Composition of NovoPassit
Composition of the drug in tablets
Each tablet contains guaifenesin (200 mg) and dry herbal extract (157.5 mg):
- common hawthorn/unicorn;
- St. John's wort;
- lemon balm;
- common hop;
- passionflower incarnata;
- valerian officinalis;
- black elderberry.
Additional components:
- Mg stearate;
- colloidal silicon dioxide;
- lactose monohydrate;
- glycerol;
- microcrystalline cellulose.
The film shell contains green Opadry “AMB 80W31115”.
Syrup composition
5 ml of solution contains 200 mg of guaifenesin and liquid extracts of medicinal herbs (387.5 mg).
Additional components:
- Na citrate dihydrate;
- orange flavor;
- sodium cyclamate;
- water;
- sodium benzoate;
- propylene glycol;
- maltodextrin;
- invert sugar syrup;
- xanthan gum;
- 96% ethanol;
- sodium saccharinate monohydrate.
Release form
The medication is available in two dosage forms:
- NovoPassit syrup;
- film-coated tablets (NovoPassit tablet p/o No. 10 10x1).
The syrupy solution has a characteristic odor. Color: brown-red to persistent brown. The solution may be slightly cloudy or clear. When the vial is immobilized, a small sediment may form, which dissolves after vigorous shaking. The solution is available in dark glass bottles of 100 or 200 ml. The cardboard pack contains 1 bottle, instructions and measuring cap.
Tablets are produced in polyethylene jars (60 pcs.) and convolutes (10 pcs.). The pack contains 1 can or 1.3 convolutes of tablets.
Bromhexine + Guaifenesin + Salbutamol
Dosage form
Syrup
Composition per 1 ml:
Active ingredients:
- Salbutamol sulfate – 0.24 mg
- corresponds to salbutamol – 0.2 mg
- Bromhexine hydrochloride – 0.4 mg
- Guaifenesin – 10 mg
Excipients:
- Sucrose (sugar) – 500 mg
- Sorbitol (70% solution) – 263 mg
- Glycerol (glycerol) – 125 mg
- Propylene glycol – 62 mg
- Sodium benzoate – 2 mg
- Citric acid monohydrate – 2.4 mg
- Sorbic acid – 1 mg
- Sunset yellow dye (FCF) – 0.028 mg
- Levomenthol (menthol) – 0.1 mg
- Blackcurrant flavor – 3 mg
- Pineapple flavor – 1 mg
- Purified water – up to 1 ml
Description
Transparent viscous liquid of orange color with a characteristic odor. Slight opalescence is acceptable.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
combined expectorant.
ATX code
: R05C
Pharmacological properties
The combined drug has a bronchodilator, expectorant and mucolytic effect. Salbutamol is a bronchodilator that stimulates beta 2 adrenergic receptors in the bronchi, blood vessels and myometrium. Prevents or eliminates bronchospasm, reduces resistance in the respiratory tract, increases the vital capacity of the lungs. Causes dilatation of the coronary arteries, does not reduce blood pressure. Bromhexine is a mucolytic agent. Has an expectorant effect, improves sputum discharge. Guaifenesin is a mucolytic agent that reduces the surface tension of the structures of the bronchopulmonary apparatus; stimulates secretory cells of the bronchial mucosa that produce neutral polysaccharides, depolymerizes acidic mucopolysaccharides, reduces the viscosity of sputum, facilitates the removal of sputum and promotes the transition of a non-productive cough to a productive one.
Pharmacokinetics
Salbugamol: when taken orally, absorption is high. Eating reduces the rate of absorption but does not affect bioavailability. Communication with plasma proteins – 10%. Penetrates through the placenta.
Subjected to first-pass metabolism in the liver and in the intestinal wall, it is inactivated by phenolsulfotransferase to 4-o-sulfate ester. The half-life (T1/2) is 3.8-6 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys (69-90%), mainly in the form of an inactive phenol sulfate metabolite (60%) within 72 hours and with bile (4%). The bioavailability of orally administered salbutamol is about 50%.
Bromhexine: when taken orally, it is almost completely (99%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) within 30 minutes. Bioavailability is low (the effect of primary “passage” through the liver). Penetrates through the placental and blood-brain barriers. In the liver it undergoes demethylation and oxidation, metabolized to the pharmacologically active ambroxol. T1/2 – 15 hours (due to slow reverse diffusion from tissues). Excreted by the kidneys. In chronic renal failure, the excretion of metabolites is impaired. May accumulate with repeated use.
Guaifenesin: absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is rapid (25-30 minutes after oral administration). T1/2 – 1 hour. Penetrates tissues containing acidic mucopolysaccharides.
Approximately 60% of the administered drug is metabolized in the liver. It is excreted by the lungs (with sputum) and the kidneys, both unchanged and in the form of inactive metabolites.
Indications for use
As part of combination therapy for acute and chronic bronchopulmonary diseases accompanied by the formation of difficult-to-discharge viscous secretions:
- bronchial asthma;
- tracheobronchitis;
- obstructive bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- emphysema;
- whooping cough;
- pneumoconiosis;
- pulmonary tuberculosis, etc.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
- tachyarrhythmia, myocarditis;
- heart defects;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- glaucoma;
- liver or kidney failure;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute stage;
- children under 2 years of age;
- sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Carefully
prescribed to patients with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, gastric and duodenal ulcers in remission, hyperthyroidism, severe diseases of the cardiovascular system; for diseases of the bronchi accompanied by excessive accumulation of secretions; children's age from 2 to 6 years; should not be used in combination with beta-blockers.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Directions for use and doses
Inside. Adults and children over 12 years of age are prescribed 10 ml (2 teaspoons) 3 times a day. Children aged 2 to 6 years – 5 ml (1 teaspoon) 3 times/day, from 6 to 12 years – 5-10 ml (1-2 teaspoons) 3 times/day. Shake before use.
Side effect
The frequency of adverse reactions was assessed based on the following criteria: very common (> 1/10), common (> 1/100 to < 1/10), uncommon (> 1/1000 to < 1/100), rare ( from > 1/10000 to < 1/1000), very rare (< 1/10000), frequency unknown (no data available to estimate frequency).
Immune system disorders.
Rarely: allergic reactions (rash, urticaria), bronchospasm (as a sign of a hypersensitivity reaction).
Not known: anaphylactic reactions including anaphylactic shock, angioedema, pruritus, severe cutaneous adverse reactions including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
Nervous system disorders
Rarely: when used in high doses, headache, dizziness, increased nervous excitability, sleep disturbance, drowsiness, tremor, and convulsions are sometimes observed.
Cardiovascular disorders
Rarely: rapid heartbeat, decreased blood pressure, collapse.
Frequency unknown: myocardial ischemia.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Rarely: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Renal and urinary tract disorders
Rarely: urine may turn pink.
Overdose
The manifestations of the described side effects may increase. Treatment is symptomatic.
Interaction with other drugs
Other beta-2 adrenergic agonists and theophylline enhance the effect of salbutamol and increase the likelihood of side effects.
The drug is not prescribed simultaneously with drugs containing codeine and other antitussives, as this makes it difficult to clear liquefied sputum.
Bromhexine, which is part of the drug, promotes the penetration of antibiotics (erythromycin, cephalexin, oxytetracycline) into the lung tissue.
It is not recommended to use the drug simultaneously with non-selective beta-adrenergic blockers, such as propranolol.
Salbutamol, which is part of the drug, is not recommended for patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and/or tricyclic antidepressants.
Diuretics and glucocorticosteroid preparations enhance the hypokalemic effect of salbutamol.
It is not recommended to take alkaline drinks at the same time as the drug.
special instructions
During post-registration use of salbutamol, there were a small number of reports of rare cases of myocardial ischemia associated with the use of this drug. There have been reports of severe skin reactions such as erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) associated with the use of ambroxol (a potent metabolite of bromhexine). If symptoms of a progressive skin reaction occur (sometimes associated with damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, nose, eyes, genitals), stop using the drug immediately and consult a doctor. It is not recommended to take alkaline solutions simultaneously with the drug. Guaifenesin turns urine pink.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Not studied. Considering the profile of side effects (dizziness, drowsiness, etc.), it is recommended during treatment to refrain from driving vehicles and machinery, and from engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Release form
Syrup.
50 ml, 60 ml, 70 ml, 80 ml, 90 ml, 100 ml, 120 ml, 150 ml or 200 ml of the drug in dark glass bottles sealed with polyethylene stoppers and screw-on plastic caps or sealed with polyethylene or polymer closures, or sealed with aluminum caps.
50 ml, 60 ml, 70 ml, 80 ml, 90 ml, 100 ml, 120 ml, 150 ml or 200 ml of the drug in polymer bottles made of polyethylene, sealed with polyethylene stoppers and screw-on plastic caps or sealed with polyethylene or polymer closures polyethylene, or sealed with aluminum caps.
50 ml, 60 ml, 70 ml, 80 ml, 90 ml, 100 ml, 120 ml, 150 ml or 200 ml of the drug in polyethylene terephthalate bottles sealed with polymer screw caps. Each bottle, along with a plastic spoon or plastic measuring cup or cap, along with instructions for medical use, is placed in a cardboard pack.
Storage conditions
Store in a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
2 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Vacation conditions
On prescription.
Indications for use
The medication has sedative and anxiolytic effects.
What does the medication help with and main indications:
- mild forms of insomnia ;
- neurotic reactions and neurasthenia , accompanied by anxiety, irritability, fatigue, fear, absent-mindedness ;
- migraine;
- headache caused by nervous tension;
- “manager syndrome” (constant mental stress);
- itchy dermatoses caused by psychological overload ( seborrheic eczema , atopic eczema , urticaria );
- climacteric syndrome;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- functional diseases of the digestive system (irritable bowel syndrome, dyspeptic syndrome, etc.).
Side effects
- decreased concentration;
- increased drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- vomit;
- diarrhea syndrome;
- constipation;
- heartburn;
- spasms;
- nausea.
The following side effects are less commonly reported:
- muscle weakness;
- fatigue;
- exanthema;
- allergic responses.
Negative symptoms disappear after completion of treatment. If other manifestations are registered, you must contact the doctor who prescribed the medication.
Instructions for use of NovoPassit (Method and dosage)
NovoPassit tablets, instructions for use
The drug must be taken three times a day, 1 tablet (in severe cases, the single dose can be increased to 2 tablets). If severe depression and fatigue are registered, morning and evening dosages are reduced to 0.5 tablets.
How to take tablets for nausea: preferably with food. The interval between doses is 4-6 hours.
NovoPassit syrup, instructions for use
The solution can be taken either diluted or undiluted. For ease of dosing, a special measuring cap is included. NovoPassit syrup should be taken three times a day, 5 ml (it is possible to increase the single dose to 10 ml). If tolerance is poor, morning and evening doses are reduced to 2.5 ml. The time interval between doses is 4-6 hours.
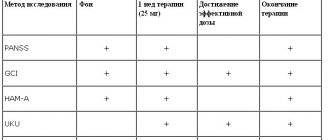
Novo-Passit in psychiatric and neurological practice
In a study at a psychiatric clinic
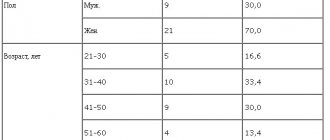
In Hradec Králova, 38 patients aged from 28 to 90 years (average age 73.5 years) took part in an open trial of the drug. These were mainly patients with neurological disorders (neurasthenia, ansiolitic neurosis, depressive neurosis), personality disorders, suffering from various forms of dementia, as well as patients with schizophrenia.
Patients received drugs in a dose of 5 ml 3 times a day for 21 days. An improvement in the clinical picture during treatment with Novo-Passit was observed in 68% of patients, and during treatment with Passit - only in 37% of patients.
The effect of both drugs on the following symptoms was assessed: sleep disturbances, drowsiness, fatigue and exhaustion, poor performance, headaches, sweating, loss of consciousness, vomiting, feeling hot or cold, attention problems, irritability, memory problems, palpitations, lack of appetite, diarrhea or constipation, hot flashes, pessimism, tearfulness, hypersensitivity, agitation and nervousness, fear for health, fear of the future, obsessions.
The positive effect of Novo-Passit was noted when influencing general mental energy, as well as the daily dynamics of symptoms: sleep disorders, drowsiness, fatigue, low performance, headaches, attention and memory disorders, anxiety. Novo-Passit has confirmed its higher effectiveness compared to Passit in affecting the following symptoms: fatigue, exhaustion, sleep disorders, headaches, absent-mindedness, memory disorders and anxiety.
Side effects included nausea and vomiting in 3 patients and 1 case of dizziness. Most signs were observed in elderly patients, only 2 young patients noted dizziness and fatigue.
During therapy with Novo-Passit, there was no clinically detectable increase in the level of laboratory parameters of biochemical functions. Most deviations were minor and were not accompanied by clinical reactions. There were moderate increases in alkaline phosphatase, glycemia, white blood cell count, urea, creatinine, and cholesterol levels.
As a result of clinical studies, no complications or side effects were identified. However, as mentioned in the literature, myasthenia gravis is considered a contraindication. Precautions are necessary when using the drug in the case of certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The proposed dosage of 5 - 10 ml 3 times a day is considered satisfactory. The main area of indications for prescribing the drug in psychiatry, according to prof. M. Zapletalek and his colleagues are considered gerontology.
At the same time, the experience of domestic psychiatrists has shown that Novo-Passit can be successfully used in child psychiatry
and, in particular, in outpatient practice. We will talk more about this in future issues of the magazine.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the influence of Novo-Passit on the learning process. Thus, Professor J. Hrbek proposed a method for studying verbal communication in laboratory conditions.
The experiment was carried out on a group of 16 healthy volunteers (university students). The subjects did not use any other stimulants. Novo-Passit was used in 2 doses (5 ml and 10 ml) and the effect on the learning process was compared with the effect of the drug Passit. Both drugs were administered at the same dose. The training lasted 4 weeks, and each subject was examined 4 times during this period. After taking Novo-Passit, the subjects showed much better results compared to Passit. The need for repetition decreased and the frequency of correct answers increased in all patients. The difference between the higher and lower doses of Novo-Passit was insignificant. The effect of Novo-Passit appeared 2 hours after administration. The drug caused calm in the subjects, which contributed to better brain activity. No noticeable side effects were identified.
Novo-Passit has undergone clinical trials in neurological hospitals.
In a Prague clinic, the drug was used in patients with headaches of vasomotor origin caused by stress of a psychoendocrine nature (menopause, menstruation).
Women received Novo-Passit at a dose of 5 ml 3 times a day for 6 weeks. The control group consisted of 15 patients. These patients took Passit in the same dose and in the same regimen as Novo-Passit. A complete therapeutic effect was observed in 11 patients (37%) and in 13 patients (43%) the drug brought a significant reduction in pain intensity. In the group using Passit, only 2 patients noted a decrease in headaches. There was a decrease in anxiety, but no effect on headaches.
Thus, it has been shown that Novo-Passit, unlike Passit , is effective in the treatment of vasomotor headaches, in the pathogenesis of which psychogenic and personal factors play a large role (Macek).
No serious side effects were noted.
In another clinic (Prof. Maiwald), 32 patients received the drug for 3–4 weeks for the same indications. Novo-Passit was effective in 27 (84%) patients. Unlike Novo-Passit, the therapeutic effect of Passit was observed in only 14 patients. In most patients, the clinical effect began to appear within 1 to 3 days from the start of administration. Side effects were observed in 3 patients. These were stomach upsets, cramps and heartburn. But in none of the cases did these reactions require discontinuation of treatment.
A total of 62 patients with neurological diseases were studied. The drug was most effective for vasomotor headaches and headaches of psychogenic etiology. Regarding neuralgia, the therapeutic effect was not convincing due to the small number of patients suffering from this disease included in the study. Improvement in clinical condition was observed in 85.2% of patients. Side effects were found in only 6 patients (9.84%). Observed side effects: short-term stomach upsets, cramps, heartburn, itching and eczema on the skin of the back and increased drowsiness. No serious side effects associated with taking Novo-Passit were noted. All unwanted effects usually resolved when the drug was taken with food. The therapeutic dose of 5 ml 3 times a day was sufficient for effectiveness for neurological indications.
Interaction
Novo-Passit is characterized by an increase or decrease in the effects of other medications used simultaneously. Medicines that relax skeletal muscles ( central muscle relaxants ) may increase the severity of side effects such as muscle weakness. Novo-Passit is able to enhance the effects of ethanol and other substances that have a depressing effect on the functioning of the nervous system.
The sedative contains St. John's wort extract , which can reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraception . A decrease in the effectiveness of immunosuppressants (medicines used after organ transplantation to reduce the risk of rejection of the transplanted tissue or organ) is also recorded. A similar effect is observed for drugs used to treat cardiovascular pathology, AIDS, diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, as well as medications that prevent the development of thromboembolism .
Active ingredient: guaifenesin
The use of guaifenesin in therapy began at the end of the last century, when its antiseptic effectiveness was discovered; its expectorant effect was discovered later. After the Second World War, the substance began to be used as a muscle relaxant and in the field of psychiatry. Guaifenesin was first tested in psychiatry by Frankl, and then by Leventhal and Ringl in 1952. A year later, the results of therapy with guaifenesin were published by Leinart. The results of these studies confirmed its high effectiveness in anxiety states accompanying various mental illnesses.
Guaifenesin mainly affects neurotic disorders. It was found that it has the greatest effect on anxiety, especially of neurotic origin (effect in 80% of patients). To a lesser extent - on a state of anxiety, accompanied by obsessive ideas.
It also eliminates fears, especially those associated with upcoming unpleasant events (exams, painful medical procedures, etc.).
Another potential area of clinical use for guaifenesin is headaches. Guaifenesin eliminates the main cause of psychogenic etiology (anxiety, tension), as well as increased muscle tone in the craniocerebral region.
Considering its excellent effect on the state of psychogenic tension with vegetative symptoms (palpitations, shortness of breath, insomnia, headaches), a number of Czech psychiatrists (M. Zapletalek and others) recommend it for the so-called. “manager disease”, i.e. for people working in a state of constant stress in leadership positions.
The drug is non-toxic, with virtually no side effects. Isolated cases of allergic dermatoses have been observed, as well as mild muscle weakness (Smith, Carraza, Ginrel).
special instructions
It is unacceptable to drink alcohol while taking NovoPassit.
In case of acute pathology of the digestive tract, the medication is prescribed with caution. Doctors should inform patients that if within 7 days the patient’s condition not only does not improve, but also worsens, then a doctor’s consultation is required.
Patients with fair skin are advised to avoid exposure to direct sunlight and refrain from visiting a solarium.
The medicine in the form of syrup is not prescribed for fructose intolerance (congenital characteristic), or for impaired absorption of galactose/glucose.
The syrup contains alcohol (12.19% ethanol). A single dose contains 0.481 grams of ethanol. Considering the characteristics of the medication, it is not recommended to drive vehicles or complex machinery during a course of taking a sedative.
Tablets or syrup - which is better?
The composition of the tablet form and the oral solution is absolutely identical. The tablets are easy to use - you can take them with you, but the syrup is easier to dose in pediatric practice.
Analogues of NovoPassit
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Alora
Motherwort extract
Cardiovalen
Liked
Carmolis
Valerian tincture
Lotusonic
Relaxil
Persen Forte
Persen
Phytosed
Sedavit
Motherwort Forte Evalar
Dormiplant
Sondox
Sedafiton
Peony tincture
Menovalen
Bromcamphor
Valerian rhizomes with roots
- Glycine;
- Calming collection;
- Tenoten;
- Tazepam;
- Persen.
Analogs of NovoPassit, which are cheaper in cost, may be inferior in quality and severity of the sedative effect (Glycine, Sedative collection, etc.)
NovoPassit or Tenoten - which is better?
Both drugs are anxiolytics, but NovoPassit additionally contains herbal extracts. Tenoten has a special series Tenoten for children , used in pediatric practice .
Reviews of NovoPassit
Reviews from doctors are mostly positive; the medication has pronounced sedative and mild anxiolytic effects.
Reviews of NovoPassit syrup
The solution is convenient to dose and is convenient to take for patients who have difficulties taking tablet forms of medications. Most often used in pediatric practice.
Reviews of NovoPassit tablets
Blisters can be taken with you; the tablets do not have a specific taste and are well tolerated without provoking negative reactions.
Plant extract Passit
The extract is prepared from 7 medicinal plants:
- Humulus lupulus (Hops)
- Hypericum perforatum (St. John's wort)
- Melissa officinalis (Melissa officinalis)
- Passiflora incarnata (Passionflower)
- Sambucus nigra (Elderberry)
- Valeriana offcinalis (Valerian officinalis)
- Crataegus oxyantha (Hawthorn)
Humulus lupulus (Hops)
Strobuli lupudi cones are used to prepare the extract. The extract contains bitter acids that have a sedative effect, the most important of which are humulone and lupulone (Tonsche, Serndt).
Hypericum perforatum (St. John's wort)
The pharmacologically active substance is quercetin galactoside – hypericin. This substance is effective for depression of psychogenic origin.
Valeriana offcinalis (Valerian officinalis)
In the mid-60s, valeropropriates were isolated and later their sedative effect was proven, which determines the effect of the drug (Schette).
Crataegus oxyantha (Hawthorn)
Hawthorn is a component of many drugs with a sedative effect due to its ability to improve cerebral circulation, as well as tonify and regulate cardiac activity. The latter effect is important in the treatment of functional disorders of the heart, such as palpitations and cardiac dyspnea in patients with neurotic disorders (Böhm, Hockers and Müller, Welsperger).
Passiflora incarnata (Passionflower)
The medicinal plant is used mainly in neurology. This extract is used in the treatment of insomnia, neurasthenia, hysteria, as well as nervous exhaustion (Leclerc). The medicine has a sedative effect and also has an analgesic effect. The tranquilizing effect of this medicinal plant has been used since 1867.
Melissa officinalis (Melissa officinalis)
Melissa has been cultivated as a medicinal plant since ancient times. It was mentioned in their works by Avicenna, Pliny and Dioscurides. It has a sedative, antispasmodic and antibacterial effect. The active component is bonin (Kagen, Kuchera).
Sambucus nigra (Elderberry)
Flowers of a medicinal plant are used to prepare Passit extract. It is used as a sedative, antipyretic and diuretic.
NovoPassit price, where to buy
The price of NovoPassit tablets varies in the range of 180-650 rubles depending on the number of tablets, region of sale and pharmacy. In Kharkov, the medicine (10 tablets) can be bought for 44 UAH (the price of NovoPassit in rubles is 110 rubles). The price of NovoPassit syrup varies in the range of 180-310 rubles. Costs may vary greatly in different regions. You can find out how much the drug costs in your city at the nearest pharmacy.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Novo-Passit tablets p.p.o.
60 pcs. Teva Pharm. enterprises s.r.o. RUR 736 order - Novo-Passit solution for internal approx. 200mlIvax Pharmaceuticals/Teva Czech.Prev.
RUR 368 order
- Novo-Passit tablets p.p.o. 30 pcs.Ivex Pharmaceuticals/Teva Czech.Prev.
RUR 492 order
- Novo-Passit tablets p.p.o. 10 pcs. Teva Pharm. enterprises s.r.o.
RUB 241 order
- Novo-Passit solution for internal approx. 100mlLIVEX-CR a.s./ Teva Czech Enterprises
260 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Novo-Passit tablets No. 60Teva
RUB 812 order
- Novo-Passit (table no. 10) Teva
RUB 236 order
- Novo-Passit tablets No. 60Ivax-CR
RUB 847 order
- Novo-Passit (bottle 100ml)Ivax-CR
RUB 274 order
- Novo-Passit (tablet No. 10) Ivax-CR
RUB 268 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Novo-Passit N10 tablets TEVA Czech Industries s.r.o., Czech Republic
52 UAH.order - Novo-Passit No. 30 tablets TEVA Czech Industries s.r.o., Czech Republic
117 UAH. order
- Novo-Passit 100 ml solution TEVA Czech Industries s.r.o., Czech Republic
80 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Novo-Passit tablets Novo-Passit tablets. p/o No. 10, IVAX Pharmaceuticals
61 UAH order
- Novo-Passit liquid Novo-Passit solution 100ml, IVAX Pharmaceuticals
92 UAH order
- Novo-Passit tablets Novo-Passit tablets. p/o No. 30, Teva Czech Industries
129 UAH order
show more
Introduction
The drug Novo-Passit has been in service with our doctors for more than 10 years and has rightfully won its rightful place among sedatives due to its effectiveness, the possibility of use in a wide variety of age groups, the absence of any side effects, high ansiolytic activity and, finally, very important for its accessibility.
Unfortunately, despite the significant experience accumulated by our psychiatrists and general practitioners in the domestic medical literature, we find a relatively small number of publications about this drug. We will try to fill this gap, following the wishes of our readers, especially since the tablet form of the drug will go on sale this year.
Composition of the drug Novo-Passit: solution Guaifenesin 4.0 (in 100 ml), plant extract Passit 7.75 g.