Adenoprosin supp rect 29 mg x10
Marketing authorization holder: SC BIOTEHNOS, SA (Romania)
Manufactured by: FARMAPRIM, LLC (Republic of Moldova)
Secondary packaging and release quality control: FARMAPRIM, LLC (Republic of Moldova) or SC BIOTEHNOS, SA (Romania)
Contacts for inquiries: BIOTECHNOS (C.O. BIOTECHNOS S.A.) (Romania)
Dosage form
, Adenoprosin®
Supp. rectal 29 mg: 10 pcs.reg. No.: LP-004871 dated 05/30/18 - Valid Re-registration date: 08/31/18
Release form, packaging and composition of the drug Adenoprosin®
Rectal suppositories are yellow to brown in color, cylindrical-conical in shape, heterogeneity of color in the form of inclusions of a darker color is allowed.
1 sup.
active complex Adenoprosin®* 150 mg,
in terms of total protein 29 mg
* biomass obtained from larvae of insects of the gypsy moth species (Lymantria dispar).
Excipients: solid fat - Suppotsir AM - sufficient quantity to obtain a suppository weighing 2000 mg.
5 pieces. — contour cell packaging (2) — cardboard packs.
Clinical-pharmacological group: Drug used for diseases of the prostate gland Pharmaco-therapeutic group: Drug for the treatment of urological diseases
pharmachologic effect
The active substance included in the drug Adenoprosin® is a biomass obtained from the larvae of insects of the gypsy moth species (Lymantria dispar), which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
The effect of the drug Adenoprosin® is manifested through pathogenetic and nonspecific mechanisms. The biologically active components of the drug reduce the formation of A2-phospholipase and the release of arachidonic acid with a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes (suppress 5-lipoxygenase). The drug reduces capillary permeability, reduces swelling and improves microcirculation in the tissues of the prostate gland.
The drug Adenoprosin® already in the first days after the start of use improves urodynamic parameters (increases the value of the maximum volumetric flow rate of urine, reduces the time of urination, reduces the amount of residual urine) and the general condition of patients with BPH and chronic prostatitis (reduces the index of chronic prostatitis, reduces the content of leukocytes in secretion of the prostate gland, improves the homogeneity of its echostructure). The drug regulates the tone and peristalsis of the lower segments of the urinary tract, reducing the frequency of urination, incl. at night, and reducing dysuric symptoms, the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder and tension when urinating.
The antioxidant effect of the drug Adenoprosin® is expressed by inhibition of lipid peroxidation due to the antioxidant water-soluble compounds of the drug.
Pharmacokinetics
The effect of the drug Adenoprosin® is the combined effect of the biologically active components of biomass obtained from the larvae of insects of the species Lymantria dispar, so pharmacokinetic studies are not currently possible.
Indications for the drug Adenoprosin®
benign prostatic hyperplasia, chronic prostatitis (as part of combination therapy).
Dosage regimen
Rectally, 1 sup. 1 time/day (preferably at night at the same time).
The duration of treatment is from 1 to 3 months, depending on the intensity of inflammatory processes in the prostate gland and the severity of BPH symptoms, as well as their combination. If necessary, the course of treatment can be repeated.
Side effect
From the digestive system: rarely - diarrhea or frequent bowel movements, itching in the anal area.
Other: allergic reactions, general weakness are possible.
Contraindications for use
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, acute urinary retention, age under 18 years, malignant neoplasms of the prostate gland.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The drug is not used in women.
Use in children Contraindicated under the age of 18 years.
special instructions
The drug should be used after bowel movements or an enema. After administration of the drug, it is recommended that the patient remain in a lying position for 30-40 minutes.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
The drug does not affect the ability to drive vehicles or operate machinery.
Overdose
To date, no cases of overdose have been registered.
Drug interactions
To date, no cases of clinically significant drug interactions between Adenoprosin® and other drugs have been reported.
Storage conditions for the drug Adenoprosin®
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children, protected from moisture and light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life of the drug Adenoprosin® Shelf life - 2 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Terms of sale
The drug is available with a prescription.
- Magazine archive /
- 2021 /
Entomological drug adenoprosin in the treatment of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and chronic prostatitis
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/urology.2021.1.39-44
A.V. Kuzmenko, V.V. Kuzmenko, T.A. Gyaurgiev
Department of Urology FSBEI HE Voronezh State Medical University named after. N. N. Burdenko”, Voronezh, Russia
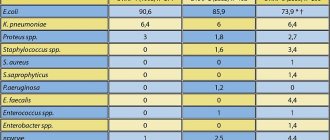
Introduction. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and chronic prostatitis (CP), as a rule, are part of the symptom complex that manifests age-related health changes in men. The combination of BPH with CP raises many questions when choosing the right treatment tactics. Currently, new medicines have been developed and are widely used - entomological preparations, which are biologically active substances with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Purpose of the study: to study the effectiveness of the use of the entomological drug Adenoprosin as part of complex therapy for patients with BPH and CP. Materials and methods. We examined and treated 60 patients with BPH in combination with chronic bacterial prostatitis category II (NIH, 1995) in the acute stage. Patients were randomized into two groups of 30 people. The comparison group (CG) received traditional therapy with α-blockers and fluoroquinolones. In the main group (MG), similar traditional therapy was carried out in combination with Adenoprosin, 1 suppository once a day for 3 months. The condition was assessed upon presentation (visit 1) and after 4 weeks. (visit 2) and after 3 months. (visit 3). The frequency of voiding, the number of nighttime urinations, the average score on the IPSS, QoL, NIH-CPSI scales, the maximum flow rate of urine, the volume of the prostate and the volume of residual urine, the results of bacterioscopic and bacteriological studies of prostate secretions were assessed. Results. Initially, the groups were comparable in all studied indicators (p>0.05). By visit 2, despite the absence of statistically significant differences (p>0.05), in the OG there was a more pronounced positive trend in most of the studied parameters, especially prostate volume. After 3 months treatment in the GS did not reveal any significant changes in indicators compared to the previous visit. In the MG by this time, there was a significant decrease in the number of daytime and nighttime urinations, an increase in the maximum urine flow rate and the average score on the NIH-CPSI, IPSS and QoL scales, as well as a decrease in the volume of the prostate and the volume of residual urine. The data obtained at visit 3 in the group are statistically significant (p Conclusion. The entomological drug Adenoprosin can become a new direction in the complex therapy of patients with BPH and CP, taking into account its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effect. However, to confirm the results obtained at this stage and A more detailed study of the mechanisms of therapeutic action of this group of drugs requires more extensive placebo-controlled clinical studies.
Key words: entomological preparations, Adenoprosin, chronic prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia
The full text of the article is available in the Doctor's Library
Literature
1. Urology. Russian clinical guidelines. Under the editorship of Yu.G. Alyaev, P. V. Glybochko, D. Yu. Pushkar. M.: GEOTAR-Media; 2018. 480 s. Russian (Urology. Russian clinical guidelines. Edited by Yu.G. Alyaev, P.V. Glybochko, D.Yu. Pushkar. M.: GEOTAR-Media; 2022. 480 pp.)
2. Gravas S, Cornu JN, Drake MJ et al. EAU guidelines on the management of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), incl. benign prostatic obstruction (BPO). 2022. Available at: https://uroweb.org/guideline/treatment-of-non-neurogenic male-luts/ Accessed 5 May 2019
3. Schaeffer AJ Classification (Traditional and National Institutes of Health) and Demographics of Prostatitis/ Urology. 2002;60(6 Suppl):5-6; discussion 6–7. Doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(02)02292-6.
4. Nickel J. Prostatitis. CUA Guidelines. Canadian Urol. Assoc. J. 2011;5(5):306–315. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22031609
5. Rees J., Abrahams M., Doble A., Cooper A. and the Prostatitis Expert Reference Group (PERG). Diagnosis and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a consensus guideline. BJU Int. 2015;116:509–525. https://doi:10.1111/bju.13101
6. Gupta N., Rogers T., Holland B., Helo S., Dynda D., McVary KT Three-Year Treatment Outcomes of Water Vapor Thermal Therapy Compared to Doxazosin, Finasteride and Combination Drug Therapy in Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Cohort Data from the MTOPS Trial. J Urol. 2018;200(2):405–413. Doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.02.3088.
7. Roehrborn CG, Barkin J., Tubaro A., Emberton M., Wilson TH, BrothertonCastro RP Influence of baseline variables on changes in International Prostate Symptom Score after combined therapy with dutasteride plus tamsulosin or either monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms: 4-year results of the CombAT study. BJU Int. 2014;113(4):623–635. Doi: 10.1111/bju.12500.
8. Roehrborn CG, Barkin J., Siami P., Tubaro A., Wilson TH, Morrill BB, Gagnier RP Clinical outcomes after combined therapy with dutasteride plus tamsulosin or either monotherapy in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by baseline characteristics: 4-year results from the randomized, double-blind Combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin (CombAT) trial. BJU Int. 2011;107(6):946–954. Doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10124.x.
9. Roehrborn CG, Oyarzabal Perez I., Roos EP, Calomfirescu N., Brotherton B., Wang F., Palacios JM, Vasylyev A., Manyak MJ Efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of dutasteride and tamsulosin treatment (Duodart ) compared with watchful waiting with nitiation of tamsulosin therapy if symptoms do not improve, both provided with lifestyle advice, in the management of treatment-naive men with moderately symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 2-year CONDUCT study results. BJU Int. 2015;7. Doi: 10.1111/bju.13033.
10. Kudryavtsev Yu.V., Sivkov A.V. Morphological changes in prostate tissue in benign hyperplasia. Experimental and clinical urology. 2010;1:18–22.
11. Bartoletti R., Cai T., Mondaini N., Dinelli N., Pinzi N., Pavone C. et al. Prevalence, incidence estimation, risk factors and characterization of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in urological hospital outpatients in Italy: results of a multi-center case-control observational study. J. Urol. 2007;178:11–15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17937946
12. Krsmanovic A., Tripp D., Nickel J. et al. Psychosocial mechanisms of the pain and quality of life relationship for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS). Canadian Urological Association Journal, 2014;8(11–12):403–408. https:// doi:10.5489/cuaj.2179
13. Kuzmenko AV, Kuzmenko VV, Gyaurgiev TA, Barannikov II Chronobiological status of patients with chronic prostatitis on the background of prostate adenoma. System analysis and management in biomedical systems. 2017;16(3):513–516.
14. Huang T., Li W., Peng B. Correlation of inflammatory mediators in prostatic secretion with chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Andrologia. 2017; e12860. https://doi. org/10.1111/and12860
15. Hu C., Yang H., Zhao Y. et al. The role of inflammatory cytokines and ERK1/2 signaling in chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome with related mental health disorders. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:28608. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27334333
16. Kuzmenko AV, Kuzmenko VV, Gyaurgiev TA Combined drug therapy of patients with BPH. Urology. 2018;1:101–105.
17. Kuzmenko AV, Kuzmenko VV, Gyaurgiev TA Efficacy of fesoterodine in patients after transurethral resection of the prostate. Urology. 2019;1:52–55.
18. Kuzmenko AV, Kuzmenko VV, Giaurgiev TA Effectiveness of macrolides in the treatment of patients with urogenital infections. R.M.J. 2019; 27(10):46–49.
19. Alyaev Yu. G., Gadzhieva ZK, Rapoport LM, Kazilov Yu.B. Medical treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men. The role of uroselectivity in drug selection. Andrology and genital surgery. 2014;1:6–14.
20. Gadzhieva ZK, Kazilov Yu.B. New possibilities of treatment of combined symptoms of the lower urinary tract in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia – prerequisites and advantages. Urologiia. 2017;1:95–102.
21. Neymark AI, Neymark BA, Torbik DV Tactics of managing a patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia with a large volume of it. Bulletin of medical science. 2017;1(5):44–53.
22. Olariu L. et al. Entomological complex with pro-apoptotic and antiproliferative effect on prostatic dysplasia cells, EUROINVENT Cat., Timisoara, 2022.
23. Dumbraveanu I., Banov P., Arian I., Tanase A. Use of entomological drugs in the complex treatment of patients with chronic prostatitis and erectile dysfunction. Moldovan Journal of Health Sciences. 2017;14(4).
24. Ghicavii V., Tanase A., Ceban E., Dumbraveanu I., Ciuhrii V. New Direction in the Treatment of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia Using Adenoprosin: Biologically' Active Entomological Medicine. Urology. 2011;78.
25. Dumbraveanu I. et al. Adenoprosin in the treatment of prostate diseases. Arta Medica. Revista medícala ptiintifi co-practica. 2015;4(57):101–104.
About the authors / For correspondence
AUTHORIZATION: A. V. Kuzmenko – Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Urology of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education VSMU named after. N. N. Burdenko; e-mail
Similar articles
- The effectiveness of fesoterodine in patients after transurethral resection of the prostate
- Use of the drug Vitaprost® (rectal tablets and suppositories) for the rehabilitation of patients after invasive diagnostic urological interventions
- Observational randomized study of the effectiveness and safety of Longidaza®, vaginal and rectal suppositories 3000 IU in the treatment of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis, urinary disorders in men and prostate fibrosis
- Combination therapy for chronic bacterial prostatitis