B12 deficiency anemia - symptoms and treatment
To correctly diagnose B12DA, an examination by a hematologist is important. To clarify and correct problems associated with the gastrointestinal tract, you will need to consult a gastroenterologist. An examination by a neurologist may be necessary to evaluate neurological manifestations.
Patient examination
During examination, the doctor may notice pallor and slight jaundice of the skin, an increase in heart rate and expansion of the boundaries of the heart. It is necessary to examine the oral cavity, especially the tongue. A neurologist can assess muscle tone and the presence of pathological reflexes.
Laboratory diagnostics
One of the most important stages of diagnosis is the evaluation of a clinical blood test . The analysis shows:
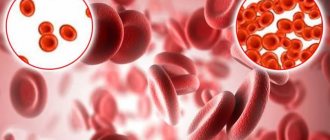
- decreased hemoglobin - anemia;
- macrocytosis - the presence in the blood of a large number of abnormally large red blood cells (macrocytes);
- hyperchromia - intense staining of red blood cells caused by an increased amount of hemoglobin in the blood;
- a decrease in the number of leukocytes and platelets may be observed.
It is necessary to perform a blood smear , in which a morphologist can see pathological forms of red blood cells:
- ovalocytes (oval-shaped red blood cells) and degenerative forms;
- an increase in the difference in erythrocyte size (RDW parameter);
- specific pathological inclusions, such as Jolly bodies and Cabot rings;
- megalocytes and megaloblasts - in severe cases.
Pathological forms of neutrophils may also occur:
- giant neutrophils;
- neutrophils with nuclear hypersegmentation (5 or more segments);
- metamyelocytes are immature neutrophilic leukocytes.
The number of young forms of red blood cells (reticulocytes) is usually reduced. If laboratory capabilities are available, additional useful information can be provided by reticulocyte indices: the average volume of reticulocytes and the average hemoglobin content in reticulocytes increases, the fraction of immature reticulocytes increases [1][2][4][5].
In a biochemical blood test:
- decreased levels of vitamin B12;
- indirect bilirubin and lactate dehydrogenase may be increased - a sign of early destruction (hemolysis) of red blood cells in the blood and the breakdown of red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow [4];
- Iron and ferritin levels are normal.
It is imperative to evaluate folic acid levels , since changes in clinical analysis for B12 and folic acid deficiency are similar, but treatment is different. If B12DA is suspected, but vitamin B12 and folic acid levels are normal, serum holotranscobalamin (active vitamin B12) determination is recommended. In case of B12 deficiency, its content is reduced. Increases in serum homocysteine and methylmalonic acid levels may be detected [2][3].
In a general urine test, persistent proteinuria may be observed - the appearance of protein in the urine. In some cases, there is an increase in the level of methylmalonic acid and homocysteine.
Additional laboratory tests that may help identify the cause of vitamin B12 deficiency:
- study of antibodies to internal Castle factor (IgG) and gastric parietal cells in blood serum;
- examination of gastric juice to identify internal Castle factor and antibodies to this factor (IgA, synthesized by parietal cells of the stomach);
- Schilling test - determines the activity of the intrinsic factor of Castle and the absorption of vitamin B12 in the intestines;
- tests for malabsorption (impaired absorption of nutrients) [5].
Prenatal diagnosis of genetically determined deficiency of the transport protein transcobalamin II is possible
Instrumental diagnostics
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs can detect minor hepatosplenomegaly - enlargement of the liver and spleen.
To identify diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that may interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12, all patients with newly diagnosed B12DA are recommended to undergo endoscopic examinations - fibrogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy . FGDS may reveal chronic atrophic gastritis, duodenitis, and a decrease in gastric secretion may be observed. In the presence of pathological changes, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the gastric mucosa with further histological examination [3][4].
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis for B12-deficiency anemia, especially with a decrease in leukocytes and platelets, is carried out with the following diseases of the blood system:
- Myelodysplastic syndrome is a group of hematological diseases in which the bone marrow does not produce enough of one or more types of blood cells: platelets, white blood cells, red blood cells.
- Aplastic anemia is anemia that occurs due to insufficient production of red blood cells due to a decrease in the number of hematopoietic stem cells.
To clarify the diagnosis, it may be necessary to perform a bone marrow puncture and its morphological examination. If B12DA is present, a morphologist describes characteristic changes in stem progenitor cells in the bone marrow:
- hyperplasia (proliferation) of the erythroid germ - stem progenitor cells from which red blood cells are formed;
- megaloblastic type of hematopoiesis, in which large cells with granular nuclei, pathological mitoses, and Jolly bodies are formed;
- impaired maturation of myeloid cells and platelet precursors: giant metamyelocytes, hypersegmentation of neutrophils, multinucleated megakaryocytes [1][2][3][4].
Diagnosis of anemia
Laboratory diagnostic methods: determination of Hb, Ht, reticulocytes, erythrocyte volume and examination of a peripheral blood smear.
Anemia is indicated by a decrease in such indicators as: Hb in men less than 130 g/l and in women less than 120 g/l; decrease or increase in reticulocytes, Ht less than 35% in women and less than 42% in men, etc.
Anemia varies according to:
- Degree of severity (mild, moderate, severe)
- Red blood cell size (microcytic, normocytic, macrocytic)
- According to the hemoglobin content in erythrocytes (hypo-, normo-, hyperchromic)
- Regenerative capacity of bone marrow (hypo-, hyper-, normoregenerative).
Types of anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia
IDA is a syndrome in which the supply of iron in the body is reduced and the synthesis of iron-containing proteins is disrupted. This type of anemia is very common and occurs in both adults and children. Manifested by a decrease in hemoglobin concentration and trophic disorders in tissues. The brain especially suffers from lack of oxygen.
Symptoms in the initial stages should never be ignored!
If suddenly the following symptoms appear for some time, then this is a serious reason to consult a general practitioner:
- constant weakness
- decreased performance
- increased fatigue
- pale dry skin
At first glance, completely harmless symptoms can lead to the development of a serious illness and cause significant damage.
The norm for an adult is up to 5 g of iron.
The state of iron deficiency is provoked by the following conditions:
- chronic and acute blood loss
- diets and fasting
- gastrointestinal diseases
- pregnancy, lactation
- physical activity, sports
If you do not seek help from specialists, then over time the symptoms expand:
- the skin becomes pale with a greenish tint, becomes flabby, dry; hair becomes dry, brittle, quickly turns gray, and begins to fall out;
- nail plates become thin, flat, and can take on a concave shape;
- A characteristic symptom only for IDA is muscle weakness!
Diagnosis of iron deficiency
A complete laboratory diagnosis is required:
- blood test (general and biochemical),
- consultation with a specialist: gynecologist, urologist, proctologist, hematologist
- You may even need a bone marrow puncture.
After diagnostic measures, the therapist prescribes an individual treatment regimen, which is carried out for a long time with iron supplements. Therapeutic dosages are prescribed until hemoglobin levels normalize, then the patient is transferred to prophylactic doses.
Modern studies have shown that following a diet with mild IDA can normalize blood counts and avoid taking iron supplements. You should include foods high in protein and iron in your diet: liver, beef tongue, veal, turkey, red sea fish, eggs, buckwheat, peaches, persimmons, apples. Dairy products and tea should be excluded, because they interfere with iron absorption.
Pay attention to your health, contact experienced specialists, because a correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of the disease! Take care of yourself and be healthy!
B12 anemia: causes
The daily requirement of the human body for vitamin B12 is from one to five micrograms. It is satisfied through its consumption with food: after entering the stomach, the vitamin is separated from protein under the influence of enzymes. In order for the body to fully absorb it, a process of connection with glycoprotein and other factors must occur. Absorption of the vitamin into the blood occurs in the lower part of the ileum, from where it passes to the tissues. Factors that can initiate the development of anemia are divided into two groups:
- Nutritional – an unbalanced diet that is unable to ensure the required amount of B12 enters the body. This often happens if the patient practices fasting, vegetarianism, or diets that minimize or eliminate the consumption of animal protein;
- Endogenous – disruptions in the process of vitamin absorption due to a deficiency of protein that binds the vitamin and converts it into an absorbable form. A similar phenomenon can be initiated by: a congenital absence of the internal Castle factor;
- inflammatory processes of the gastric mucosa in a chronic form;
- condition after gastric excision surgery;
- condition after partial removal of the ileum or duodenum;
- inflammation of the small intestine (enteritis), pancreas (pancreatitis);
- gluten enteropathy;
- granulomatous inflammation of the digestive tract (Crohn's disease);
- protrusions of the intestinal wall - (diverticula);
- neoplasms of the jejunum of a malignant nature;
- helminthic infestations caused by different types of helminths.
The reasons may lie in physical and mental dependence on alcohol intake, in the use of Colchicine, Neomycin, as well as a number of oral contraceptives.
B12 anemia: treatment
Treatment tactics for B12-deficiency anemia are developed by CELT specialists according to diagnostic results and individual patient indications. If the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment will be carried out for life, and every five years an endoscopic examination of the gastric mucosa will be required, eliminating the risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
In order to compensate for the deficiency of the vitamin, the patient is prescribed intramuscular administration. Treatment of diseases and disorders that initiated the development of anemia is carried out:
- elimination of helminths;
- taking digestive enzymes;
- operations for diverticula and malignant tumors;
- food with a high content of animal protein;
- taking glucocorticoids for disorders of the production of internal factor.
If you start treating anemia in a timely manner, your blood counts will return to normal in one and a half to two months. Neurological symptoms persist for up to six months; if treatment was started at an advanced stage, they are irreversible and cannot be cured.
The Department of Hematology at CELT welcomes candidates, doctors and professors of medical sciences with over twenty-five years of practical and scientific experience. You can make an appointment with them online or by contacting our operators. No less experienced and qualified specialists perform septoplasty in the otolaryngology department.
At CELT you can consult a hematologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
By making an appointment with a hematologist, you can get a comprehensive consultation. The doctor is competent to treat various blood diseases, most of which can be identified in the early stages and prescribe timely treatment to cope with the disease quickly and easily.