Indications
Ministry of Health of Russia
G40.0 Localized (focal) (partial) idiopathic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with seizures with focal onset
G40.1 Localized (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with simple partial seizures
G40.2 Localized (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with complex partial seizures
G53.0 Neuralgia after herpes zoster (B02.2+)
FDA recommendations
Partial seizures with or without secondary generalization
Neuralgia after shingles
Restless legs syndrome
UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency guidelines
Epilepsy
Neuropathic pain
Literature:
- A short reference book on psychopharmacology, pharmacotherapy and mental pathology / Kozlovsky, Vladimir Leonidovich. - St. Petersburg: SpetsLit, 2015.
- The influence of Pregabalin on the cardiovascular system: dissertation of a candidate of medical sciences: 14.00.25 / Dolgova Natalya Yurevna; [Place of defense: Kursk State Medical University]. - Kursk, 2009. - 112 p.
- Modern psychotropic drugs used in psychiatry: educational and methodological manual / [Olga Fedorovna Pankova, Artem Vyacheslavovich Alekseev, Alexander Viktorovich Abramov]; Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education "Russian National Research Medical University named after N. I. Pirogov" (FGAU HE RNRMU named after N. I. Pirogov of the Ministry of Health of Russia), Department of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology. — Moscow: Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogova Ministry of Health of Russia, 2022. - 135 p.
Treatment regimen
Dosage and dose selection
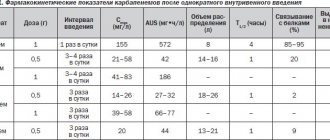
- 900-1800 mg/day in three divided doses
- Neuralgia after shingles (immediate release): 300 mg on day 1; 600 mg in two divided doses on day 2; 900 mg in three doses on day 3.
- Neuralgia after herpes zoster (extended release): 600 mg in the morning on day 1; 1200 mg per day in two divided doses on day 4.
- Restless legs syndrome (sustained release): 600 mg per day in one dose, around 5 p.m.
- Convulsions (adults and children over 12): initial dose 900 mg/day in three divided doses; recommended dose 1800 mg/day in three divided doses; the time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours.
- Convulsions (children 5-12): initial dose 10-15 mg/kg per day in three divided doses; within three days, increase to 25-35 mg/kg per day in three doses; maximum dose 50 mg/kg per day; the time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours.
- Convulsions (children 3-4): initial dose 10-15 mg/kg per day in three divided doses; within three days, raise to 40 mg/kg per day; maximum dose 50 mg/kg per day; the time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours.
- If gabapentin is added to another anticonvulsant, increase the dose of gabapentin slowly over a week.
- Some patients with pain or anxiety may benefit from taking immediate-release gabapentin only twice a day.
- Very high doses can be divided into more than 3 doses per day.
- Any broken half of a tablet that is not used within a few days should be thrown away.
- Gabapentin extended-release tablets should not be crushed or chewed.
- Gabapentin extended-release tablets must be taken with food.
- If very strong sedation occurs, most of the daily dose can be taken at night
How quickly does it work?
The cramps go away after 2 weeks.
The pain goes away in 2 weeks or less.
May reduce anxiety in various disorders for several weeks.
Expected Result
Disappearance of symptoms.
If it doesn't work
If the pain does not go away after 6-8 weeks, you need to increase the dose or discontinue the drug.
How to stop taking it
Reduce dose for at least a week. If taken abruptly, epileptics may experience seizures [1].
Treatment combinations
- Gabapentin is itself an augmentant that is added to other anticonvulsants in the treatment of epilepsy; to lithium, atypical antipsychotics and anticonvulsants in the treatment of bipolar disorder.
- Gabapentin is added to antidepressants in the treatment of neuropathic pain
- In the treatment of anxiety, gabapentin is a second-line drug of choice, added to antidepressants or benzodiazepines [1].
Hernia resorption
- home
- Services
- Treatment methods
- Hernia resorption
Resorption is a method of reducing or completely disappearing an intervertebral disc herniation without surgical treatment.
This voluminous article was prepared by our doctor P.D. Kovzelev.
The latest scientific study from 2015 tells us that herniated discs can be reduced without surgery ! Moreover, this is not just an ordinary study, but an entire meta-analysis - this is the highest level of evidence in modern medical science. Literally 10 years ago, if a doctor had said that the hernia had decreased, at least they would not have understood him. There was an opinion that if a disc herniation or protrusion has already appeared, then this is a death sentence and only surgery can help. Now, thanks to science and the ability to look inside the spine using MRI, we can clearly say that resorption is a reality and it is available in St. Petersburg.
Mechanisms of resorption of intervertebral disc herniation:
Loss of water from the disc and its gradual drying out.
Absorption of the hernia by our immunity. An analogy for understanding: a hernia is like a splinter in the finger for the immune system - it is foreign. He “eats” it with his protective macrophage cells.
For those interested, you can read more about the mechanisms of resorption in Wikipedia, article “resorption of intervertebral hernia.” Our article is a little about something else.
Standard picture demonstrating the process of spinal degeneration.
Science does not yet fully understand the mechanisms, the terms of resorption are also blurred, some scientists write about 21 months, which is certainly a long time. But back pain, and even the kind that happens with a real large hernia, is no joke and it’s impossible to endure it for 2 years .
Then, for our patients and adherents of standard medicine, it seems logical to turn to neurosurgeons. The logic is quite simple and understandable: “no hernia, no problem.” But the situation with surgical treatment is more complicated than it might seem to the average person . In a large percentage of cases, patients experience a recurrence of the hernia, the biomechanics of the region changes, and if the intervertebral disc is completely removed and an artificial one is installed, then the chance of damage to the above or underlying discs and joints is 70%. That is why foreign neurosurgeons resort to surgical treatment only in 5% of cases.
Schematic flow of the operation.
By the way, the situation here is not so rosy and operations are performed inadequately often, although over the past 5 years the picture as a whole looks much better. After all, the best operation is the one that was not performed, says medical wisdom.
What are the ways out of the situation and are there any at all?
Of course have.
Treatment of pain syndromes, hernias and disc protrusions is the main focus of our clinic. Looking ahead, we will say that only 2 patients out of 100 require surgery after a course of treatment with us.
How do we achieve such results?
- Specialists . At our clinic, we have formed a team of specialists who are well versed in the problem of pain and spinal injuries. We have gathered young, ambitious and competent doctors. Only a fresh look at the problem and the most current knowledge can help us cure almost every patient with an intervertebral hernia.
- Progressive treatment methods and, in particular, physiotherapy and PRP therapy . When we talk about physical therapy, we usually remember something from the old clinics. But our clinic has the most modern methods and equipment. For example, a healing magnet Super inductive system with a power of 2.5 Tesla, which is almost 2 times more than the standard 1.5 Tesla in MRI scanners! This is the only device in St. Petersburg that is available to anyone ; we purchased it specifically for our patients. We also use the injection method - introducing platelet-rich plasma to the site of the hernia, which greatly accelerates regeneration.
- Patient trust . This is really important, because the treatment process requires full dedication and trust, first of all, from you, the patients. This is a long, labor-intensive process, joint work between the doctor and the patient. Trust in us is reflected in the popular rating of the ProDoctors website and at the time of writing this article, Smart Clinic ranks 1st in St. Petersburg among specialized clinics . We also have only positive reviews on all sites. Thank you for that.
Here are the three main pillars on which our work and your resorption are built.
What does resorption look like?
Clinical case No. 1.
Patient, 33 years old. Long-term medical history of herniated disc removal, disc infection, repeated surgeries, long-term use of antibiotics, and severe pain. At the time of examination, the patient was not sleeping adequately and was clinically depressed.
Clinical picture: severe pain in the legs, constant lumbago to the point of falling, lack of sleep.
Treatment: antibiotics, variation of the resorption protocol, sacroiliac joint blockade, then 1 month once a week PRP injections (plasma therapy).
Only 2 months passed between the MRI before and after , which is surprising even for me. In this case, we see a good result, the main goal was to reduce pain and restore quality of life - it was achieved.
Pay attention to fatty degeneration of muscles. Those. The muscles themselves are of large good volume, but at the same time they have layers of fat. This suggests that at one time a person was actively involved in some type of physical education, and then stopped. Sitting a lot and not experiencing regular physical activity.
Clinical case No. 2.
Patient, 45 years old. He turned to me for help after another shooting in the lower back. Has a long course of back pain. An MRI was performed, which revealed a huge disc herniation with a tendency to sequestration (separation). Neurosurgeons said that surgery was urgently needed, but the patient did not want to rush into making such a decision.
Clinical picture: pain in the right leg, numbness, slight loss of strength.
Treatment: standard for the resorption protocol. 12 days daily, then 1 month once a week PRP injections (plasma therapy).
The pain decreased by more than 2/3 of the initial value after 10 days.
There were 7 months between the before and after MRI. In this case, we see an excellent result, complete resorption of the sequestrum and partial resorption of the hernia. The patient underwent a second course of treatment with the goal of achieving complete resorption, but because... the required deadlines have not passed, then 3 MRIs have not yet been received.
Patient interaction format and treatment.
In-person consultation with a doctor, analysis of all your complaints, detailed neuro-orthopedic examination and examination of MRI images. A comprehensive solution to the question of the effectiveness of treatment and its necessity. We always explain the clinical picture to the patient and show MRI images so that the person is as informed as possible about the state of his health.
Treatment. The treatment format itself consists of daily visits to our clinic, regular examination and questioning by your attending physician, and receipt of direct treatment. Duration of procedures is from 1 to 1.5 hours per day.
The cost of treatment is currently 2990 rubles per day according to the terms of the promotional offer. The duration of therapy is 12-14 days, depending on the severity of your condition.
An MRI is required before and after treatment.
Frequently asked questions and their answers
1. Is there resorption? Yes, sure.
2. What are the chances that the hernia will shrink without surgery? Everything is determined individually. A recent MRI (no older than 1-3 months) and an in-person examination of the patient are required. Sometimes you can tell with certainty even just by looking at an MRI.
3. How long should I wait before the second MRI after treatment with you? Again, everything is decided individually. 3 months, in our opinion, is rapid resorption. 6 – Standard.
4. And all this time I will live with back pain? Of course not. Pain treatment begins from the first day. Typically, after a week, patients experience a 50% reduction in pain, sometimes more.
5. Then why the second MRI only after 3-6 months? Because pain reduction is not resorption. Most often, the cause of pain is muscle spasm, tissue swelling, or damage to the spinal joint. We eliminate these problems and the pain goes away. But the resorption process itself is not so fast.
6. Does it happen that treatment doesn’t help? This also happens, although it is extremely rare. Or there are cases when surgery is clearly needed and conservative treatment is out of the question. Medicine is not mathematics and no one can calculate the result with 100% accuracy. If somewhere you are given guarantees in matters of health, we recommend that you at least be wary.
Comparison with surgical treatment
The table has a horizontal swipe
| Index | Surgical treatment | Hernia resorption at Smart Clinic |
| Cost of treatment | In different clinics from 100,000 to 500,000 rubles | 30,000 – 50,000 rubles. |
| Efficiency | It largely depends on the specialist. | High efficiency due to the unification and use of hardware treatment methods. |
| Complications | Occurs from 1 to 12% according to official data. | Complications are practically excluded. |
| Severity of complications | From minor to disability. | Extremely rarely - relapse of pain syndrome. |
| Duration of treatment | 1 day. | 12-16 days |
| Periods of incapacity for work | From 1 to 6 months | Treatment takes place on an outpatient basis without interruption from work. If necessary, sick leave may be issued. |
| Rehabilitation | Long-term | Short-term, begins at the final stage of treatment. |
| The likelihood of recurrent disc herniation | About 15% | No more often than on a healthy disk, because natural healing occurs. |
MRI consultation
Our doctors can look at your MRI for free and tell you whether resorption is possible in your particular case!
To do this, you must send files from a disk or flash drive made no later than 3 months at the time of application. Also briefly state your medical history in a letter: when and how the disease began, how long it lasts, are there any exacerbations, what are the current complaints, etc.
Mail for sending MRI –
Patient Guide
Also, in order to increase understanding of this process, our doctor, Pavel Dmitrievich Kovzelev, wrote a free guide to resorption for our patients. You can download it and read it in detail by clicking on the “download” button. 25 page manual, lots of pictures, MRI, everything is clear and signed. There is also humor. Enjoy it for your health.
Summary of our neurologist Pavel Dmitrievich Kovzelev.
“There is no magic or wizardry in the resorption process itself. The existence of hernias in such quantities was discovered not so long ago, this is due to the widespread introduction and affordable price of MRI. It would not be reasonable to assume that nature and evolution have not built into our bodies mechanisms to heal when a herniated disc occurs. In this case, we only help and speed up this process.”
Sign up for hernia resorption
Special patient groups
Patients with kidney problems
Reduce dosage [1].
The use of gabapentin in patients with renal failure younger than 12 years of age has not been studied.
Patients with liver disease
Use in normal dosage [1].
Patients with heart disease
No special recommendations [1].
Elderly patients
Elderly patients are more likely to experience side effects (ataxia, edema) [1].
Children and teenagers
- Gabapentin is approved for use in the treatment of seizures in children over 3 years of age [1].
Pregnant
- There have been no adequate studies in pregnant women [1].
- All risks should be weighed and compared
- When treating bipolar disorder or psychosis, discontinue gabapentin during pregnancy; For patients with bipolar disorder, stop taking gabapentin until pregnancy; You can resume taking it immediately after birth.
Breast-feeding
- The medicine passes into breast milk.
- It is recommended that you stop taking gabapentin or stop breastfeeding
addictive
Due to the same effect on the nervous system, both Pregabalin and Gabapentin, when used in large doses, can cause rapid, persistent dependence.
Reference! According to statistical data in Russia, the main population abusing these medications are people aged 20-35 years.
When taking Pregabalin or Gabapentin for pharmacological purposes, dependence on them is extremely rare. But over time, the body begins to break down and remove them faster, which provokes a person to increase the dosage . This helps to restore the previous effect of these drugs, but leads to addiction . To prevent this, you need to contact your doctor to adjust your therapy.
Side effects and other risks
Mechanism of side effects
Side effects are caused by blockade of voltage-gated calcium channels.
Side effects
- Sedation, dizziness
- Ataxia, fatigue, nystagmus, tremor
- Edema
- Blurred vision
- Nausea, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth, dyspepsia
- In children under 12: emotional instability, increased mobility, impaired thinking
- Dangerous side effects: anaphylaxis and angioedema, suicidal ideation
- Weight gain: yes
- Sedation: yes, often; especially strong at high doses
What to do about side effects
- Wait;
- For sedation, take at night;
- Reduce dose;
- Switch to another drug [1].
Long term use
Safely
addictive
No.
Overdose
Confusion of speech, sedation, diarrhea, blurred vision
Content:
- Description and scope
- Gabapentin and Pregabalin: differences in side effects
- Gabapentin and Pregabalin: comparison and differences in overdose
- addictive
- Comparison of contraindications
The group of antiepileptic (anticonvulsant, psychotropic) drugs includes a wide range of drugs, including Gabapentin and Pregabalin. Despite the general focus, they have slightly different effects, a range of side effects and contraindications. Comparing all the qualities of both drugs will help you find out how effective and safe each of them is.
Expert advice
Well studied as a remedy for cramps and neuralgia after shingles, but most often used off-label;
Off-label use is justified as a first-line remedy for neuropathic pain, a second-line remedy for anxiety;
There is not enough evidence for off-label use in bipolar disorder; lamotrigine has a stronger evidence base;
There is insufficient evidence for off-label use in schizophrenia [1].
Gabapentin and Pregabalin: comparison and differences in overdose
Both drugs can cause poisoning if the recommended dosage is accidentally or unintentionally exceeded or when treated concomitantly with other anticonvulsants.
Signs of Gabapentin intoxication include:
- slurred speech;
- fatigue;
- dizziness;
- moderate sedative effect.
Symptoms of Pregabalin poisoning are:
- depression;
- hallucinations (most often frightening);
- confusion;
- causeless mood swings;
- loss of hunger;
- loss of taste;
- memory losses;
- convulsions and/or tremors;
- lack of coordination;
- absentmindedness;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and many others.
A comparison of the signs of poisoning with these drugs showed that the symptoms are much more severe with Pregabalin. However, there is currently no data on deaths due to overdose of both drugs.
Special instructions for the use of Gabapentin
The drug should be discontinued or replaced with an alternative drug gradually, reducing the dose over at least 1 week. Abrupt cessation of antiepileptic drug therapy in patients with epilepsy can provoke status epilepticus. Ineffective for the treatment of absence seizures. During pregnancy, it is used only if the expected benefit to the mother justifies the possible risk to the fetus (possible slowdown in fetal growth if the therapeutic dose of 3600 mg is exceeded in terms of mg/m2). Excreted in breast milk. Its effect on breastfed newborns is unknown, so it should only be used during breastfeeding if the benefit to the mother clearly outweighs the risk to the baby. During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from potentially dangerous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions. The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin in children under 3 years of age as adjunctive therapy for epilepsy and in children under 12 years of age as monotherapy have not been established. The safety and effectiveness of treatment for neuropathic pain in patients under 18 years of age have not been established. If drowsiness, ataxia, dizziness, increased fatigue, nausea and/or vomiting, weight gain appear in adults, and drowsiness, hyperkinesia and hostility in children, treatment should be discontinued.
How does Gabapentin work?
An analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid, Gabapentin, unlike it, does not bind to glutamate, benzodiazepine, or opiate receptors. It acts selectively, directly reducing the activity of the central nervous system centers responsible for the development of seizures during epileptic seizures and other pathological conditions. The drug is not similar to GABA mimetics. In the body, it prevents the penetration of calcium ions through cell membranes, thereby blocking the development of severe pain. At the same time, the drug slows down the death of neurons, preventing further development of the pathological process, and normalizes night sleep.
After administration, the contents of tablets and capsules dissolve under the action of gastric juice and are absorbed into the blood. Food does not affect the rate of absorption of drugs. The effect of the medication develops within 2–3 hours. At the same time, the components of Gabapentin do not bind to blood proteins and practically do not form toxic metabolites. The drug is transformed over 7–8 hours, then gradually eliminated from the body by the kidneys. In case of disturbances in the urinary system, the elimination period can increase to 24 hours. For this reason, adjustments to the treatment regimen may be necessary for people with kidney failure. Residues of the medication do not accumulate inside and are not deposited in tissues.
Composition and dosage form of the drug
The active compound of the drug is Gabapentin, which acts on specific centers of the brain. Effective for relieving pain and convulsions in epileptic disorders. The medicine is intended for oral administration and is produced in two pharmaceutical forms:
- Gapabentin 300 tablets: containing 300 mg of gabapentin per 1 piece;
- capsules of the same name and dosage.
Among the auxiliary and formative compounds of the drug: starch, talc, magnesium stearin, calcium hydrogen phosphate.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Gabapentin
Gabapentin is structurally similar to GABA, however, its mechanism of action differs from other drugs that interact with GABA receptors (valproate, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, GABA transaminase inhibitors, GABA uptake inhibitors, GABA agonists and GABA prodrugs). At therapeutic concentrations, it does not bind to the following receptors: GABA A and B, benzodiazepine, glutamate, glycine and N-methyl-d-aspartate. In vitro studies of labeled gabapentin have identified new peptide receptors in rat brain tissue, including the neocortex and hippocampus, which may mediate the anticonvulsant activity of gabapentin and its derivatives (the structure and function of gabapentin receptors are not fully understood). Rapidly absorbed when taken orally. Bioavailability is not proportional to the dose - with increasing dose it decreases and is: at a dose of 300 mg - 60%, at 1600 mg - 30%, respectively. Absolute bioavailability - 60% (capsules). Food, including those high in fat, does not affect the pharmacokinetics of the drug. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved 2–4 hours after oral administration. Plasma concentrations are dose proportional. The maximum plasma concentration is 4.02 mcg/ml when used at a dose of 300 mg every 8 hours and 5.5 mcg/ml when used at a dose of 400 mg. Passes through the BBB and enters breast milk. Distribution volume - 57.7 l. In patients with epilepsy, the minimum concentration of gabapentin in the CSF is approximately 20% of that in plasma. The binding to plasma proteins is very weak (less than 5%). Practically not metabolized. Excreted by the kidneys. Removal from blood plasma has a linear relationship. The half-life averages 5-7 hours, does not depend on the dose (at a dose of 300 mg - 5.2 hours, at a dose of 400 mg - 6.1 hours). The elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance of gabapentin are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. Removed by hemodialysis. The clearance of gabapentin from blood plasma is reduced in elderly people and patients with impaired renal function; the half-life for creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min is 52 hours. Pharmacokinetics do not change with repeated use.