One of the most common pathologies in the modern world is vegetative-vascular dystonia. It is diagnosed in 80% of the population. In pediatric practice, VSD is detected in 25% of cases. However, there is still no consensus regarding the definition of pathology.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a symptomatic complex that includes damage to various organs and systems. In order to diagnose the disease, determine the causes of its development and carry out the correct treatment, we recommend contacting the Yusupov Hospital. For research, the clinic’s specialists use equipment that meets quality and safety standards. Therapy is prescribed according to the latest international recommendations.
The formulation of VSD is found only in domestic medicine. However, there is no such disease in the international classification of diseases ICD-10. The symptom complex is combined into such a concept as “autonomic dysfunction” (ICD-10 code F 45.3).
Causes
Vegetative-vascular dystonia affects various systems and organs. Symptoms may appear already in fetal development. It has been proven that the largest number of diagnosed cases are detected between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Among the main reasons for the development of VSD are the following:
- hereditary burden;
- physiological features of the structure of the body;
- psycho-emotional or physical stress;
- hormonal instability;
- chronic somatic pathologies;
- history of traumatic brain injury.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital quickly identify the causes of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In accordance with the identified etiological factors, a treatment program is developed. Make an appointment
Sudden vegetative-vascular attack
The so-called “vegetative-vascular crises”, which in practice occur like panic attacks, deserve special attention. The sudden onset of feelings of fear and anxiety is accompanied by severe somatic symptoms (palpitations, inability to breathe). They are extremely difficult for patients to tolerate and lead to complete social maladjustment. Moreover, a person is constantly in painful anticipation of a second attack.
In some patients, the attack appears suddenly. Others note a clear relationship with potentially threatening or stressful situations. This could be being in society, a cramped room or space, exciting news, etc.
In addition to severe anxiety and fear, the patient experiences palpitations, a lump in the throat, a feeling of lack of air and the inability to breathe. Choking, dizziness, increased heart rate, as well as disorientation in space and time lead to a feeling of fear of death. A panic attack often causes an ambulance to be called.
Kinds
Doctors distinguish the following forms of vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- according to the hypertensive type;
- hypotonic type;
- according to the cardiac type;
- mixed type.
VSD of the hypertensive type. This type of pathology is accompanied by rises in blood pressure to high values. In this regard, headache, dizziness, weakness, flashing “spots” before the eyes, and a feeling of nausea appear. VSD of the hypotonic type. A symptom of this form of pathology is a decrease in blood pressure. Difficult to diagnose due to the general nature of the manifestations. Mixed type VSD is characterized by regular changes in blood pressure from high to low values. Mixed vegetative-vascular dystonia most often appears due to a hereditary predisposition. Clinical symptoms of this form of the disease are panic attacks, increased anxiety, and irritability. VSD of the cardiac type Occurs against the background of other diseases. It manifests itself as pain in the heart area.
Expert opinion
Author:
Tatyana Aleksandrovna Kosova
Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, neurologist, reflexologist
According to the latest statistics, VSD is diagnosed in 50–70% of the population. At the same time, it is not possible to identify a pattern regarding age and gender. The onset of the disease can occur at any period of life. Among adolescents, vegetative-vascular dystonia is detected in 25–40% of cases.
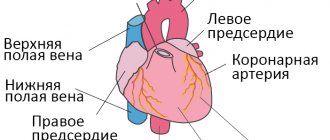
VSD refers to a complex of pathological symptoms united by a common concept. Diagnosing the disease can be difficult due to the variety of clinical signs. At the Yusupov Hospital, ECG and EchoCG are prescribed for examination. In addition, MRI, CT, 24-hour Holter monitoring, EEG and laboratory tests are used. Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, doctors select the correct therapy. The amount of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms. Depending on the prevailing symptoms, certain groups of drugs are prescribed.
Patients often underestimate the danger of VSD. Without treatment, the disease becomes more complicated. This worsens the patient's condition and requires serious therapy. Therefore, when the first pathological signs appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis and quality treatment are the key to a speedy recovery.
Panic attacks with VSD
VSD and panic attacks are considered completely different conditions. Many patients confuse these diseases because they differ in other similar symptoms. During an attack of dystonia and at the time of a panic attack, a release of adrenaline, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine occurs (observed in the sympathetic form). Therefore, many experts diagnose people with a tendency to panic attacks as VSD.
This conclusion is considered erroneous. To eliminate vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is necessary to take medications, and the treatment of panic attacks is carried out using psychotherapy methods.
It is easy to confuse VSD and a panic attack. Experts in the post-Soviet space practically do not diagnose panic attacks. They are treating the disease. To eliminate the symptoms of panic attacks, you do not need to take medications.
To stabilize blood pressure parameters, to combat headaches and pathologies in the heart area, the help of a psychotherapist is needed. This deviation is a neurosis. Vegetative vascular dystonia is considered a deviation of the autonomic nervous system. This condition requires the use of medications.
Symptoms
Due to the fact that vegetative-vascular dystonia affects various organs and systems, the pathology has a variety of clinical manifestations. The nervous, cardiovascular, and genitourinary systems may be involved in the process. As a result, a misleading impression of the presence of other diseases is created. Experienced doctors at the Yusupov Hospital carry out differential diagnosis of conditions and identify VSD in the shortest possible time. Common symptoms of pathology are:
- Psychoneurotic: headaches, dizziness, anxiety, tearfulness. Patients are concerned about irritability, a tendency to panic attacks, sleep disturbances, daytime sleepiness, and apathy.
- Respiratory: periodic attacks of suffocation, feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, rapid breathing, inability to take a deep breath.
- Cardiac: rapid heartbeat, feeling of pain in the heart area, chest tightness, irregular heart rhythm.
- Peripheral somatic syndromes: arthropathy, myopathy, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Genitourinary: erectile dysfunction, urination and defecation disorders.
- Thermoregulatory: changes in body temperature, feeling of chills.
- Dyspeptic: abdominal pain, feeling of nausea, increased gas formation. The stool becomes unstable, heartburn and belching appear.
Numerous positive reviews indicate the successful work of the Yusupov Hospital specialists. Doctors have been successfully identifying VSD for many years, despite the complexity of diagnosis.
Symptoms for different forms of VSD
Patients with the cardiac form of VSD are bothered by pain in the heart of a stabbing, aching, pressing nature that does not go away after taking nitroglycerin.
Patients feel palpitations, cardiac tremors, and interruptions in the functioning of the heart. The pulse can be frequent or rare, blood pressure can be low or high. During an exacerbation of VSD symptoms, patients experience a feeling of fear of death and a “lump in the throat.” They cannot calm down, rush about and demand urgent action. A panic attack unsettles a person from normal life. After an attack, patients remain fearful for a long time.
A sign of VSD is insomnia and impaired sleep quality. After a sleepless night, the patient feels exhausted and his mood worsens. The smallest trigger factor can throw a VSD patient out of balance. If VSD occurs of the respiratory type, patients experience attacks of suffocation, dissatisfaction with inhalation, chest pain, and a feeling of lack of air.
Patients suffering from hypotonic type VSD lose consciousness during a vegetative crisis, their skin becomes pale and sweaty, and their legs and arms become cold.
Dysfunction of the digestive system is manifested by heartburn, nausea with vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Patients are bothered by cramping pain in the abdomen.
Patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia complain of pain in the joints and muscles, and they develop osteochondrosis.
In the mixed form of VSD, manifestations of all types of vegetative-vascular dystonia are determined. VSD of the hypertensive type is usually combined with functional venous hypertension, respiratory and myocardial syndromes, arterial hypotension - with respiratory syndrome and functional venous hypertension, less often with myocardial syndrome.
The cardiac form of neurocirculatory dystonia is most often combined with respiratory syndrome, functional venous hypertension and regional cerebral dystonia. Functional venous hypertension as a leading syndrome is determined in combination with myocardial and respiratory syndromes. During a crisis, all symptoms of VSD worsen. The attack begins suddenly and goes away.
Dizziness
The cause of dizziness during VSD may be a violation of cerebral vascular tone. The condition of cerebral vessels is influenced by many factors - from unpleasant news to the release of adrenaline into the blood due to stress. The catalyst for reactions that develop during VSD are:
- mental stress;
- acute and chronic stress;
- burdened heredity;
- diabetes mellitus and other chronic diseases;
- diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- pathology of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, gonads.
In case of dizziness due to VSD, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital examine patients using modern devices from the world's leading manufacturers.
Patients undergo magnetic and magnetic resonance imaging, radiography of the cervical spine, and electroencephalography. If an exacerbation of VSD symptoms occurs due to a decrease in blood pressure, coffee and green tea, a piece of dark chocolate, and lemongrass tincture help. You can add a spoonful of honey to the tea. In case of a severe attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the patient should be laid down and fresh air should be allowed into the room. Treatment begins with a sedative or sedative. After measuring blood pressure, a decision is made on the advisability of drug therapy.
The cause of dizziness during VSD may be a pathology of the cerebral vessels. How to strengthen cerebral vessels during VSD? To increase the elasticity of the walls of arteries and capillaries, neurologists prescribe the following medications for cerebral vessels:
- vitamin C is an antioxidant, whose role is to protect the walls of blood vessels from destruction under the influence of free radicals, enhances the functions of vitamin P;
- vitamin P – contains a complex of polyphenols and bioflavonoids, which help strengthen capillaries and prevent the loss of vascular tone;
- nicotinic acid (vitamin PP) - expands capillaries and prevents the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels.
If you feel dizzy with VSD, medications are prescribed that contain microelements that strengthen the walls of blood vessels and stimulate metabolism: potassium, selenium, silicon.
How to relieve dizziness with VSD? The pharmaceutical industry produces herbal preparations that improve blood circulation in the brain. These are nicotinic acid derivatives, products based on garden periwinkle and Ginkgo Biloba extracts. Nicotinic acid derivatives dilate large vessels, although small capillaries are also affected by them.
Ginkgo Biloba extracts are included in the preparations Tanakan, Bilobil, Ginkor Fort. When taken orally, they perform several tasks:
- relieve vasospasm;
- increase the permeability of the vascular wall;
- relieve swelling;
- has an antioxidant effect;
- accelerate metabolism in nervous tissue.
Garden periwinkle contains a special group of alkaloids that have a pronounced antispasmodic effect on blood vessels, accelerate metabolism, and increase microcirculation in the vessels of the brain. Mexidol helps well against dizziness with VSD.
Headache Syndrome of vegetative-vascular dystonia manifests itself in many ways.
Headache, as the most important symptom of VSD, occurs mainly in people who are susceptible to fears and phobias, strong emotions after stress. How does a headache hurt with VSD? Patients give the following description of headaches with VSD:
- is not strong and harsh;
- may be accompanied by fainting, nausea, dizziness, ringing or noise in the ears, unsteadiness of gait;
- begins in the morning, does not leave a person all day and is distinguished by its constancy;
- in pain, the patient has difficulty perceiving the world around him;
- When you tilt your head, the pain intensifies and becomes throbbing.
During a headache attack, the patient feels as if he is wearing a helmet and is squeezing his head.
Where does the headache occur with VSD? The pain is localized in a specific area or spreads throughout the head. Patients feel a feeling of discomfort in the back of the head and neck. During an attack, one ear may become blocked; sometimes the patient feels as if there is something pressing in the temples, eyes and forehead. To get rid of headaches, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital suggest that patients eliminate traumatic factors, bad habits, normalize work and rest patterns, and nutrition. Hypnosis, manual therapy, and acupuncture are effective in treating headaches due to autonomic disorders. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are fluent in non-drug treatment methods and use proprietary rehabilitation methods.
Make an appointment
What is VSD
Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD), or neurocirculatory syndrome, is a functional disorder of the autonomic nervous system, in which a complex of symptoms appears that are not characteristic of a specific disease. Examination of patients with suspected VSD most often does not reveal changes in the structure of internal organs, but may show deviations in their function at the border of normal.
Autonomic dysfunction cannot be called a full-fledged disease; this diagnosis is not included in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). But therapists, cardiologists and neurologists continue to make this diagnosis to patients in whom the examination did not reveal any disorders, and complaints of poor health continue.
It is believed that manifestations of pathology arise due to disturbances in the coordination of the two structures of the autonomic nervous system. It consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, which differ in their effects on the body. The activator of sympathy is the hormone adrenaline, so it performs the following functions:
- increases the number of heart contractions;
- increases blood pressure;
- stimulates the release of glucose into the blood;
- dilates the arteries of the brain, lungs and heart;
- reduces saliva secretion;
- suppresses peristalsis of the digestive tract;
- dilates the bronchi and enhances gas exchange;
- enlarges pupils;
- causes spasm of the sphincters of the bladder and digestive tract.
These reactions are necessary to protect the body in a dangerous situation, to activate it to escape. The parasympathetic nervous system works in the opposite direction. It reduces blood pressure, accelerates peristalsis of the intestines and urinary organs, and constricts the pupils and bronchi. The parasympathetic activator is the substance acetylcholine. It slows down the heartbeat, reduces blood glucose levels and relaxes all the sphincters in the body.
Autonomic dystonia occurs when the sympathetic or parasympathetic system is activated spontaneously, for no apparent reason. Therefore, a person suddenly has an increased heartbeat while at rest, his blood pressure rises, and he is worried about anxiety.
But often vegetative-vascular dystonia is a precursor to serious diseases. Having arisen at a young age without treatment, after a few years it leads to the formation of arterial hypertension, heart disease, digestive tract and hormonal disorders.
Diagnostics
Vegetative-vascular dystonia has various clinical manifestations. In this regard, it is necessary to carefully carry out diagnostics to differentiate pathological conditions. The main research methods include:
- clinical blood test;
- biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- blood for thyroid hormones;
- rheoencephalography;
- ECG;
- EchoCG;
- 24-hour Holter monitoring;
- MRI.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use modern equipment. With their help, it is possible to establish the causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia in the shortest possible time. Experienced specialists select effective treatment aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the pathological condition.
Treatment
Therapy for vegetative-vascular dystonia begins with a visit to a psychotherapist and lifestyle changes.
Medicines are used exclusively in complex treatment. The drug and dosage are determined by doctors at the Yusupov Hospital after examining the patient. For VSD, neurologists prescribe the following medications:
- antidepressants;
- sedatives;
- tranquilizers;
- nootropic drugs.
Antidepressants are necessary to get rid of the manifestations of depressive conditions that are observed with vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Medicines quickly relieve anxiety and depression, improve sleep quality and increase appetite. For vegetative dystonia, antidepressants are prescribed first, since eliminating depression simultaneously reduces other manifestations of VSD. With prolonged use, the drugs are addictive. Antidepressants cause side effects that include various disorders of the central nervous system, increased sweating, heart rhythm disturbances and nausea. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are careful when choosing a drug for the treatment of VSD. The most harmless and effective antidepressants are azafen, deprim, cipralex. Sedatives reduce anxiety. In the treatment of VSD, drugs based on medicinal herbs, barbiturates, bromine and magnesium preparations are used. Herbal remedies are considered the safest, since they have minor side effects and do not have significant contraindications. For VSD, neurologists use drugs based on valerian extract (Novo-Passit, Dormiplant, Persen) and hawthorn (Kralal, Fitosed). Barbiturates have significant side effects. They can be addictive, and if the dosage is slightly exceeded, they can lead to poisoning. The safest drugs in this group are Corvalol, Barboval, Valocordin. They are prescribed for the cardiac form of VSD.
Tranquilizers are effective medications that provide a quick but short-term sedative effect. They relieve feelings of fear, worry, anxiety, and relieve emotional stress. Drugs of this pharmacological group are not prescribed during pregnancy and weakened immunity, children and mental patients. VSD therapy is carried out with gentle medications with a gradual transition to more powerful drugs. To treat VSD, doctors use diazepam, nozepam, oxazepam, seduxen, and elenium.
Nootropic drugs include drugs that affect certain brain functions:
- activate mental activity;
- improve memory;
- increase learning abilities.
The use of drugs in this group relieves patients with VSD from weakness and apathy, promotes clarity of consciousness, and eliminates psychomotor retardation. Nootropics have mild side effects and low toxicity. Most often, doctors prescribe glycine, phenibut, piracetam, nootropil, and fezam for VSD.
Crises with vascular dystonia. Symptoms and treatment in adults
Panic attack
– sympathoadrenal crisis. A huge amount of adrenaline is released into the blood. A sharp headache occurs, blood pressure rises, the heart “jumps out of the chest,” the skin turns pale. Fingers and toes become cold and numb. A person feels a strong feeling of anxiety and fear. The crisis passes on its own. After it, the patient feels exhausted for a long time.
Vagoinsular crisis
occurs when insulin is released into the blood. As a result, glucose levels drop sharply and heart failure occurs. It seems to stop. The patient feels short of breath. The pulse slows down, the pressure drops, and the vision becomes dark. Fainting may develop. The skin turns red and there is increased sweating. There may be diarrhea and flatulence.
Complications
Many people do not attach importance to such a diagnosis as vegetative-vascular dystonia. This opinion is wrong. Like any disease, VSD can lead to complications. Among them:
- hypertension;
- hypotension;
- visual impairment;
- anemia;
- depression;
- weight loss;
- involuntary urination.
In this regard, doctors recommend seeking medical help when the first pathological signs appear. This will help to identify the problem in time and carry out a course of treatment.
Advantages of treating VSD at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a multifactorial disorder in the body; its successful treatment requires an integrated approach and coordinated work of doctors of many specialties. Among the undeniable advantages of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg), it is worth mentioning 3 key points:
- High professionalism of doctors - the staff consists of more than 300 experienced practicing doctors and diagnosticians of 67 medical specialties. Leading corresponding members of the Russian Academy of Sciences, academicians, professors, doctors and candidates of medical sciences advise here. The clinic was the first in Russia to receive accreditation according to the international standards for assessing the quality of medical care JCI. Joint Commission International, considered the highest level of accreditation worldwide.
- Ultra-modern technical base - equipped with the latest generation diagnostic and treatment equipment from the world's leading manufacturers. This allows you to create your own scientific and clinical developments in almost all medical areas. For many years, the clinic of JSC "Medicine" has served as a clinical base for the Department of Therapy and Family Medicine of the Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov (RNIMU) and is among the innovatively active healthcare institutions in Moscow.
- High-quality medical care - the effectiveness and safety of treatment is guaranteed by the principle of Academician N.A. Semashko, which states: “One patient - one doctor.” The attending physician is assigned to each patient and works closely with colleagues from related medical specialties. A developed diagnostic base and medical care technology built according to international standards make it possible to make a diagnosis at an unprecedented speed. In just 1 day from the moment of the initial examination and diagnostic measures, you can receive detailed results of laboratory tests, detailed diagnostic reports and doctor’s recommendations.
It is important to know: VSD is not a critically severe disorder, but can provoke one in the absence of proper medical care. In case of early access to a doctor, treatment time is significantly reduced and financial costs are reduced. Don’t delay your visit, make an appointment at a time convenient for you, and we will help you regain your health!
Prevention
In order to reduce the risk of developing symptoms of VSD, the following preventive recommendations must be followed:
- to live an active lifestyle;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress;
- do not abuse alcohol or caffeine-containing drinks;
- stop smoking;
- adhere to a rational and balanced diet.
These medical advice will help minimize the possibility of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
When the first signs of pathology appear, you must contact a doctor for a medical examination. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital in Moscow will perform a full course of diagnostics necessary to identify vegetative-vascular dystonia. They will prescribe treatment that will relieve the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
You can ask questions or make an appointment with a doctor by phone.
Make an appointment
Vascular dystonia. Symptoms and treatment
- Sympathicotonia is the predominance of the tone of the sympathetic nervous system. It is characterized by: pale skin, vasoconstriction, hypertension, tachycardia, dilated pupils, intestinal lethargy, heightened anxiety, and a feeling of fear.
- Vagotonia is the reverse state of sympathicotonia. Accompanied by redness of the skin, dilation of blood vessels, sweating, hypotension, bradycardia, constriction of the pupils, acceleration of bowel function, and irritability.
Sometimes the symptoms of VSD are mosaic; in this case, sympathetic and parasympathetic disorders are present simultaneously.
Therapy is selected individually, taking into account the main manifestations and the predominance of one or another department.