for long-term follow-up of patients to monitor treatment and the degree of compensation. The level of this substance reflects hyperglycemia - an increase in sugar, typical of diabetics.
An endocrinologist will explain to you the expediency of the research. If your doctor has prescribed tests for sugar and other substances to assess carbohydrate metabolism, we invite you to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis with us. We use modern equipment to obtain accurate results.
ACDC
A blood test for ACCP consists of determining the titer of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide and is one of the accurate methods for confirming the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. With its help, the disease can be detected several years before symptoms appear.
What does the ACDC analysis show?
Citrulline is an amino acid that is a product of the biochemical transformation of another amino acid - arginine. In a healthy person, citrulline does not take part in protein synthesis and is completely eliminated from the body.
But with rheumatoid arthritis, citrulline begins to integrate into the amino acid peptide chain of proteins in the synovial membrane and cartilage tissue of the joints. The “new” modified protein, which contains citrulline, is perceived by the immune system as “foreign” and the body begins to produce antibodies to citrulline-containing peptide (ACCP).
ACCP is a specific marker of rheumatoid arthritis, a kind of harbinger of the disease at an early stage, with high specificity. Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide are detected long before the first clinical signs of rheumatoid arthritis and remain throughout the disease.
Methodology of analysis and its significance
To detect ACCP, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used. A blood test for ACCP is carried out according to the “in vitro” principle (translated from Latin - in a test tube), serum from venous blood is examined. The ACCP blood test can be ready within 24 hours (depending on the type of laboratory).
Detection of ACCP in rheumatoid arthritis may indicate a more aggressive, so-called erosive form of the disease, which is associated with more rapid resolution of joints and the development of characteristic joint deformities.
If the test result for ACCP is positive, then the prognosis for rheumatoid ACCP arthritis is considered less favorable.
1 Blood test for ACCP
2 Blood test for C-reactive protein
3 Blood test for ACCP
ACDC. Reference values
The normal range for the ACCP test is approximately 0-5 U/mL. The so-called “ ACCP norm ” may vary depending on the laboratory. The “ACCP norm” values for women and men are the same.
The so-called “ Increased ACCP ”, for example, ACCP 7 units/ml or more, indicates a high likelihood of rheumatoid arthritis. An analysis result assessed as “ ACCP negative ” reduces the likelihood of rheumatoid arthritis, although it does not completely exclude it. A rheumatologist with experience in diagnosing and treating rheumatoid arthritis should always evaluate the ACCP values and interpret them; only a rheumatologist can take into account all the nuances.
To get tested for ACCP, you need to come for examination on an empty stomach.
Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- early synovitis;
- osteoarthritis;
- polymyalgia rheumatica;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- Raynaud's disease;
- reactive arthritis;
- sarcoidosis;
- scleroderma;
- Sjögren's syndrome;
- SLE;
- vasculitis;
- juvenile RA.
If you want to know the cost of a blood test for ACCP, please call.
Contact center specialists will tell you the price of the ACDC and explain how to prepare for the study.
Inorganic substances, macro and microelements
A biochemical blood test for trace elements is a study that allows you to comprehensively assess the condition of the body, the functionality of systems and organs, identify symptoms of diseases or determine which vitamins and minerals a person lacks.
Most often, biochemical tests are taken to determine the content of vital (essential) elements in the blood:
- calcium;
- potassium;
- sodium;
- chlorine;
- magnesium;
- phosphorus;
- copper;
- gland;
- zinc
A blood test for microelements allows you to:
- reflect the functional state of organs and systems;
- identify an active inflammatory process;
- establish the fact of a violation of water-salt metabolism;
- identify rheumatic processes;
- correctly diagnose and prescribe effective treatment that will be effective;
- prevent the development of diseases.
Knowing the microelement profile of the body is important for the correct prescription of vitamin-mineral complexes, since some initially beneficial microelements in high concentrations become hazardous to health. An imbalance of vitamins and minerals can lead to:
- decreased immunity;
- diseases of the skin, hair, nails;
- allergies, bronchial asthma;
- diabetes, obesity;
- hypertension;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- scoliosis, osteoporosis, osteochondrosis;
- blood diseases;
- intestinal dysbiosis, chronic gastritis, colitis;
- infertility, decreased potency in men;
- delayed mental and physical development.
You can take a biochemical blood test for microelements at any of our laboratory offices. The study should be carried out on an empty stomach; it is recommended to stop taking medications 3 days before. You can get additional information by phone.
Blood test for uric acid levels
Uric acid is the final breakdown product of purines. Every day a person receives purines through food, mainly meat products. Then, with the help of certain enzymes, purines are processed to form uric acid.
In normal physiological quantities, uric acid is needed by the body; it binds free radicals and protects healthy cells from oxidation. In addition, just like caffeine, it stimulates brain cells. However, high levels of uric acid have harmful consequences, in particular, they can lead to gout and some other diseases.
Testing uric acid levels makes it possible to diagnose uric acid metabolism disorders and related diseases.
1
Rheumatological examination
2 Rheumatological examination
3 Rheumatological examination
When to conduct an examination:
- with the first attack of acute arthritis in the joints of the lower extremities, which arose without obvious reasons;
- with recurrent attacks of acute arthritis in the joints of the lower extremities;
- if you have relatives in your family who suffer from gout;
- for diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome;
- with urolithiasis;
- after chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy for malignant tumors (and especially leukemia);
- with renal failure (the kidneys excrete uric acid);
- as part of a general rheumatological examination necessary to determine the cause of joint inflammation;
- with prolonged fasting, fasting;
- with a tendency to excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Uric acid level
The level of uric acid is determined in the blood and urine.
Uric acid in the blood is called urecemia , and in urine - uricosuria . An increased level of uric acid is hyperuricemia , a decreased level of uric acid is hypouricemia . Only hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria are of pathological significance.
The concentration of uric acid in the blood depends on the following factors:
- the amount of purines entering the body with food;
- synthesis of purines by body cells;
- the formation of purines due to the breakdown of body cells due to disease;
- the function of the kidneys, which excrete uric acid in the urine.
Under normal conditions, our body maintains normal uric acid levels. An increase in its concentration is one way or another associated with metabolic disorders.
Normal levels of uric acid in the blood
Men and women may have different concentrations of uric acid in the blood. The norm may depend not only on the gender, but also on the age of the person:
- in newborns and children under 15 years of age – 140-340 µmol/l;
- in men under 65 years old – 220-420 µmol/l;
- in women under 65 years of age – 40-340 µmol/l;
- in women over 65 years of age – up to 500 µmol/l.
If excess of the norm occurs for a long time, then crystals of uric acid salt (urate) are deposited in joints and tissues, causing various diseases.
Hyperuricemia has its own symptoms, but can also be asymptomatic.
Reasons for increased uric acid levels:
- taking certain medications, such as diuretics;
- pregnancy;
- intense loads in athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor;
- prolonged fasting or eating foods containing large amounts of purines;
- some diseases (for example, endocrine), consequences of chemotherapy and radiation;
- impaired metabolism of uric acid in the body due to a deficiency of certain enzymes;
- insufficient excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
How to reduce uric acid levels
Those who suffer from gout know how much trouble an increased concentration of uric acid can cause. Treatment of this disease must be comprehensive and must include taking medications that reduce the concentration of uric acid in the blood (xanthine oxidase inhibitors). It is recommended to drink more fluids and reduce the consumption of foods rich in purines.
It is also important to gradually lose excess weight, since obesity is usually associated with increased uric acid. The diet should be designed so that the amount of foods rich in purines is limited (red meat, liver, seafood, legumes). It is very important to give up alcohol. It is necessary to limit the consumption of grapes, tomatoes, turnips, radishes, eggplants, sorrel - they increase the level of uric acid in the blood. But watermelon, on the contrary, removes uric acid from the body. It is useful to consume foods that alkalize urine (lemon, alkaline mineral waters).
Markers of osteoporosis
Laboratory diagnosis of osteoporosis includes tests for the following indicators:
- calcitocin is a hormone that maintains a constant level of calcium in bone tissue, preventing its destruction,
- parathyroid hormone - indicates the effectiveness of calcium metabolism, controls the flow of calcium and phosphate from the bones into the blood,
- Deoxypyridinoline (DPID) is the most specific marker of bone destruction; is the main material of collagen cross-links,
- Osteocalcin is a key non-collagenous bone protein; its content reflects the metabolic activity of osteoblasts,
- b-Cross Laps is a degradation product of type 1 collagen; an increase in its concentration indicates an acceleration of the process of collagen destruction.
A blood test is performed to diagnose osteoporosis. A comprehensive assessment of several indicators allows you to accurately diagnose and identify the causes of osteoporosis.
The disease is characterized by a violation of the structure of bone tissue, a decrease in bone mass. Accompanied by an increase in the activity of osteoclasts - cells that destroy bones. Osteoblasts - creating cells - do not fill the resulting cavities, as a result of which the tissue is not restored. Several functional techniques are used for diagnosis:
- bone densitometry,
- radioisotope bone scan,
- trepanobiopsy.
Laboratory diagnostics is the final stage of examination. It allows you to confirm the doctor’s assumptions and identify the conditions for the course of the disease.
You can get tested at any office of the Health Laboratory CDC. It takes about 7 days to diagnose osteoporosis. We will inform you additionally when the results are ready.