What are probiotics?
These are representatives of non-pathogenic microorganisms that restore the natural microflora and remove toxins from the body. Contain from one to several strains of beneficial bacteria.
Properties of probiotics:
- Increases human immunity.
- Block the proliferation of harmful microorganisms.
- Decomposes and removes toxins.
- Promotes the production of vitamins.
- Improves digestion.
- They localize fermentation and putrefaction of digestive products in the large intestine.
The main composition of probiotics is lactobacilli (help remove toxins from the body) and bifidobacteria (have a binding effect).
Let's look at the characteristics and effects of both drugs.
I'm panicking
Irina
September 7, 2020
Save. Help. What to do. I'm 31 years old. Exactly 2.5 months ago, on June 23, I was sick or caught a virus. The whole family ate homemade okroshka, and in the evening my husband and I drank wine and went to bed. At night I got sick in my stomach and had diarrhea. I walked a couple of times, then fell asleep. In the morning, weakness, nausea and diarrhea again. There is no temperature and never was. I started drinking enterofuril, but it didn’t help because it didn’t have time to be absorbed. A day later, my son and my mother started having diarrhea with water (they also ate okroshka), although my husband and older daughter had nothing. Then everything went back to normal for them, but I’m still shaking (sorry), I very rarely walk properly, sometimes I can pass loosely in the morning, and smoothly in the evening, but the stool has become thin as a pencil, this has never happened in my entire life. The chair was always decorated, the thickness was 3 times greater and strictly once a day, but now it’s either a porridge of porridge or a thin ribbon. Sometimes once a day. Sometimes porridge 5 times a day. Rumbling, twisting, swelling, some kind of overflow, as if there was water in the intestines, pain on the left, spasms. I can’t eat anything, especially salads. They come out right away, an hour later there are already pieces of tomatoes in the stool. I'm tired. But the most interesting thing is that I lost weight from 58 to 51. Well, it’s clear that I eat practically nothing, oatmeal with water in the morning, broth with chicken at lunch, buckwheat in the evening without anything. I cry constantly because of this, I have no strength. I want plums and fruit. I started smoking out of nerves; I had never smoked before. I did the following tests and examinations, went to the gynecologist (smears, ultrasound) and they said everything was fine. I went to an endocrinologist (ultrasound, hormones TTG, T4, T3) and the tests were perfect. I gave urine with sediment microscopy, the urine is excellent. I did an ultrasound scan of the kidneys, adrenal glands and urinary glands. All organs are working normally, the ultrasound said everything was fine, the liver and pancreas and the spleen and gall bladder, the organs are normal. I took biochemistry. Alt, Ast, gamma GT, total amylase, pancreatic amylase, lipase, phosphatase, creatinine, urea, serum calcium, cholesterol, total protein, bilirubin. All tests are good. I also tested my reactive protein, it was 0.6, that is, normal, I tested my ferritin, it was slightly elevated. The norm is up to 120, I have 159, I donated blood to the clinic with microscopy of a smear and leukocytes. formula. ESR 4, leukocytes 7 (the norm is up to 10), hemoglobin 134, in general everything is normal except the neutrophil segment, they are lowered 44.6% of the norm from 47, and lymphocytes, on the contrary, are increased 42.7% of the norm to 37. I donated blood yesterday. Before this, I took it 2 months ago and the same thing happened there, lymphocytes were increased, neutrophils were decreased, only there the values were a little higher. My plasma glucose is 4.95 mmol. I submitted my stool to the OCI, but nothing was found. The coprogram contains intracellular starch, which normally should be absent, plant. Digestible fiber is moderate. the quantity should also not be there, and the muscle fibers that are not changed are also moderate. quantity, there shouldn’t be them either. Stool pH 6.0 is slightly acidic, the rest is normal. Blood pressure is always 115/70. I measure the temperature every day morning/evening 36.0-36.3, WHAT SHOULD I DO??? When will my intestines return to normal, whatever I didn’t drink. I drank a mountain of pro and prebiotics. I noticed that when I start drinking enterofuril, my stools are better and the spasms go away, I take a tablet sometimes, and when I stop, my stools are porridge again, there is no blood in the stool. Tell me what other tests to take. Maybe calprotectin? And why is my ferritin elevated and my neutrophils and lymphocytes have been jumping for 2 months?! And can my kilos go away because I only eat oatmeal and broth, and cry almost every day. The anxiety doesn't leave me. I'm afraid that some kind of cancer, or ulcer, or Crohn's disease has developed during these 2.5 months. This has never happened in my life. Even if there was a rotovirus, then within a week everything returned to normal, including the stool. And now I’ve been suffering for the 3rd month, yesterday I ate shawarma, and within an hour it was already in pieces in the stool. There was some kind of quick transit from her. Help me with some advice. Today I received a coprogram of stool, there is neutral fat, a moderate amount of mucus and a small amount of yeast-like fungi, the tongue has a white coating lately. Maybe there is some kind of thrush in the intestines and this is causing diarrhea. I don’t know what to do anymore. In the morning there is rumbling, intestines wander everywhere, swell. What should I drink?! How to treat all this?
The question is closed
I'm panicking
Acipol
It contains beneficial bacteria (kefir grains) and lactobacilli, which stabilize the microflora of the intestinal tract. The drug also blocks the growth of harmful microorganisms, normalizes metabolism, peristalsis and bowel movements.
Produced in capsules. There is also a form designed for children from 3 months.
Applicable in situations:
- For dysbacteriosis.
- For intestinal infections.
- With prolonged antibiotic therapy.
- With inhibition of weight development in children.
- For prolonged diseases of the respiratory system.
- Allergic reactions associated with digestion.
- For atopic dermatitis.
It is prohibited for use by people with individual intolerance to probiotic components. No side effects were recorded.
Take the drug orally with the required amount of water. The duration of the course and portions are determined by the attending physician, taking into account the age, duration and form of the disease.
The usual dosage for adults is 1 capsule 3 or 4 times a day . Serving for children under 3 years of age – 1 capsule 3 times a day, the capsule must be opened and mixed in water or milk formula. To prevent diseases - 1 capsule 1 time per day, period of use is 2 weeks.
After antibiotics
In their second study, the researchers looked at what happens in the gut when a person takes probiotics after a course of antibiotics. Twenty-one healthy volunteers were treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics (ciprofloxacin and metronidazole) for one week. They then either took the same supplement as in the first study twice daily for 4 weeks, an autologous fecal microbiota graft representing a sample of the subjects' own pre-antibiotic microbiota taken via upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, or nothing. and constituted the control group.
This time, none of the subjects taking probiotics were resistant to colonization. Antibiotics killed most of the natural microbiome, allowing exogenous strains to spread. However, this came at a cost: natural gut bacteria were restored over a longer period in the probiotic group compared to the control group. The return to baseline of host intestinal cell gene expression was also suppressed in the probiotic group during the six-month follow-up period.
Alexander Khoruts, a gastroenterologist and director of the gut microbiota medical program at the University of Minnesota, who was not involved in the study, said he was surprised that the probiotics showed any significant effect at all, even such a small one. It.
Khoruts primarily treats patients with difficult-to-treat C. difficile infections, and nearly all of his patients say they took probiotics. While he's not arguing with them, other than encouraging them to eat more fermentable foods, Khoruts says the evidence supporting the benefits of probiotics is weaker than many people think. “In my literature review (although many may disagree), I did not find any convincing evidence , at least for C. difficile infection, of any beneficial effect of taking probiotics ,” the doctor states.
One significant limitation is the apparent lack of randomized trials providing data on the safety of probiotics, a topic addressed by a systematic review presented in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Despite the results of the Weizmann Institute of Science study, it is still unknown whether taking probiotics during or after a course of antibiotics actually slows down the restoration of the natural microbiome, and whether such disturbances can cause problems. The composition of the probiotics varies and, according to Knight, the researchers administered an extremely high dose. In addition, the study design did not include analysis of clinical outcomes.
However, long-term impairment after a course of antibiotics is associated with a number of health problems, including infections, obesity, allergies and chronic inflammation, says Elinav. In his opinion, long-term impairment caused by the probiotics his team was studying " could potentially lead to long-term side effects in individuals consuming them ."
Knight notes that the study was conducted on healthy volunteers who were administered antibiotics for research purposes only. In reality, people take antibiotics when they suffer from some disease. Will probiotics slow down the restoration of natural intestinal microflora in this case?
“This study does not address this issue at all,” Knight says. “It discusses the administration of antibiotics to healthy subjects, whose situation may be quite different from the clinical patient population.”
Khoruts believes that the harm from taking most probiotics is likely to be minimal. However, for him “this is quite enough to stop prescribing them and think about what to believe. "I believe the prescribing physician should have a healthy degree of skepticism regarding claims made regarding such products."
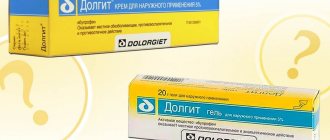
Linex
A multicomponent product that contains 3 types of beneficial microorganisms (lactic acid bacteria) - enterococci, lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. Normalizes the acid-base level in the intestines, microflora, stool, metabolism and strengthens the immune system.
It is also produced in the form of capsules (the main form), as well as drops and sachets, and is used for the following indications:
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Acute diarrhea in the chronic stage.
- Flatulence and bloating.
- For gastroentercolitis in all forms.
- For intestinal infection.
Linex is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to the components of the product and in case of lactase deficiency.
Among the side effects, various manifestations of an allergic reaction (rash or itching) are extremely rare. It is not advisable for pregnant women and women to take it during breastfeeding, since there is not enough information about the safety of taking Linex during these periods.
The course of therapy and dosage are prescribed by a specialist. Adults and children over 12 years of age usually take 2 capsules 3 times a day , children from 2 to 12 years old - 1-2 capsules per day. Dosage for children under 2 years of age and infants – 1 capsule per day. Taken orally with the required amount of water.
Bacterial and biological preparations for the correction of dysbiosis and their rational use
Miroshnik O.A., Ph.D.
The article was published in Omsk Medical Newspaper No. 8 (29), May 1997.
In recent years, new approaches to treatment have become widespread, related to the restoration of the natural ecology of the body and based on the use of active biological products. One aspect of this approach is the normalization of the altered microbial landscape of the body with the help of bacterial and biological products. Currently, through the efforts of new industrial and commercial structures, the traditionally existing shortage of bacterial and biological products has been largely eliminated. Moreover, in addition to such long-familiar drugs as bifidumbacterin, lactobacterin, colibacterin and bificol, many new drugs have appeared, among which it is difficult for doctors, pharmacists and patients to navigate. We hope that the systematization of bacterial preparations proposed in this publication intended to correct the biocenosis of mucous membranes will help more complete and effective use of their entire rich arsenal in everyday practice.
1. BACTERIAL PREPARATIONS - EUBIOTICS
The most significant group of bacterial drugs are eubiotics
- medicines containing as active substances certain strains of representatives of the microflora of a healthy human body
.
It is known that bacteria that normally populate the mucous membranes have an antagonistic effect on pathogenic and opportunistic microflora and provide vitamin-forming and enzymatic functions. 1.1. Preparations of the bifidobacteria family.
The most famous and widely used eubiotic drug is Bifidumbacterin
, containing bifidobacteria of the bifidum species. It is this type of bifidobacteria that predominates in the intestines of newborns and children of the first years of life, therefore bifidumbacterin is the basic drug for correcting intestinal biocenosis in children. The indications for the use of bifidumbacterin are very wide, but the main ones are intestinal dysfunction due to dysbacteriosis, acute intestinal infections (AI), use for prophylactic purposes in weakened children with anemia, rickets, diathesis and during the early transfer of children from breastfeeding to artificial feeding, etc. d..
There are four main forms of release of Bifidumbacterin: vial, ampoule, tablet and powder in laminated foil bags
. The use of bifidumbacterin in pediatrics dictates extremely stringent requirements for the quality of the drug, and, above all, for the absence of foreign microflora. In this regard, the tablet form of bifidumbacterin is approved for use only from three years of age. From the neonatal period, only Bifidumbacterin in powder, bottles or ampoules is approved for use. A number of significant advantages have the form of Bifidumbacterin in powder produced by JSC “Partner”, which is a mixture of dry bifidobacteria with chemically pure lactose, packaged in gas-tight bags made of laminated aluminum foil. The production technology of this drug involves the removal of the cultivation medium and the almost complete absence (less than 10%) of dead bacterial cells. Therefore, when the drug dissolves, an almost colorless opalescent suspension without a pronounced odor or taste is formed. Lactose, which promotes the growth of bifidobacteria in the intestines, slightly increases the dissolution time of the drug.
Bifidumbacterin-forte
- a complex bacterial preparation containing bifidobacteria of the bifidum species immobilized on stone activated carbon. Upon contact with the intestinal mucosa, the sorbent allows the growth of bifidobacteria in the form of individual microcolonies. The drug has all the properties of bifidumbacterin and at the same time the antitoxic effect inherent in the sorbent. The drug has a more pronounced clinical effect and is able to normalize the disturbed intestinal biocenosis at an earlier time compared to conventional bifidumbacterin. The drug is used after a meal and does not require prior dissolution in water.
Bifidumbacterin in suppositories
used for the treatment of intestinal dysfunction with damage to its distal parts (colitis, proctitis) and in gynecological practice (senile nonspecific bacterial colpitis, bacterial vaginosis, impaired vaginal cleanliness of 3-4 degrees, preparation of the birth canal for childbirth, etc.).
Bifidin
as an active ingredient it contains bifidobacteria of the Adolescentis species, which have a wider spectrum of carbohydrate fermentation. However, this type of bifidobacteria grows in the intestines of adults and children over three years of age. In children under one year of age, Bifidobacterium adolescentis is found only if they are bottle-fed. The drug is prescribed to children over three years of age with intestinal disorders accompanied by dysbacteriosis, sick children on early artificial feeding, with a protracted course of intestinal dysfunctions, with repeated isolation of pathogens after acute intestinal infections.
Bifilong
contains bifidobacteria of the species longum, which are the second in quantitative content after bifidobacteria of the species bifidum, representatives of the normal microflora of breastfed children. There is currently no industrial production of Bifidin and Bifilong.
Bifiliz
- a combined preparation containing bifidobacteria of the type bifidum and lysozyme (in one bottle 5 doses and 10 mg, respectively). Lysozyme has bifidogenic, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, reparative and antimicrobial effects. The optimal combination of bifidobacteria and lysozyme in this preparation allows us to enhance the therapeutic effect of each component.
In Novosibirsk, CJSC NPF Vector-Biomed has mastered the production of Bifidobacteria Concentrate
, which is a suspension of bifidobacteria, the bifidum species, in a milk culture medium. The drug is registered as a food supplement and is distributed through a distribution network of doctors. The advantage of the Concentrate is that the bifidobacteria in the preparation are in the growth phase and, therefore, they are more active. However, the fact that to achieve a clinical effect requires taking the Concentrate in doses tens of times higher than those used in treatment with pharmacopoeial bifidumbacterin (8000 and 300 doses, respectively) casts doubt on this.
In Novosibirsk, Bio-Vesta LLC produces an almost similar drug - Liquid concentrate of bifidobacteria (Biovestin)
, the active substance in which is bifidobacteria of the Adolescentis species, the features of which are mentioned above.
1.2. Preparations of the lactobacilli family
Lactobacilli, together with bifidobacteria, are also the main representatives of the normal human microflora. Lactobacilli are present in all parts of the digestive tract, from the oral cavity to the colon, are the predominant flora of the genital tract, and are found in breast milk.
The first attempts at the therapeutic use of lactobacilli to correct biochemical processes occurring in the intestines were made by I.I. Mechnikov 100 years ago. Subsequently, a pronounced antagonistic activity of lactobacilli was discovered against putrefactive opportunistic microorganisms and pathogens of acute intestinal and infections, which is associated with the ability of lactobacilli to form lactic acid, hydrogen peroxide, lysozyme and other substances with antimicrobial action against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The reparative properties and immunomodulatory role of lactobacilli have been revealed, manifested in particular in the ability to increase the general level of secretory Ig A and titers of specific secretory antibodies, enhance phagocytosis, etc. The role of lactobacilli in reducing cholesterol levels in the blood, preventing the production of carcinogens and in the destruction of oxalic acid is discussed. thereby preventing the formation of oxalates in the body.
Lactobacterin is widely used in our country.
, created in the early 70s based on lactobacilli of the plantarum species, which, like bifidobacteria, have an antagonistic effect against pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Indications for its use are similar to those of bifidumbacterin.
Acilact , was developed at the Moscow Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology named after G.N. Gabrichevsky
, which includes lactobacilli of the species acidophilus. Unlike lactobacilli of the plantarum species, acidophilic lactobacilli used for the preparation of Acylact belong to the category of obligate microorganisms for humans. The criteria for selecting a new industrial species of lactobacilli were the ability of bacteria to form acids, antimicrobial activity, adhesive properties that promote long-term preservation in the intestines, resistance to the action of digestive secretions and antibiotics used. The new drug Acylact meets all these conditions.
Acylact is used for indications common to other bacterial preparations: intestinal dysbiosis, acute intestinal infections, chronic enterocolitis, as well as inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa. Since Acylact is characterized by increased acid-forming activity, it is preferable for the treatment of dysbiosis in patients with hypoacid conditions and reduced intestinal motility.
The reduced content of lactose in Acylact, combined with the high ability of the acidophilic lactobacilli that form the basis of the drug to break down lactose, makes Acylact the drug of choice for the treatment of intestinal dysbiosis in patients with milk intolerance (lactase deficiency).
The use of Acylact for 2-3 courses in children with atopic dermatitis leads to normalization of initially depressed immunity and improvement of clinical symptoms.
Acylact can be used to treat gynecological diseases accompanied by disturbances of the vaginal microflora, but in this case it is more convenient to use Acylact in suppositories
. Normally, the vaginal microflora is represented mainly by lactobacilli, the so-called Dederlein bacilli, which maintain an acidic environment in the vagina and suppress the growth of opportunistic microorganisms. Acylact in suppositories is used for pathological conditions associated with a deficiency of lactoflora of the female genital tract, which are especially significant for the following diseases:
- Senile colpitis. The degree of colonization of the vaginal mucosa by lactobacilli depends on the production of estrogen, therefore, in the postmenopausal period, with estrogen deficiency, the level of lactoflora decreases, which is associated with the development of a number of symptoms of senile colpitis (dryness, atrophy of the mucosa, etc.), as well as an increase in the frequency of urinary infections.
- Nonspecific bacterial colpitis caused by staphylococcus, Escherichia coli or their association.
- Persistent violation of the purity of vaginal secretions up to 3-4 degrees.
- Bacterial vaginosis, which is known to be characterized by the proliferation of anaerobic flora and a sharp depletion of the vaginal mucosa in lactobacilli. In this case, Acylact is included in complex therapy, which also includes the use of metronidazole or clindamycin.
- Long-term courses of antibiotic therapy that suppress the natural microflora of the vagina.
- Prevention of bacterial colpitis and cystitis with frequent changes of sexual partners.
- In combination with other drugs in the treatment of chlamydia and mycoplasma infection of the female genital tract.
- Preparation of the birth canal for childbirth, since the biocenosis of the newborn’s intestines that forms from the first hours of life largely depends on the microbial landscape of the mother’s birth canal.
A contraindication to the use of Acylact in suppositories is candidiasis, since in some cases a rapid shift in pH to the acidic side promotes the growth of fungi. Acylact in this case is used after specific antifungal therapy or after the use of Bifidumbacterin in suppositories.
Acilact is also available
, the use of which by resorption in the mouth is indicated for inflammatory diseases of the gums and oral mucosa
Acipol
- a combined preparation consisting of lactobacilli acidophilus and heat-inactivated kefir grains (Kefir grains), available in tablets of 5 doses. The drug is highly active against pathogenic and opportunistic microflora and normalizes some immunological parameters. Acipol is prescribed from the first days of a child’s life for acute intestinal infections, dysbiosis, weakened patients with signs of exudative diathesis and other allergic manifestations.
1.3. Preparations of the colibacterium family
A drug from the colibacterium family - Colibacterin
is the very first domestic bacterial preparation. It contains an antagonistically active strain of non-pathogenic Escherichia coli M-17. Some experts believe that this strain, isolated many years ago, has now somewhat lost its antagonistic activity and ability to take root in the intestines. Colibacterin is used mainly for chronic diseases of the colon in elderly people, in whom the microflora of this part of the intestine is populated predominantly by E. coli, as well as for dysbacteriosis caused by the presence of hemolyzing forms of E. coli.
Combined drug Bifikol
contains bifidobacteria of the bifidum species and Escherichia coli strain M-17, therefore, its action and indications for use are in many ways similar to those of Bifidumbacterin and Colibacterin.
Many eubiotic drugs are also produced abroad, but due to the high cost, attempts to widely introduce them on the Russian pharmaceutical market have so far been unsuccessful.
Bifiform
(Ferrosan)
is available in capsules with a gastroinsoluble coating and contains bifidobacteria of the bifidum species and enterococci.
Primadophyllus
company
(Nature's Way)
is available in two forms.
The powder for preparing the suspension contains bifidobacteria of the infantus and longum species and lactobacilli of the acidophilus and banmosus species. This form is intended for children from the first days of life to 5 years. The capsule version of the drug additionally contains bifidobacteria of the brevis species and is intended for children aged 6 to 12 years. Primadophilus is distinguished by the absence of allergenic factors in its composition; capsules are more convenient to take compared to powders, which must first be dissolved in water. Another foreign drug - Probionik (Enrich)
is a chewable tablet with a pleasant strawberry flavor containing bifidobacteria of the species adolescentis, infantis, longum and lactobacilli acidophilus. These drugs are certified as food supplements and are usually distributed through a network of private distributors. It should be noted that the cost of one package, designed for a 6-8 week course of treatment, is about 25 US dollars. dollars for Primadophilus and about 20 US. dollars for Probionik, which puts effective, inexpensive and well-known Russian drugs beyond competition.
2. DRUGS - PROBIOTICS
Another large class of biological products used to correct dysbiosis and treat diarrheal diseases are probiotics.
. Probiotics are activators of the growth of normal microflora and release substances that suppress the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
The best known probiotics are those containing pure spores of the bacteria Bacillus subtilis strain IP 5832. These are Bactisubtil
(Hoechst Marion Roussellt, currently Aventis) and
Flonivin BS
(ICN)
. In Russia, a similar drug called Bactisporin
is produced by the NPO Immunopreparat in Ufa.
The difference between Bactisporin is that it contains lyophilized live bacteria Bacillus subtilis strain No. 3H. The new drug Biosporin
is designed on the basis of the association of two types of spore-forming microorganisms B.subtilis 3 and B.licheniformis 31. The industrial production of the drug is carried out by the TsVTP BZ MO RF. Biosporin is characterized by pronounced specific activity against Staphylococcus aureus and fungi of the genus Candida. It has been established that Biosporin, along with pronounced selective antagonistic activity against pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms, is characterized by the ability to significantly enhance the body's defense reactions - increase the phagocytic activity of blood leukocytes, induce the production of endogenous interferon, etc.
All drugs based on spores of the bacteria Bacillus subtilis have a similar mechanism of action. The bacillus spores germinate into a vegetative form in the small intestine. This process reaches its maximum in the ileocecal region. When spores germinate, enzymes are released that promote the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and an acidic environment is formed that prevents decay processes and the growth of pathogenic bacteria. In addition, enzymes cause direct lysis of the cell walls of Proteus, Escherichia coli, and pathogenic staphylococcus. Since this strain of bacilli was obtained artificially and is not a physiological component of the intestinal biocenosis, caution is recommended when prescribing drugs from spore-forming microorganisms: their use in short courses and with a weak effect from the previous use of eubiotic bacterial drugs.
Linex
(Lek)
is more physiological , containing acidophilus lactobacilli bacteria, bifidobacteria infantis species and fecal streptococci as active ingredients. Lactic acid bacteria produce lactic, acetic and propionic acids. The acidic environment they create in the intestines is unfavorable for the growth of pathogenic microorganisms. Lactic acid bacteria are involved in the resorption of monosaccharides, stabilize the membranes of intestinal epithelial cells and regulate the absorption of electrolytes. Representatives of normal microflora (bifidobacteria and fecal streptococci) contribute to the restoration of intestinal biocenosis.
Enterol
(Biocodex)
contains lyophilized fungi Sacchoromyces boulardii.
The drug normalizes the disturbed balance of intestinal microflora, promotes the production of secretory Ig A by lymphoid cells of the intestinal mucosa. Enterol is effective for diarrhea caused by taking antibiotics, including pseudomembranous colitis caused by clostridial spore-forming microflora. Hilak
(Ludwig Merkle)
- a liquid containing a sterile concentrate of metabolic products of intestinal flora symbionts, biosynthetic lactic acid, short-chain volatile fatty acids and other components.
These biological products change the acidity of the intestinal contents to the acidic side, create unfavorable conditions for the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and stimulate the growth of normal microflora, improve the physiological functions of the gastrointestinal tract, promote the regeneration of the mucous membrane, and restore the disturbed water-electrolyte balance in the intestinal lumen. Hilak is indicated for intestinal dysfunctions and allergic diseases associated with intestinal dysbiosis, for the prevention of dysbiosis and acute intestinal infections that occur during sudden changes in climatic conditions (travelers' diarrhea), etc. Lactulose
- a synthetic disaccharide produced under different brand names (
Normaze, Laktofalk, Duphalac, Portolac,
etc.) can also be classified as probiotics. Lactulose does not undergo hydrolysis in the small intestine and enters the colon unchanged, where it creates a natural nutrient medium for the growth of lactic acid bacteria, resulting in the formation of lactic and short-chain fatty acids, increased acidity and increased peristalsis of the large intestine. The drug inhibits the growth of salmonella in the intestine, reduces the formation of nitrogen-containing substances and prevents the absorption of ammonia in the colon. Lactulose is used for chronic constipation, salmonellosis, digestive disorders associated with putrefactive processes as a result of food poisoning in infants and children under 10 years of age, as well as for hepatic encephalopathy.
Unusual properties have been discovered in the synthetic proteolytic enzyme inhibitor PAMBA
(BYK GULDEN)
.
PAMBA increases the growth of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and Escherichia coli, while simultaneously reducing the proteolytic activity of Proteus, pseudomonads and other microorganisms and enhancing macrophage phagocytosis. Pantothenic acid also has bifidogenic properties ( Calcium pantothenate, Panthenol
), included in many multivitamin preparations, or used as a separate preparation.
3. BACTERIOPHAGES
bacteriophages are successfully used to sanitize mucous membranes, skin and wound surfaces from pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria.
. Bacteriophages are viruses that exclusively infect bacteria; they are environmentally friendly biological objects for humans and can be used to treat dysbacteriosis, acute intestinal infections, and purulent skin infections at any age.
Bacteriophages, like other viruses, are absolute intracellular parasites; their reproduction occurs in a living cell. Having penetrated the bacterium through phage-specific receptors located on its surface, the phage DNA changes the synthesizing mechanisms of the cell, forcing the bacterium to synthesize phage DNA and proteins. At a certain stage, the bacterium is destroyed, and a new generation of daughter bacteriophages emerges from it. An important property of bacteriophages is their high specificity; they selectively lyse not only bacteria of a certain type, but even their individual serological groups. Bacteriophages accurately find and destroy only those bacteria against which their action is directed, without affecting the normal microflora of the body, not to mention its own cells. This is precisely what explains the absence of side effects and contraindications to the use of bacteriophages, which makes their use in pediatric practice especially attractive. The emergence of antibiotic resistance in bacteria does not affect their sensitivity to bacteriophages, so the latter are often active even against multidrug-resistant hospital microflora. However, the specificity of bacteriophages should be taken into account: each type of phage is recognized as its target only by those serotypes of bacteria that have certain phage-specific receptors. Therefore, it is necessary to prescribe bacteriophages under microbiological control of the sensitivity of the given pathogen to them.
The domestic industry produces a wide range of medicinal bacteriophages: Staphylococcal, Streptococcal, Coli, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Typhoid, Dysenteric, Salmonella
.
There are also their combined forms: Coliprotein bacteriophage
,
Intesti bacteriophage
(contains phages of Shigella Flexner serovar 1,2,3,4,6 and Sonne, salmonella (paratyphoid A and B, enterilitis, typhimurium, cholera suis, Oranienburg), enteropathogenic groups of Escherichia coli , Protea vulgaris and mirabilis, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and pathogenic enterococci),
Pyobacteriophage combined
(contains phages of staphylococci, streptococci, pathogenic Escherichia coli, Proteus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Consonant, but still different, the purified polyvalent Pyobacteriophage
contains phages of staphylococci, streptococci, pathogenic Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus and Klebsiella pneumoniae
. This drug is distinguished by the highest degree of purification from bacterial metabolites, which significantly improves its taste and makes it the first choice for children under one year of age. The purified polyvalent Klebsiella bacteriophage
is active against
Klebsiella pneumonia, ozena, and rhinoscleroma
. Bacteriophage are usually produced in liquid form or in tablets; currently, the production of combined Pyobacteriophage and Staphylococcal bacteriophage in the form of liniment has also been launched.
So far, bacteriophages have been most widely used in the treatment of intestinal dysbiosis, acute intestinal infections, enterocolitis, and purulent-inflammatory diseases of the throat and nose. However, the scope of their clinical application is much wider and they can be successfully used to treat surgical, urogenital, skin and other infections.
There is no mention of phage therapy in foreign manuals. But it is necessary to take into account that, firstly, phage therapy is a special direction in bacteriology, developed by Russian scientists, and, secondly, the use of bacterial preparations for therapeutic purposes in Western standards is generally extremely limited. For example, in the USA, almost all bacterial preparations are classified as food additives, and, therefore, are not included in standard treatment programs. Bacterial preparations fall into the sphere of interest of nutritionists who have tasks other than medical ones. Perhaps it is not an exaggeration to say that Russia has accumulated much more scientific material and experience in the use of bacterial preparations in medicine.
4. IMMUNOGLOBULIN PREPARATIONS
A fundamentally new direction in the treatment of dysbacteriosis and acute intestinal infections is associated with the creation in our country of an original drug, a complex immunoglobulin preparation.
(KIP) KIP contains human immunoglobulins of three classes: Ig A (15-25%), Ig M (15-25%) and Ig G (50-70%). What distinguishes CIP from all other immunoglobulin preparations used in Russia is the high content of Ig A and Ig M, an increased concentration of antibodies to enteropathogenic bacteria of the intestinal group (Shigella, Salmonella, Escherichia, Klebsiella, etc.), a high concentration of antibodies to rotaviruses, as well as oral mode of application.
Ig M, which is part of the CIP, has a bactericidal effect on pathogenic microorganisms, Ig A makes it difficult for them to attach to the epithelium of the mucous membrane, reproduce and ensures rapid removal from the intestine, Ig G neutralizes microbial toxins and viruses, mediates the “sticking” of bacteria to macrophages with their subsequent phagocytosis . In addition to removing pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms from the body, CIP promotes the growth of normal intestinal microflora (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, enterococci and non-pathogenic Escherichia coli), increases the production of secretory Ig A and normalizes altered indicators of systemic immunity. The oral method of taking CIP ensures the delivery of large doses of the active substance to the lesion site with a subsequent decrease in the adsorption of pathogens on the epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa and a local immunomodulatory effect.
A large comparative study showed that among all possible treatment regimens for acute intestinal infections in children, it is CIP therapy that gives the best results, assessed by such parameters as the duration of symptoms of intoxication and diarrhea syndrome, re-seeding of pathogens, changes in the intestinal biocenosis and the dynamics of the main indicators of immunity.
A positive effect of CIP in the treatment of allergic dermatoses was noted. This is explained by an increase in the level of secretory Ig A, as a result of which the local resistance of the gastrointestinal mucosa increases and the removal of allergens from food from the intestine increases.
The main indications for the use of CIP are the following diseases and pathological processes:
- Intestinal dysbiosis in children and adults, caused by any factors (post-acute intestinal infections, long-term and irrational antibiotic therapy, chronic diseases, stress, immunodeficiency states, etc.).
- Acute intestinal infections. The possibility of obtaining a pronounced therapeutic effect 2-3 days after the start of administration makes CIP the drug of choice in the treatment of acute intestinal infections (including rotavirus etiology) in children of the first year of life.
- Chronic enterocolitis.
- Complex therapy of allergic dermatoses combined with intestinal dysfunction.
- Immunodeficiency states with disorders mainly in the humoral immunity.
At the Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology named after G.N. Gabrichesvsky, together with f, a combination drug Kipferon
in rectal and vaginal suppositories, which includes KIP in an amount of 50 mg and recombinant interferon-alpha2a in a dose of 500,000 IU.
5.FOOD ADDITIVES
To correct the intestinal microflora, special food additives are used that contain dietary fibers related to carbohydrates, which are not digested by digestive enzymes, but serve as a nutrient substrate for the microflora of the large intestine. Dietary fibers that have a stimulating effect on the intestinal microflora include oligosaccharides, in particular fructooligosaccharides, the most famous representative of which is inulin
. A large amount of inulin is contained in Jerusalem artichoke root crops. There are several food supplements containing Jerusalem artichoke concentrate (Jerusalem artichoke concentrate, Topivit, Jerusalem artichoke concentrate, etc.). Fructooligosaccharides and, in particular, inulin significantly stimulate the growth of bifidobacteria in the intestine, change the pH of the large intestine to the acidic side, promote the formation in the intestine of short-chain fatty acids and other biologically active substances that have a beneficial effect on the intestinal biocenosis.
6. HEALTHY FERMENTED MILK PRODUCTS
Characteristics of drugs used to correct mucosal biocenosis would be incomplete without mentioning fermented milk products containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. These products are intended for daily nutrition and have certain regulatory functions. There are hundreds of recipes for such products produced abroad; several dozen have been developed in Russia. A number of fermented milk products are also produced in Omsk. So in the composition of the fermented milk mixture Narine
includes acidophilic lactobacilli and their metabolic products.
Pastolakt
contains special strains of acidophilus bacillus and bifidobacteria growth factors.
Acidolact
contains acidophilic lactobacilli with lactic acid streptococcus.
Bifido-containing products are represented by Bifilin
, obtained from bifidobacteria of the species
Adolescentis
and characterized by deep hydrolysis of the protein component, and
Bifidok
- kefir, enriched with bifidobacteria of the species
bifidum
.
7. RATIONAL THERAPY FOR PATIENTS WITH INTESTINAL DYSBACTERIOSIS
The scheme for correcting intestinal dysbiosis can be divided into several stages.
1. Sanitation of the intestines from opportunistic microflora.
Traditional treatment of patients with intestinal dysbiosis involves preliminary decontamination of the intestine using antimicrobial agents. However, the latter often cause side effects that make it difficult to draw up a rational treatment program, especially for a child. In most cases, effective and safe decontamination of the intestine from opportunistic bacteria is possible by replacing antimicrobial agents with safer and highly effective bacterial preparations: CIPs and bacteriophages. Enteral administration of KIP 1 dose 1-2 times a day has a sanitizing effect against most gram-negative enteropathogenic bacteria (Escherichia, Klebsiella, Proteus, as well as Shigella and Salmonella). Depending on the opportunistic microflora present, bacteriophages are additionally prescribed internally (Intesti-bacteriophage, combined Pyobacteriophage, purified polyvalent Pyobacteriophage, Staphylococcal or Klebsiella bacteriophages). If there is an overgrowth of clostridia, Enterol is used.
2. Replacement therapy with bacterial drugs.
After antimicrobial therapy, depending on the identified deficiency of a particular type of bacteria, bacterial preparations are prescribed for 4 weeks in standard doses. In children, Bifidumbacterin or Bifidumbacterin-forte is more often used, in adults - Bifidumbacterin, Bifidumbacterin-forte or Bifikol, in the elderly - Bifikol or Colibacterin. Then, in order to maintain the clinical effect, dry Acylact is indicated for 2 weeks, which helps increase acidity in the intestines and stabilize the composition of the microflora. The use of bacterial preparations is combined with the use of Hilak-Forte drops in moderate therapeutic doses. For constipation, Lactulose and Acylact or Bifidumbacterin in suppositories also have a good effect.
Simultaneously with the start of treatment, the patient takes vitamins A, E and group B as part of multivitamin preparations (Glutamevit, Complivit, Kvadevit, Unicap-M, Centrum, etc.), enzyme preparations: Festal, Panzinorm-Forte, Digestal (for constipation) or Mezim -Forte, Pancreatin, Pankurmen, Pancintrat (for diarrhea syndrome).
3. Maintenance therapy.
After a course of bacterial preparations, food supplements containing inulin (Jerusalem artichoke concentrate, Topivit, Jerusalem artichoke concentrate, etc.) are prescribed for 2-3 weeks. After the main course of treatment, herbal medicine is prescribed (infusions of St. John's wort, sage, yarrow, plantain leaf, mint, etc.), in the selection of which much attention is paid to individual intolerance to herbs, manifested by dyspeptic complaints, changes in gastrointestinal motility, and allergic reactions. The full course of treatment ends with a 3-4 week intake of adaptogenic agents. The patient is also given recommendations on a balanced diet, including the use of medicinal fermented milk and vegetable products.
When carrying out this therapy, it is necessary to keep in mind that dysbiosis is not an independent nosological unit, but only a pathogenetic link of the underlying disease, therefore the main attention should be directed precisely to its decoding and treatment.
Thus, doctors and patients today have a sufficient choice of means to preserve and maintain the balance of the normal microflora of the body. The task is their rational and targeted use, taking into account the individual characteristics of the biocenosis of a particular patient, which depends on an understanding of the differences in the action of individual drugs and a clear understanding of the therapeutic goals pursued when prescribing them.
Recommended reading:
Elisabeth Kütter. Phage therapy: bacteriophages as anibiotics. PHAGE THERAPY: BACTERIOPHAGES AS ANTIBIOTICS. Elizabeth Kutter, Evergreen State College, Olympia, WA 98505 - Nov. 15, 1997. (PDF)
Elisabeth Kütter “Phage therapy: bacteriophages as antibiotics”
“PHAGE THERAPY: BACTERIOPHAGES AS ANTIBIOTICS. Elizabeth Kutter, Evergreen State College, Olympia, WA 98505 - Nov. 15, 1997 rar .
What are the differences and similarities between such similar probiotics?
When treating a child or adult with a severe form of the disease, choosing Linex or Acipol, one must keep in mind the specifics and qualities of each drug.
Similarities include:
- Prescribed for the same indications (dysbacteriosis, intestinal infections, disruption and maintenance of microflora during the period of taking antibiotics).
- Both Linex and Acipol belong to the group of 3rd generation probiotics, both contain beneficial bacteria and elements that ensure their normal functioning.
But there are also differences that must be taken into account when prescribing:
- Linex, unlike Acipol, contains 3, not just one type of beneficial bacteria.
- Linex contains many more beneficial microorganisms than Acipol.
- Acipol is allowed to be taken by children only from 3 months, while Linex is applicable to infants, pre-mixed in water or formula.
- The risk of further development of diarrhea is less when taking Linex than Acipol, due to the wide range of components.
Looking at all the similarities and differences, the opinion is formed that Linex is superior to Atsipol in all respects, but the second is produced in Russia, while the first is in Slovenia, which determines the price categories.
Acipol is a less expensive drug and is used for dysbiosis caused by prolonged use of antibiotics. for moderate intestinal diseases. during inflammatory processes and mild poisoning. Quickly restores and normalizes microflora and removes toxins from the body.
Linex is suitable for newborns, as it contains bacteria suitable for the baby’s microflora. It is also used when it is necessary to neutralize the effect of several types of pathogenic bacteria at once, in acute diseases and in the event of intestinal paresis. Normalizes peristalsis, microflora, stool and food absorption.
Why are prebiotics useful and probiotics useless?
President of the scientific society “Microbiota”, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Chicherin I.Yu.: “Dear friends and colleagues, as well as everyone who is interested in the very pressing problem of maintaining and restoring intestinal microflora (microbiota).
According to the World Health Organization, up to 95% of the world's inhabitants suffer from intestinal dysbiosis. Almost no disease occurs without negative consequences for the intestinal microbiota. But the most common destructive effect on intestinal microbes is the use of antibiotics. In a relatively healthy person with a body weight of about 70-75 kg, the colon contains about 2-2.5 kg of living biomass of microorganisms (normoflora), and the number of species reaches 1-1.5 thousand (!).
Every doctor, including patients, must understand that the antibiotic used does not select the point of application in the body and will ultimately suppress all microbes that are sensitive to it. The use of antibiotics for pneumonia, cystitis, bronchitis, etc., as they say, both cures and cripples. On the one hand, it helps to cure the underlying disease for which it was prescribed, but on the other hand, it causes enormous collateral damage to sensitive microbiota, and primarily to the intestinal one. With the banal use of antibiotics, the content of beneficial microorganisms in the intestines can decrease by 3-6 orders of magnitude, i.e. a thousand to a million times!
For more than 50 years, both in our country and throughout the world, for the correction of microecological disorders in the intestines (dysbacteriosis, dysbiosis), the main means (95-97%) were preparations based on living microbes - probiotics. In normal medical practice, if a doctor, when analyzing stool for dysbacteriosis, detected a decrease in one or another type of normal microflora, then he would first of all prescribe a probiotic to the patient based on the type of normal flora whose deficiency was recorded. There are not enough bifidobacteria, let's “add” bifidobacteria in the composition of the drug that the doctor likes best, etc.
In recent years, the strategy for maintaining and restoring the intestinal microbiota has been revised!
A group of Russian scientists (more than 40 scientific papers, 2010-2015) managed to obtain convincing evidence that the use of traditional drugs based on living microbes - probiotics - is not the most effective and safe way to correct microecological disorders in the intestines.
It was found:
!!! The survival rate of living cells during transit through the gastrointestinal tract is less than 0.0001% (one ten-thousandth of a percent).
That is, on average, only 1 out of 1,000,000 (million) microbial cells ingested as part of a probiotic reaches the colon (the main habitat of normal flora). And no acid-resistant capsules used in some probiotics can save the situation: not 1, but 4-5 cells survive.
Each person has their own individual strains (autostrains) of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, E. coli, etc. in their intestines. And probiotics are made on the basis of “universal” industrial strains of microbes. Probiotic cells that reach the colon alive in more than 70% of cases enter into an antagonistic relationship with the patient’s autostrains
of microorganisms
; in other words, they are
bioincompatible
. Probiotic microbes have a lymphocytotoxic effect, because. The patient’s immune system is able to determine which microorganisms (self or foreign) enter the gastrointestinal tract. Probiotic microorganisms are foreign to the patient’s individual microbiota.
!!! The thesis about the replacement effect of probiotics, which existed for several decades, turned out to be a myth.
Probiotic cells that reach the colon in a viable state do not take root in the intestinal mucosa. In probiotics, the main active principle turned out to be not microbial cells, as was previously thought a priori, but their metabolic products - exometabolites, and the microbial cells themselves only inhibit the process of restoration of the microbiota during dysbacteriosis.
The simultaneous use of certain probiotics with antibiotics, as television commercials constantly repeat, is in fact scientifically absurd and unfounded.
Probiotic cells are sensitive to most antibiotics even in those small concentrations that are created by antibiotics in the blood, and in the intestines the concentrations of antibiotics are tens to hundreds of times higher. It is obvious that such advertising misleads the consumer and, apparently, pursues only commercial goals. In addition to the above, in Europe over the past 7 years not a single new probiotic based on living microbes has been registered, but in our country the picture is the opposite.
The eternal Russian question - what to do?
The answer is simple, and currently it finds full understanding and agreement among specialists in this field - to maintain and restore your own individual microbiota, the one that formed in you after birth.
This is much more effective and safer than trying to populate the intestines with “good” but foreign strains of microorganisms!
This can only be achieved: through the use of prebiotics, i.e. drugs that do not contain live microbes, but contain substances that selectively stimulate the reproduction of the patient’s individual microbiota.
This very important conclusion is scientifically substantiated in experimental work by a group of Russian scientists and has been confirmed in clinical practice at the Educational and Scientific Medical Center of the Presidential Administration of the Russian Federation.”
PS This class of drugs is represented on the Russian market by Bactrum, produced by the research and production company Optisalt. As a prebiotic, Bactrum has undeniable advantages over drugs containing live microbes (probiotics), namely:
* Unlike probiotics (which have less than 0.0001%), prebiotics have high bioavailability.
1) prebiotic substances reach the colon 95-97% unchanged.
2) They are not affected by aggressive factors of the gastrointestinal tract - acidity, enzymes, bile, peroxide compounds, immunoglobulins, etc.
3) prebiotics do not come into conflict (antagonistic relationships) with the patient’s own microbiota; on the contrary, they serve as exclusive food for it.
4) After fermentation (utilization) of the patient’s own normobiota strains, prebiotics create favorable physiological conditions for its further existence in an active state by acidifying the intracavity environment (lowering pH).
Bactrum - instructions, composition, action, contraindications and reviews about Bactrum
* Prebiotics, unlike probiotics, are not only possible, but also should be taken simultaneously with antibiotics.
Firstly, antibacterial drugs do not inactivate prebiotics, because they do not contain living cells, and secondly, simultaneous administration helps protect the patient’s intestinal microbiota from the negative concomitant effects of antibiotics prescribed for infectious pathologies of other organs.
The most important conclusion is that the prebiotic effect of Bactrum supports and restores the patient’s own intestinal microbiota, rather than trying to unsuccessfully populate the intestinal mucosa with “good” but alien strains of microorganisms. The process of restoring one’s own (indigenous) microbiota always proceeds most efficiently and safely, because is an integral part of the formed microbiocenosis since the birth of a person and does not need to “pass passport control” before the immune system and the body as a whole. The most important thing is that this conclusion has been proven many times and is scientifically substantiated.
How to choose the right probiotic?
The low level of education of the population in pharmacology makes it difficult to choose the appropriate remedy; therefore, the best way to choose a probiotic is to help the attending physician, who has carefully studied the disease, the patient’s condition and has developed a method of treating the patient.
However, there are some recommendations when choosing:
- The drug must be known for sale and should only be purchased from pharmacies of trusted companies.
- You should not take a drug that has expired.
- The drug should be selected based on individual tolerance to the components.
Medicine and healthComment
Rotavirus - treatment and prevention
Moiseeva Tatyana Sergeevna
Pediatrician, Infectious disease specialist
April 25, 2021
intestinal infections sooner or later. After acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI and influenza), this is the most common reason for visiting a doctor in childhood. They are a problem not only for the child, but also for the whole family. Perhaps the most common intestinal infection at the moment is rotavirus or, as parents often call it, “intestinal flu”.
Regardless of the social status of the family and the sanitary and hygienic situation in the house, from birth to 5 years, almost all children suffer from rotavirus gastroenteritis . According to statistics, more than 137 million people worldwide suffer from this infection every year, approximately a quarter of whom are hospitalized. Unfortunately, there are cases with fatal outcomes, including in children. Rotavirus gastroenteritis is most severe in children when they first encounter the virus, which usually happens between the ages of 6 and 18 months. In babies who are bottle-fed, the risk of infection and a more severe course is slightly higher.
Adults are also susceptible to this infection. You can become infected repeatedly during your life, since natural immunity to the virus is type-specific (it protects only against a specific type of rotavirus and does not protect against others). With repeated contact with the virus, the disease is usually less severe, but the person is contagious and can spread the infection.
So, what is rotavirus? There is an opinion that rotavirus got its name because it enters the human body through the mouth, this is not true, the virus is called that because its external structure resembles a wheel (from the Latin - rota), hence the name. There are several types, slightly different from each other in structure, but causing the same clinical picture of the disease.
The route of transmission of this infection is fecal-oral, that is, to put it simply, it is a “disease of dirty hands.” The virus is very contagious; just 10 particles of the virus are enough to make you sick. Rotavirus persists for a long time on any surface, even with thorough cleaning. Therefore, very often several family members, including adults, are sick with this infection at the same time, and outbreaks occur in children's groups. It is worth noting that you can only become infected from a sick person; pets do not get sick from “human” rotaviruses.
The incubation period for rotavirus infection ranges from several hours to 5-7 days. It is characterized by general malaise, weakness, refusal to eat, increased body temperature and symptoms of damage to the gastrointestinal tract (frequent watery loose stools, vomiting, abdominal pain). At the first signs of illness, you must seek medical help! After examining the child, the doctor will assess his condition, the need for hospitalization, and prescribe examination and treatment.
To diagnose the infection, stool testing for rotavirus is used using the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method; the result is usually ready in 1-2 days. But treatment must begin at the first symptoms of the disease, without waiting for results. Therapy is carried out according to symptoms, and practically does not depend on test results. Tests are prescribed to make sure that it is a rotavirus infection and in case of complications, so that doctors understand what exactly they are dealing with.
To treat children who do not need hospitalization and remain at home under the supervision of a pediatrician, so-called pathogenetic therapy is used, aimed at replacing the fluid that the child loses during illness with loose stools and vomit.
The most important rule for a mother with rotavirus is to give her child a few sips every 5-10 minutes. If the child refuses, then feed him from a spoon or from a syringe (after removing the needle). You should not let your child drink large amounts of liquid at one time, even if they are very thirsty, as this may cause vomiting. You need to be patient and constantly, despite the protests, give him water, water, water. It is desoldering that helps avoid dehydration and hospitalization.
In addition to water, special saline solutions from the pharmacy are used to water the child, containing salts that are lost by the body during illness (Hidrovit, Humana, Electrolyte, Gastrolit, Regidron, etc.). In the absence of special drugs, you can use a homemade solution until you purchase them. You can prepare it by taking a liter of boiled water, adding 1-2 tablespoons of sugar (without a slide), half a teaspoon of table salt and one-third of a teaspoon of baking soda. The prepared solution can be stored for no more than a day. Children should not be fed with milk, juices, fruit drinks, vegetable broths, or carbonated drinks.
The second important component of the treatment of rotavirus infection is diet therapy . During the acute illness and 2-3 weeks after it, the child is prescribed a gentle diet, with the exception of dairy products, juices, raw fruits and vegetables. The child should eat more often than usual, in small portions. Food should be as gentle as possible on the stomach - not spicy, not fatty, not hot, not fried.
For young children who are breastfed or bottle-fed, the issue of further feeding is decided individually with a pediatrician. If frequent loose stools persist in bottle-fed children, the option of temporarily switching to a formula with a reduced lactose content (lactose-free, low-lactose, etc.) is possible. For infants, the issue of partially replacing breast milk with a formula with a reduced lactose content or adding special enzymes to breast milk that help the milk to be absorbed in the baby’s intestines (lactase enzyme preparations) is being resolved.
Also used in therapy are such groups of drugs as: enterosorbents (Smecta, Filtrum-sti, Enterosgel, etc.), probiotics (Enterol, Linex, Bifiform, Acipol, etc.), prebiotics (Hilak-forte, Duphalac, etc.), enzymes (Creon 10000, Mezim-forte, Pancreatin). You should not give these drugs to your child on your own; you should consult a doctor, as you need to understand the advisability of taking them at different periods of the disease.
, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy can be carried out . The decision to prescribe drugs in this group is made only by the doctor.
Antibacterial therapy is worth considering separately. Antibacterial therapy is not carried out for uncomplicated rotavirus infection. But in some cases, doctors still prescribe antibiotics. And it's not just a matter of habit. This is due to the fact that acute intestinal infections are not only of a viral nature, but also of a bacterial nature (Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Yersinia and some others). And it is not always possible to determine with 100% accuracy from the symptoms what caused the symptoms: a viral infection, a toxic infection or a bacterial one. There are also mixed causes and atypical course of the disease, so the issue of prescribing antibacterial drugs remains at the discretion of the attending physician.
Very important! If watering the child turned out to be ineffective and the child continues to vomit, weakness increases, he urinates less than usual (the interval is 3-4 hours), then there are direct indications for hospitalization of the baby in a hospital, where he will be prescribed infusion therapy (intravenous fluid).
Currently, there is a unique opportunity to protect your baby from rotavirus infection . The Rotatek® vaccine has been certified in Russia and has been successfully used abroad for several years. The vaccine protects against the five most common types of rotavirus and prevents severe forms of other types of the virus. For a full course of vaccination, 3 vaccines must be administered. The convenience of using the vaccine lies in the fact that it is presented in the form of drops for oral administration, and not in the form of a syringe for intramuscular injection. The first dose of the vaccine is at 6-12 weeks of age, then 2 more at an interval of at least 4 weeks. Revaccinations, that is, repeated injections of the vaccine after a full course of vaccination from 3 stages, are not required.
The vaccine is intended for children from 6 weeks to 32 weeks , and is not used in adults. This is due to the fact that the first encounter with the virus and the most severe course of the disease occurs during this period. In the future, after the immune system has become “acquainted” with the virus, the likelihood of developing a serious illness decreases and immunoprophylaxis with a vaccine is no longer so relevant.