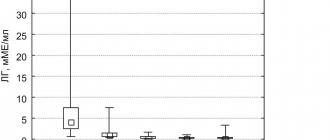
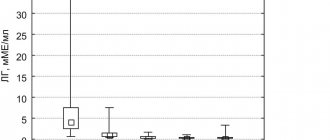
Triptorelin-long lyof d/prig susp IM injection 3.75 mg No. 1
Caution should be exercised in patients taking anticoagulants, as hematoma may develop at the injection site.
Uterine fibroids and endometriosis
Before starting treatment, pregnancy must be excluded.
The drug Triptorelin-long should be prescribed only after in-depth diagnosis of uterine fibroids and endometriosis (laparoscopy and/or hysteroscopy).
Throughout the entire treatment period, including for 3 months from the date of the last injection, non-hormonal contraceptives should be used. Due to the possible effect of Triptorelin-Long on bone mineral density, treatment should not be recommended for a period of more than 6 months. Repeated courses of therapy with triptorelin or other GnRH analogues are not recommended.
Treatment of uterine fibroids should be carried out under ultrasound control, since a rapid decrease in the size of the uterus in some cases can lead to the development of uterine bleeding of varying duration and intensity.
For uterine fibroids, the most appropriate combination of therapy with Triptorelin-long followed by surgical treatment. The administration of triptorelin leads to a significant reduction in the size of the myomatous uterus, which facilitates the surgical technique. It is especially advisable to conduct a course of triptorelin therapy in young patients in order to preserve reproductive function, when organ-saving surgery can be performed using laparoscopic techniques.
During the first month, bleeding/bloody discharge from the vagina of varying intensity and duration is possible. If spotting/bleeding continues after the first month, it is necessary to determine the concentration of estradiol in the blood plasma. If the concentration of estradiol decreases to less than 50 pg/ml, other organic lesions may be present.
After discontinuation of triptorelin therapy, ovarian function is restored within 7–12 weeks. Given that menstruation should cease during triptorelin therapy, the patient should be appropriately instructed to notify her physician if regular menstruation continues.
Prostate cancer
At an early stage, the drug Triptorelin-long causes a temporary increase in the concentration of testosterone in the blood plasma. As a result, during the first weeks of therapy, the appearance and intensification of clinical symptoms (in particular, bone pain, dysuric disorders) may be observed, which are transient in nature, and for which symptomatic therapy should be carried out. As with other GnRH agonists, isolated cases of spinal cord compression or urinary tract obstruction may occur. In cases of spinal cord compression or urinary tract obstruction, standard treatment for these complications should be prescribed and, in emergency cases, orchiectomy (surgical castration) is suggested.
Patients should be closely monitored during the first few weeks of therapy (plasma testosterone concentration should not exceed 1 ng/ml), especially in patients with metastatic lesions of the spinal cord, patients at risk of spinal cord compression or urinary tract obstruction. For the same reason, special attention should be given at the beginning of treatment to patients with signs of spinal cord compression identified during a preliminary examination. During the initial phase of therapy, the use of additional antiandrogen drugs should be considered to prevent an initial increase in plasma testosterone concentrations and worsening of clinical symptoms.
Epidemiological data have shown that patients may develop metabolic abnormalities (eg, impaired glucose tolerance) during androgen deprivation therapy; increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. However, prospective data have not confirmed an association between GnRH agonist treatment and increased cardiovascular mortality. Patients at high risk for metabolic and cardiovascular disease should be carefully assessed before treatment and closely monitored during androgen deprivation therapy.
At the beginning of therapy, a temporary increase in the activity of acid phosphatase in the blood plasma may be observed.
Function of the gonads and pituitary gland
The use of triptorelin in therapeutic doses leads to suppression of the gonad-pituitary gland system. Normal functioning of the gonads and pituitary gland is usually restored after cessation of therapy. The results of a diagnostic test of pituitary gonadotropic function performed during and after cessation of therapy may therefore be incorrect.
Osteoporosis
The use of GnRH agonists may cause a decrease in bone mineral density (BMD).
In men, long-term androgen deprivation with bilateral orchiectomy or GnRH analogues may be associated with an increased risk of bone loss and may lead to osteoporosis and increased risk of bone fracture.
Preliminary data suggest that the use of bisphosphonates in combination with GnRH may reduce BMD loss. Particular attention should be paid to patients with risk factors for osteoporosis (for example: chronic alcohol dependence; smoking; long-term therapy with drugs that reduce BMD, such as anticonvulsants or glucocorticosteroids; a history of hereditary osteoporosis; malnutrition or malnutrition).
In women, the use of GnRH agonists may be responsible for the decrease in BMD by an average of 1% per month over six months of treatment. Every 10% decrease in BMD leads to an approximately 2-3-fold increase in the risk of bone fracture.
In most women, BMD recovers after cessation of therapy.
There are no available data on the use of triptorelin in patients with established osteoporosis or with risk factors for osteoporosis (eg, chronic alcohol dependence; smoking; long-term therapy with drugs that reduce BMD, such as anticonvulsants or glucocorticosteroids; history of hereditary osteoporosis; insufficiency or eating disorders, such as anorexia neurosis). Given that a decrease in BMD is more likely in such patients, treatment with triptorelin should be prescribed on an individual basis and should only be initiated if the benefit obtained from treatment outweighs the risk. Additional testing should be considered to avoid loss of BMD.
Pituitary tumor
Rarely, the use of GnRH agonists may reveal the presence of a previously undiagnosed gonadotropic pituitary adenoma. Pituitary hemorrhage is characterized by sudden headache, visual disturbances and ophthalmoplegia.
Depression
Patients receiving triptorelin therapy are at increased risk of developing depression (which may be severe). Patients should be informed about the possible development of depression, and if depression develops, should receive appropriate therapy. Patients with known depression should be closely monitored during therapy.
QT
prolongation Long-term androgen deprivation may prolong the QT interval. A risk/benefit assessment should be performed before prescribing triptorelin to patients with congenital long QT syndrome, electrolyte abnormalities, or chronic heart failure; or patients taking drugs that may prolong the QT interval or drugs that may cause torsade de pointes (TdP), such as Class IA (eg, quinidine, procainamide) or Class III antiarrhythmic drugs (eg, amiodarone, sotalol).
Carrying out ovulation induction as part of ART
When treating infertility using IVF, Triptorelin-Long should only be used under the supervision of a specialist with experience in this field.
When carrying out IVF, the drug Triptorelin-long is used to stabilize the concentration of endogenous sex hormones with the subsequent administration of gonadotropins to stimulate follicle growth. The use of triptorelin helps to avoid premature spontaneous ovulation of stimulated follicles, which increases the effectiveness of the IVF program as a whole.
It is recommended to use the drug Triptorelin-long with caution during IVF in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, because stimulation of a large number of follicles is possible.
Due to the fact that the use of the drug Triptorelin-long can lead to the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, regular clinical monitoring is necessary, including ultrasound of the ovaries.
It is necessary to determine the concentration of estradiol in the blood plasma in order to monitor the ovarian response during ovulation induction as part of ART (interruption of the ovulation stimulation cycle in case of excessive ovarian response and cessation of gonadotropin injections) and clinical manifestations of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Dose adjustment
It is necessary to adjust the dose of antihypertensive drugs when used together with Triptorelin-long.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Currently, there is no data on the possible effect of the drug Triptorelin-long on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. However, the use of the drug can lead to the development of such undesirable reactions as headache, decreased vision, drowsiness, which can negatively affect the ability to drive vehicles and perform potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions. If the symptoms described above occur, you should refrain from driving vehicles and machinery.