Cerebrolysin is a prescription drug in ampoules for intravenous and intramuscular administration, obtained from pig brain.
The medicine has a nootropic effect and is used for cognitive impairment, to restore the body after a stroke, head injury and other organic brain lesions.
The issue of selecting Cerebrolysin analogues is relevant for those for whom the injection form is not suitable, if the patient cannot afford the expensive drug or there are other reasons. Check with your doctor for the choice of substitutes; many of them are not sold freely in pharmacies.
pharmachologic effect
The medicine is synthesized from pig brain and has many beneficial effects:
- enhances the restoration of damaged areas of the nervous system and has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- prevents the death of neurons in damaged tissue;
- helps improve cognitive functions, concentration and memory processes;
- improves the processes of energy metabolism of the brain.
The drug is particularly beneficial for patients with Alzheimer's disease when it is a disease-modifying drug. Cerebrolysin reduces the frequency and severity of clinical relapses of the disease, reduces accumulated damage inside the brain, and slows the increase in disability for a long time.
Indications for use of Cerebrolysin
The medication is prescribed by a doctor for the treatment of children and adults with the following diseases:
- damage to the brain and spinal cord due to trauma;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- dementia of various nature;
- recovery after ischemic stroke;
- chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency;
- in childhood – mental retardation, attention deficit, hyperactivity.
In the presence of status epilepticus and acute renal failure, the medication is replaced with approved analogues.
Indications and contraindications for Cerebrolysin
The instructions indicate the following pathologies for which the medication can be prescribed:
- disorders of the nervous system of various etiologies;
- consequences of a stroke;
- delay in the mental development of children;
- mental disorders with the appearance of absent-mindedness, memory impairment, etc.
Cerebrolysin is contraindicated in patients with epilepsy, renal dysfunction, and individual intolerance to the component composition.
For children and pregnant women, the medication is prescribed if indicated. Despite the lack of toxic effect, the drug requires caution when used in these groups of patients.
Cerebrolysin - instructions for use
The drug is sold by prescription and used as prescribed by a doctor. Method of use: intravenously, as part of droppers with glucose, saline or Ringer's solution, intramuscularly. The method of administration is influenced by the severity of the disease and the age of the patient, and the prescribed number of ml. So, up to 5 ml is administered intramuscularly, from 5 to 10 - intravenously, over 10 ml - added to droppers.
The course of treatment is 10-20 days, the medicine is administered every day. In case of severe organic lesions of the brain, it is possible to increase the course, according to the scheme after 2-3 days.
When to inject Cerebrolysin - morning or evening
Cerebrolysin is a nootropic drug that is best injected in the morning. When administered in the evening, an undesirable reaction is possible - insomnia or insomnia.
The patient’s well-being during and after injection is influenced by the speed of manipulation. Well tolerated if the medicine is administered slowly. With rapid infusions, a person complains of fever, dizziness, sweating, and confusion.
Analogs of Cerebrolysin
The price of Cerebrolysin depends on the number of ml in the ampoule and varies from 1 thousand to 3.5 thousand for 5–10 pieces. Usually one package is not enough for a course, so treatment becomes inaccessible to some categories of patients, in particular, pensioners. How to replace Cerebrolysin depends on the patient’s indications and complaints, the presence of contraindications, financial capabilities, and preferences for the form of the drug (ampoules or tablets).
Modern analogues of Cerebrolysin with prices and country of origin
| Analogue | Price, in rubles | Manufacturer country |
| Cerebrolysin | 1000-3500 | Germany or Austria |
| Cortexin | 800-1400 | Russia |
| Actovegin | 550-1650 | Austria or Russia |
| Cerakson | 600-1700 | Spain |
| Mexidol | 250-1600 | Russia |
| Piracetam | 30-180 | Russia |
| Cerebrolysate | 350-550 | Russia |
| Cerepro | 400-1700 | Russia |
Cerepro
The Cerepro analogue consists of choline alfoscerate in the form of ampoules and capsules. Used for dementia, ischemic stroke, head injury, cerebrovascular insufficiency, as a nootropic. Prescribed by a doctor and available with a prescription.
Analogues of Cerepro with a similar composition:
- Alfocholine (Belarus);
- Gleatser (Russia);
- Gliatilin (Italy);
- Nooprin (Russia);
- Cereton (Russia), etc.
Cytoflavin
The domestic analogue Cytoflavin improves brain metabolism. The medicine consists of succinic acid, riboxin, nicotinamide, riboflavin. Available in ampoules and tablets, available by prescription for cerebrovascular diseases, cerebral infarction, neurasthenia.
Magnesium
The Magnesium multivitamin complex replenishes the deficiency of magnesium citrate and ascorbate. It is used after injuries, for nervous disorders, and for the rehabilitation of people with cardiovascular diseases.
Other drug analogues
To restore cognitive abilities and brain functionality, a huge number of analogues better and worse than Cerebrolysin have been developed.
| A drug | Active substance | Manufacturer | Cost (rubles) |
| Vinpocetine (tablets, solution) | Vinpocetine | Sotex PharmFirm, DEKO company, Binnopharm ZAO, Novosibkhimpharm, Ellara LLC, Biosintez OAO, Moskhimfarmpreparaty im. N.A. Semashko, ALSI Pharma, MAKIZ-PHARMA, Valenta Pharmaceuticals, Northern Star (Russia) | 40-50 |
| Picamilon (solution, tablets) | Nicotinoyl gamma-aminobutyric acid | JSC Vitamin Plant Pharmstandard, Russia; JSC Novosibkhimpharm, Russia; JSC Chemical and Pharmaceutical Plant AKRIKHIN, Russia; JSC Biokhimik, Russia | 80-100 |
| Thiocetam (tablets, ampoules) | Piracetam + Thiotriazolin | JSC "Galichfarm" Ukraine | 500-550 |
| Carnicetine (capsules) | Acetylcarnitine | PRO LLC PIK-PHARMA (Russia) | 500-550 |
| Nootropil (tablets | Piracetam | UCB Pharma SA (Belgium), Jelfa SA (Poland) | 200-250 |
| Instenon (tablets) | Hexobendine dihydrochloride + Etophylline + Etamivan | ALKALOID (Macedonia); HAFSLUND NYCOMED (Austria) | 4500-5000 |
In practice, medications are used in the form of solutions for intramuscular and intravenous administration, tablets.
Cerebrolysin or Cortexin - which is better for adults and children
Cortexin is a cheaper analogue of Cerebrolysin in ampoules, also obtained from pig brain. Available in powder, dissolved in sodium chloride, water or novocaine before use. The drug is administered intramuscularly once a day, for severe lesions - twice a day. Is a painful injection.
Cerebrolysin substitute has similar effects. The medicine improves cognitive function, improves metabolism in damaged brain tissue and protects cells from destruction and adverse factors, accelerates the synthesis of peptides and metabolic processes. Restrictions on use include pregnancy and individual intolerance to the components.
Cerebrolysin is a similar drug in the form of ampoules ready for administration. It has the same therapeutic effects as Cortexin. Has positive reviews from doctors.
What is the difference between the two analogues:
- The cost of Cortexin is lower.
- Cerebrolysin is not used for status epilepticus and acute renal failure; in this case, Cortexin is the drug of choice.
- For children and adults with mild brain damage, Cortexin is recommended; for severe conditions, Cerebrolysin is more often prescribed.
Which is better, Cortexin or Cerebrolysin, depends on the severity of the patient’s condition, indications, history of contraindications, and financial capabilities.
Drugs available in both forms
Many pharmaceutical companies produce Cerebrolysin substitutes in two dosage forms - for oral and parenteral use.
Cavinton
It is produced in the form of parenteral solution and tablets. The drug is effective in the treatment of cerebrovascular disorders, neurological and systemic pathologies. The drug prevents the development of ischemia in brain cells and restores cognitive function after a stroke. The active ingredient in the medicine is vinpocetine.
Cavinton is used for:
- hypoxia and ischemia;
- decreased concentration and attention;
- decreased intelligence and memory;
- encephalopathy of discirculatory type;
- Meniere's syndrome.
Cavinton is not prescribed for:
- cardiac pathologies with disturbances in the rhythm of myocardial function and hypertension;
- kidney failure;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The tablets are taken orally three times a day, 1-2 tablets after meals. The solution for parenteral use is administered by injection or drip. The solution should be used once a day. After a course of injection therapy, the patient is transferred to taking tablets.
Side effects:
- blood pressure fluctuations and arrhythmia;
- dizziness and headache;
- insomnia or drowsiness;
- dyspepsia;
- skin rash, hyperemia, itching, as well as allergic rhinitis and bronchospasms.
Mexidol
This is a membrane-protective drug based on ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate. The medicine is prepared in tablets and solution for injections.
Mexidol has the following properties:
- antihypoxic and antisiolytic;
- nootropic and anticonvulsant;
Mexidol is used for:
- impaired cerebral blood flow;
- encephalopathy;
- withdrawal syndrome;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries;
- infectious stomatitis and caries.
Mexidol is not prescribed for:
- severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys;
- allergies to the composition;
- breastfeeding and childbearing.
Also not prescribed to children under 12 years of age, pregnant women and mothers whose children are breastfed. Prescribed with restrictions for sharp fluctuations in blood pressure - hypertension and hypotension.
Mexidol is used intravenously by injection or dropper, as well as intramuscularly. Acute attack of stroke - therapy is carried out from the first hours of the attack 200-300 mg 2-3 times a day. After the patient’s condition has stabilized, they switch to oral medication.
The maximum dosage per day of Mexidol for cerebrovascular pathologies is 800 mg. Treatment of dementia is carried out with tablets - 3 doses per day, 1-2 pieces each
Side symptoms:
- dyspepsia;
- insomnia;
- headache;
- urticaria and bronchospasms.
Vinpocetine
Vinpocetine corrects blood flow when blood flow in the brain is impaired. The active ingredient is vinpocetine. The medicine is produced in the form of a solution and tablets.
Vinpocetine is used for:
- encephalopathies and migraines;
- cerebral infarction;
- atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries;
- head injuries;
- Meniere's syndrome;
- dementia;
- withdrawal symptoms – medication and alcohol.
Not prescribed for:
- cardiac diseases and arrhythmias;
- intolerance to components;
- hemorrhagic stroke.
Vinpocetine is not used in pediatric practice, in the treatment of women with breastfeeding and childbearing. Tablets should be taken 1-2 tablets three times a day, course from 2 weeks to 2 months.
The solution is injected into a vein only by drip. Dosages are prescribed by the doctor individually to each patient.
Negative symptoms:
- skin allergies;
- dyspepsia;
- sleep disturbance and headache.
See also:
TOP 10 analogues of Cavinton - a substitute in tablets and other forms
Cerebrolysin or Actovegin - which is better for blood vessels in adults
Actovegin is an analogue of Cerebrolysin injections, also available in tablets for maintenance therapy. It is based on a hemoderivative of calf blood. Among the therapeutic effects are activation of metabolism in tissues, improvement of trophic processes and stimulation of regeneration.
To figure out which is better – Actovegin or Cerebrolysin, and whether these drugs can be taken at the same time, you need to compare them:
- both drugs have a nootropic effect;
- for ischemic stroke, dementia, neurological pathologies, any medication can be used;
- Cerebrolysin is better for improving cognitive functions - memory, attention, learning;
- Actovegin is often prescribed for peripheral circulatory disorders and diabetic polyneuropathy;
- Sharing is possible, and two medications cannot be taken into one syringe.
What is best in a particular case is determined by the doctor.
Cerebrolysin or Ceraxon
Ceraxon is a nootropic drug based on citicoline, prescribed for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, head injury and cognitive impairment. Often used for older people.
One of the differences between the analogue of the drug Cerebrolysin is the additional form in the form of an oral solution. It is packaged in a bottle with a dispenser syringe or disposable sachets.
Ceraxon ampoules are administered intramuscularly or intravenously, depending on the indications and severity of the patient’s condition. Then it is possible to enhance the effect with an oral solution.
The analogue restores damaged brain cells, improves cognitive functions, prevents the death of ischemic tissue, and reduces the severity of neurological manifestations of diseases.
Ceraxon differs from Cerebrolysin in its lower price and the presence of an additional release form - an oral solution. Both medications are used for recovery from TBI and stroke, and in cases of impaired cognitive function. However, Cerebrolysin is also used in children with developmental delay, hyperactivity and attention deficit disorder, and Alzheimer's disease. The mechanisms of action of drugs are different due to the incoming substances - Cerebrolysin consists of polypeptides, the cheap analogue Ceraxon contains citicoline.
Citicoline is also contained in the drugs Proneuro, Recognan, Neypilept, etc. Which is better is determined by the doctor specifically for each patient.
Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of Cerebrolysin in the treatment of patients with chronic cerebral ischemia.
Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of Cerebrolysin in the treatment of patients with chronic cerebral ischemia. Pharmacoeconomic aspects
E.I. Chukanova. Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine, Russian State Medical University
Due to the prevalence of vascular diseases of the brain, the variety of their forms and characteristics of the course (cerebral vascular crises, transient ischemic attacks (TIA), strokes, sometimes combined disorders of cerebral and coronary circulation), the difficulty and not always effective treatment of cerebral circulatory disorders is becoming more and more Recently, attention has been paid to their prevention, that is, early diagnosis and treatment of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency [2, 3, 5, 6, 11, 12, 14, 16].
The pathogenesis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is caused by cerebral circulatory failure in a relatively stable form or in the form of repeated short-term episodes of dyscirculation, which can be asymptomatic or manifest clinically. The degree of structural changes in the brain during dyscirculation can range from changes in individual neurons, gliocytes and white matter fibers to infarctions of various sizes and localization [2, 8, 16], which ultimately manifests itself as focal changes in the brain substance, diffuse changes in the white matter and cerebral atrophy.
In conditions of chronic brain hypoperfusion, compensation mechanisms are depleted, the energy supply of the brain becomes insufficient, as a result of which functional disorders first develop, and then irreversible diffuse morphological changes in the brain, which prepare the brain tissue for the development of stroke. The formation of any focus of ischemic damage is accompanied by the synthesis and secretion of a wide range of regulatory peptides, directed migration of inflammatory cells, and activation of various signaling molecules. It has been shown that when changes occur in the infarction zone, an imbalance of cytokine status occurs with a deficiency of protective anti-inflammatory interleukins and trophic factors, in particular NRF [1, 2]. NRFs are physiologically active polypeptides that regulate the growth and differentiation of neurons in developing systems and their functional stability. In adulthood, NRFs protect neuronal structures from traumatic, hypoxic, ischemic and other damage [2].
One of the drugs with proven neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effects is Cerebrolysin [1, 6, 9, 10]. It is based on natural neuropeptide and growth factors isolated from the brain of pigs. The main mechanisms of action of Cerebrolysin are the regulation of brain energy metabolism, the actual neutrophic effect and modulation of the activity of endogenous growth factors, interaction with neuropeptide and neurotransmitter systems. Experimental studies have shown that Cerebrolysin reduces the brain's need for oxygen, creating its increased resistance to hypoxia factors, the antioxidant properties of the drug have been proven due to the inhibition of free radical oxidation and lipid peroxidation, as well as a positive effect on the homeostasis of microelements (magnesium, selenium, vanadium manganese) with antioxidant properties. Cerebrolysin has also been proven to have a positive effect on the state of cholinergic neurons, accompanied by a significant change in the level of acetylcholinesterase, which apparently is one of the mechanisms of the nootropic effect of the drug [9, 10].
A pharmacoeconomic study was conducted on the effectiveness of the drug Cerebrolysin in patients with chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency.
The purpose of the study was a pharmacoeconomic analysis of the effectiveness of treatment with Cerebrolysin in patients with different stages of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency. The objectives of the study included: studying the clinical effectiveness of Cerebrolysin in patients compared to the control group, identifying features of the progression of discirculatory encephalopathy (DE) and its outcomes in patients of the main and control groups, comparative assessment of the economic effectiveness of Cerebrolysin.
Material and methods
The study group consisted of 154 patients with DE stages I, II and III, who were undergoing outpatient treatment and receiving the drug Cerebrolysin, prescribed in a dose of 5–10 ml for 10 days. In addition, patients in the study group received “basic therapy,” which was maximally unified and included aspirin (100 mg/day), dipyridamole (150 mg/day), glycine (900 mg/day) and Enap. Enap was prescribed in an individual dose, depending on the stage of hypertension and the level of initial pressure. Blood pressure correction reached a level of 120/70 mm Hg. Art. – 140/80–85 mm Hg. Art. depending on the duration of blood pressure, the severity of cerebral perfusion disorders and the initial level of blood pressure at the beginning of the study. If the effect of Enap on lowering blood pressure was insufficient, Enap was combined with Arifon at a dose of 2.5 mg/day. The control group included 118 patients with DE, clinically comparable to patients in the study group. Patients in the control group received “basic therapy”, similar to patients in the study group. All patients of the main and control groups were treated as outpatients and were observed for a year.
The neurological status of patients was recorded before inclusion in the study, and then at the end of the 1st, 6th, and 12th months. The main and control groups were comparable in gender, age, etiology, severity and predominant localization of the pathological process. The study was conducted openly. The randomization method was used to recruit patients.
The distribution by stages of DE was: DE I – 40 patients, DE II – 51, DE III – 63 patients. The etiological factors of DE were: arterial hypertension - in 57 (37.09%) patients, atherosclerosis - in 35 (22.7%), a combination of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension - in 62 (40.3%) patients. For the purpose of a detailed assessment of the neurological status and the possibility of subsequent data processing, the following scales were used: MFI-20, MCA:FMA (Motor Club Assessment: Functional Movement Activities), Tinnetti scale (Functional Mobility Assessment in Eldery Patients), Spielberger anxiety scale (State-Trait Anxiety Inventory), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Mini Mental State Examination MMSE, Recovery Locus of Control questionnaire [7].
In view of the different scales and different directions of the scales used, for the convenience of presentation and perception of the material, we found it convenient to describe the dynamics of the mentioned indicators in terms of relative changes, speaking about the percentage of improvement (or deterioration) of the corresponding indicator in relation to its initial state. At the same time, the difference (95%) between the indicators of the study and control groups, differing by more than 2.5 times, was considered reliably significant; and at 90% - 2 times.
In addition to clinical examination, all studied patients underwent laboratory, instrumental and neuroimaging studies.
Research results
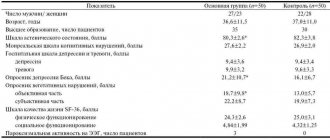
After the first course of treatment with Cerebrolysin in doses of 5 and 10 ml/day, a statistically significant effect of the drug on all studied scales was observed, with the exception of its effect on the score of “violent laughter and crying”. The use of Cerebrolysin at a dose of 5 ml/day for a course of 10 days showed a lesser clinical effect, however, when considering the effect of Cerebrolysin on the severity of asthenic syndrome and indicators of emotional status, it was noted that asthenic symptoms regressed by 59.6%, the prevalence of cephalgic syndrome decreased by 91 .2%. At the same time, scores on the anxiety (9.6±2.5 points) and depression (2.9±0.8) scales indicated the absence of anxiety-phobic and depressive disorders.
In table Figure 1 shows the severity of clinical manifestations of DE at the end of the first course of treatment with Cerebrolysin compared to the control group.
In addition to the effect on the severity of asthenic syndrome, anxiety, motivation and cognitive impairment in patients with stage I DE, Cerebrolysin was also effective against axial reflexes (16.9 and 23.7%), as well as vestibular ataxia (20.9 and 37. 8%). When analyzing the clinical picture in patients with DE II and DE III, a statistically significant effect of the drug on the score of the “movement” scale, amyostatic syndrome, cerebellar and frontal ataxia was noted.
By the beginning of the second course of treatment with Cerebrolysin in patients with DE I (6th month of observation), the “trace” effect remained during treatment at both a dose of 5 and 10 ml/day. In patients with DE II and DE III, the corresponding effect remained at a dose of 10 ml/day in relation to asthenic syndrome, anxiety and motivation.
After the second course of treatment with Cerebrolysin (7th month of observation), a statistically more significant effect of the drug on the scores of the selected scales was noted (Table 2), with the exception of the degree of influence of the drug on the severity of asthenic syndrome and neuropsychological characteristics in patients with stage I DE, which is most likely due to a good restoration of these functions as a result of complex treatment. The second course of treatment with Cerebrolysin statistically significantly improved the scores on the scales of movement, ataxia, pseudobulbar and amyostatic syndromes (CI 90–95%).
The “trace” effect of Cerebrolysin persisted until the 12th month of observation at all stages of the disease.
The study also assessed the risk of progression of DE and the occurrence of acute vascular episodes during treatment with Cerebrolysin compared to the control group. The number of patients with a stable condition, with a progressive course and with episodes of exacerbations - the development of TIA and strokes, compared with the control group, was taken into account. The risks of progression of DE and the occurrence of acute vascular episodes (TIA and stroke) during treatment with Cerebrolysin compared to control are presented in Table. 3. The risk of progression and development of complications during DE is calculated using the formula: A/(A+B)/C/(C+D) [4]. As can be seen from table. 3, when treated with Cerebrolysin at various dosage regimens with two courses per year for 10 days, a statistically significant effect of the drug on the progression of the disease in patients with DE stages I, II and III was noted. The odds ratio for progression when treated with Cerebrolysin at a dose of 5 ml/day was 0.1–0.2–0.3 according to the stages of the disease, respectively, and at a dose of 10 ml/day – 0–0.15–0.26 compared with the group control – 0.6–0.6–0.64. The effect of the drug on the occurrence of strokes was equally pronounced: with DE II in the control – 0.13, with treatment with Cerebrolysin at a dose of 5 ml – 0.04, at a dose of 10 ml/day – 0.04. With DE III in the control group, the OR for stroke development was 0.15, with treatment with Cerebrolysin at a dose of 5 ml/day – 0.07, with a dose of 10 ml/day – 0.03. No strokes were observed in stage I DE.
According to the results of the analysis, treatment with Cerebrolysin in the doses used was well tolerated by patients, the percentage of side effects was 2.6% (4 patients).
Pharmacoeconomic analysis
The above calculations took into account direct medical costs (excluding costs for the treatment of concomitant diseases): for inpatient treatment, which includes the cost of bed days, consultations with specialists, examinations and non-drug treatment; and direct non-medical costs. Interhospital differences in rates were not taken into account.
When selecting price parameters, the following sources were used: information bulletin “Medicine (medicines, equipment, , pharmaceutical bulletin”, “Tariffs for medical services provided to the adult population in accordance with the Moscow city compulsory health insurance program.” The above calculations took into account direct medical costs: prices for hospitalization, beds/days in the neurological department, the cost of specialist consultations, the cost of examinations and non-drug treatment; direct non-medical costs. Inter-hospital differences in tariffs were not taken into account. The cost of drug treatment was taken as a single time slice for December 2010 and converted to American dollars at the rate of 1 US dollar = 30.5 rubles. The cost of each unit of the drug (tablet, capsule, bottle, ampoule, etc.) was calculated to determine the costs of drugs in a hospital setting and for outpatient treatment. Then the cost of each drug unit was multiplied by the number of medicinal units used, then the cost of all medicines was added up and divided by the number of patients.
When determining the cost of treatment for patients with different stages of DE included in the main and control groups (without taking into account the costs of treatment of concomitant somatic pathology) per patient (completed case), the following were taken into account: the costs of basic therapy, the costs of treatment that arose when prescribing the “basic therapy" side effects, costs of treatment of TIA, cerebrovascular crises and strokes for the entire observation period; and calculation of direct non-medical costs. The main indicator in all cases was the cost of treatment per patient. The main indicator in all cases was the cost of treatment per patient. Determining the cost of basic therapy in patients of the main and control groups with different stages of DE showed that the average cost of basic therapy was $280.6 US.
The total cost of treatment of DE of different stages, including the cost of consultations, examinations, basic therapy, as well as the cost of treatment of strokes and other vascular episodes that occurred during the observation period, including the cost of direct non-medical costs, was: for DE I – $1315.92 US; with DE II – 1820.0$ US; with DE III – $2044.0 US. Taking into account the possibility of increasing treatment costs as the disease progresses, the given figures should be increased to the following values: for DE I – $2105.4 US; with DE II – 2912.0$ US; with DE III – $3352.2 US.
After calculating the cost of treatment for patients in the control group, it was determined under conditions of treatment with Cerebrolysin. The cost of drug treatment - the cost of basic therapy and Cerebrolysin was equal to $373.6 US for a dosage of 5 ml/day, and $466.6 US for a dosage of 10 ml/day. In table Table 4 shows a calculation of the cost of TIAs and strokes that developed in various subgroups in patients receiving Cerebrolysin.
By summing up all the cost terms, we can calculate the cost of direct medical costs for the treatment of one patient per year when prescribing Cerebrolysin at various dosage regimens (Table 5)
Knowing the cost of indirect medical costs per 1 patient with TIA and stroke per year (for patients in the study group and the control group), which was 35.89 and 634.5 US$, we can calculate the cost of direct medical and non-medical costs per 1 patient per year at treatment with Cerebrolysin (Table 6).
If the cost of disease progression and the development of strokes and other vascular episodes is taken into account, these figures increased.
By summing up the cost of consultations, examinations, basic therapy, the Cerebrolysin drug itself and additional funds required for the treatment of strokes and other complications that arose during observation (including non-medical costs) in patients with various stages of DE, we obtained the following cost indicators of direct medical and non-medical costs of treating one patient per year (Table 7).
Comparative indicators of pharmacoeconomic cost-effectiveness analysis are presented in Table. 8.
It should also be noted that in the study we did not take into account the indirect costs associated with establishing disability, which are many times higher than the medical (direct and indirect) costs of treatment (especially in patients of young, working age). In addition, the costs of rehabilitation treatment for patients with stroke can significantly increase the costs of preventive treatment.
Thus, the study showed that Cerebrolysin in daily doses of 5 and 10 ml for 10 days significantly improves cognitive function and reduces the severity of asthenic syndrome and depression in patients with DE. After completion of the course of treatment, Cerebrolysin has a long-lasting trace effect, lasting up to 3-4 months due to the dosage of the treatment used. The clinical effects of Cerebrolysin are confirmed by the identified significant reduction in the rate of progression of DE, as well as a statistically significant reduction in the risk of developing TIAs and strokes. Cerebrolysin has a low percentage of side effects and is well tolerated, including by patients in older age groups.
A cost-economic analysis showed that the administration of Cerebrolysin and “basic therapy” for all dosage regimens, despite the significant cost of neuroprotective therapy, turned out to be more cost-effective compared to the cost of managing patients who received only “basic therapy” aimed at correcting risk factors development of cerebrovascular pathology, which is associated with a decrease in the rate of progression of the disease and the occurrence of exacerbations during the course of the disease - the development of TIAs and strokes.
Literature
1. Gomazkov O.A. Neurotrophic and growth factors of the brain: regulatory specificity and therapeutic potential. Sat. "Advances in Physiological Sciences". 2005; 36 (2): 1–25. 2. Gusev E.I. Skvortsova V.I. Cerebral ischemia. M.: Medicine, 2001; 248. 3. Oganov R.G. Risk factors and prevention of cardiovascular diseases. G. Quality of life. Medicine. 2003; 2: 10–15. 4. Fletcher R.I. etc. Clinical epidemiology. Fundamentals of evidence-based medicine. M.: 1998; 347. 5. Fritas G.R., Boguslavsky J. Primary prevention of stroke F neurol and psych. Stroke. 2001; Issue 1: 7–21. 6. Chukanova E.I. Encephalopathy. Diss. Doctor of Medical Sciences M.: 2005. 7. Scales, tests and questionnaires in medical rehabilitation. Rukov. for doctors and scientists co-workers / Edited by A.N. Belova and O.N. Shchepetova. M.: Antidor, 2002; 439. 8. Akai F., Hiruma S. Neurotrophic factor-like effect of FPF 1070 on septal cholinergic neurons after transections of fimbria-fornix in the rat brain. Histol Histopathol. 1992; 7:213–221. 9. Albretch E. et al. The effects of Cereblysin on survival and sprouting of neurons from cerebral hemispheres and from the brainstem of chick embryons in vitro. Adv Biosci. 1993; 87:341–2. 10. Alvarez XA et al. Cerebrolysin protects against neurodegeneration induced by -amyloid implants in rats. The international Journal of neuropsycholpharmacology. 2000a; 3:S359. 11. Argentine C., Prencipe M. The Burden of stroke: a need for prevention. In: Prevention of Ischemic Stroke/ Eds.C. Fieschi, M. Fischer. London: Martin Dunitz 2000; 1–5. 12. Bogousslavsky J. On behalf of the European Stroke Initiative. Stroke prevention by the practitioner. Cerebrovasc Dis. 1999; 9:Suppl 4:1–68. 13. Brunner LL Kanter DS Manson JE Primary prevention of stroke. New Eng J Med. 1995; 333:1392–1400. 14. Goldstein LB, Adams R, Becker K et al. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association. Stroke. 2001; 32: 280–299. 15. Leppala JM, Virtamo J, Fogelholm R, et al. Different risk factors for different stroke subtypes. Stroke. 1999; 30:2535–2540. 16. Plum F. Neuroprotection in acute ischemic stroke. JAMA. 2001; 285:1–4.
Cerebrolysin or Mexidol - which is better?
An analogue of Cerebrolysin in 5 ml ampoules is the antioxidant domestic drug Mexidol. It differs in its spectrum of action and indications.
The Mexidol analogue has an antioxidant, antihypoxic, nootropic, and anticonvulsant effect. During a course of treatment, it improves blood supply to the brain and metabolism in tissues, and reduces anxiety. Used for acute forms of cerebrovascular accidents, encephalopathy, head injury, mild cognitive and anxiety disorders. Available in ampoules and tablets to enhance the therapeutic effect. The tablet form is suitable for those patients who do not have the opportunity to use injections.
Which is better, Mexidol or Cerebrolysin, depends on the indications.
Cerebrolysin or Piracetam
Piracetam is an analogue of Cerebrolysin in tablets, capsules and injections. The drug is weaker because it has a nootropic effect, improves metabolism in brain cells, and affects the properties of blood cells.
The main indications for the use of the analogue are the treatment of cognitive impairment after a stroke or other organic brain lesions, the treatment of decreased attention, dizziness, and tinnitus. Not used for hemorrhagic stroke.
Piracetam is produced by manufacturers under the following trade names:
- Piracetam;
- Lutsetam;
- Nootropil.
It is also included in complex preparations with cinnarizine - Phezam, Nookam, Omaron.
What to choose from analogues, consult your doctor.
Cerebrolysin substitutes in tablets
There are analogues of Cerebrolysin, which are manufactured in tablet form. They are more convenient to use in outpatient and home settings. As a rule, drugs in tablets are prescribed after completing a course of injections.
Aminalon
Aminalon is a nootropic, which is made on the basis of gamma-aminobutyric acid and is used in the treatment of systemic pathologies and disorders of blood microcirculation in the vessels of the brain.
Aminalon is prescribed for:
- encephalopathy;
- head injuries;
- alcohol syndrome;
- polyneuritis;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries;
- hypertension;
- dizziness due to autonomic disorders;
- decreased memory and intelligence;
- impairment of cognitive functions;
- stroke and cerebral ischemia.
Children are prescribed for:
- birth damage to the central nervous system and cerebral palsy;
- delay in speech and intellectual development;
- Meniere's syndrome.
Do not use Aminalon:
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- if you are allergic to components in the medication and have hemophilia;
- in pediatrics up to 5 years.
Tablets should be taken orally twice a day, 2 pieces before meals. The maximum daily dosage is 2000 mg. Doses per day for children depend on age - 1-3 years - 1000 mg, 4-6 years - 1500 mg, after 7 years - 2000 mg. You also need to take the medicine twice a day. The average course of therapy is 2-4 weeks.
Side effects:
- skin allergies;
- dyspepsia;
- fluctuations in blood pressure and insomnia.
Nootropil
Nootropil is a nootropic drug, which is made on the basis of piracetam and is available in parenteral solution, capsules and tablets.
Use the medication for:
- coma due to intoxication and injury;
- decrease in memory, intelligence;
- dizziness of neurological or vascular etiology;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- alcohol withdrawal;
- sickle cell anemia in childhood;
- cortical myoclonus.
Nootropil is also used during the post-stroke rehabilitation period.
Nootropil is not used in children under 12 months of age, as well as for:
- sensitivity to the drug composition;
- insufficiency of kidney function;
- cerebral hemorrhage.
Daily doses are prescribed in accordance with the diagnosed pathology. The tablets should be taken 2-3 times per day:
- dizziness, failure of autonomic organs – 2400-4800 mg;
- myoclonus – 7200 mg, increasing to 24000 mg;
- childhood dyslexia (from 8 years old) – 3200 mg.
Adverse reactions:
- asthenia;
- depression, hallucinations, irritability and overexcitement;
- seizures and epilepsy;
- drowsiness, lethargy;
- dyspepsia;
- skin allergic reactions.
Vinpotropil
This is a cerebroprotective drug with nootropic properties. Vinpotropil expands the lumen of cerebral vessels and corrects blood flow to all parts of the brain. It is a corrector of blood microcirculation in cases of cerebral circulation disorders. The main components in the medicine are vinpocetine and piracetam.
The drug is used for:
- post-stroke condition (ischemic type);
- parkinsonism and encephalopathy;
- intoxication with ethanol and medications;
- dizziness, Meniere's syndrome and migraine pain.
- brain injuries;
- decrease in cognitive functions.
Medicine is not prescribed for:
- allergies to ingredients in the composition;
- heart rhythm disturbances and coronary artery disease;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- insufficiency of liver and kidney functions.
The drug is not used in pediatrics, during lactation and pregnancy.
Prescribe with caution when:
- disturbances in the hemostasis system and bleeding;
- hepatitis and alcoholism;
- epileptic seizures.
Vinpotropil is administered dropwise - 1-2 ampoules of medicine per 500 ml of sodium chlorine. The medication course is 10-15 days. Tablets and capsules are taken twice or thrice a day, 1 piece. Duration of therapy is 14-180 days.
Pantogam
It is produced in the form of oral syrup and tablets with the active ingredient calcium hopantenate. The drug has nootropic and anticonvulsant properties. Pantogam increases the resistance of neurons to hypoxia and the effects of toxic substances, has a sedative effect, but does not cause inhibition of psychomotor reactions.
Tablets are prescribed for:
- cognitive impairment due to damage to brain cells;
- schizophrenia;
- cerebrovascular insufficiency, which is provoked by atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- extrapyramidal disorders;
- epileptic seizures;
- psycho-emotional overload;
- decreased intelligence, memory and physical activity;
- perinatal encephalopathy and developmental retardation in children;
- Cerebral palsy and neurosis-like disorders - stuttering, tics, speech impairment.
The drug is not prescribed for:
- hypersensitivity to components;
- severe kidney pathologies;
- phenylketonuria (for syrup);
- lactation and pregnancy (for tablets);
- child under 3 years of age.
The tablets should be taken after meals (after 15-20 minutes). The standard dosage per day for adults is 1.5-3 g, for children – 0.75-3 g. The dosage should be divided into 3-4 doses. The doctor sets individual dosages for each patient, based on pathology, age and positive dynamics in treatment.
Side symptoms:
- rhinitis, rashes on the epidermis, conjunctivitis;
- drowsiness and insomnia;
- noise in ears;
- dyspepsia.
See also:
TOP 12 cheap analogues of Theraflu - Russian substitutes for the drug in tablets and powder
Cerebrolysin or Cerebrolysate
The two drugs have a similar mechanism of action and therapeutic effects and are available in ampoules. Cerebrolysate (Cellex substitute) is more effective for cerebral palsy, nerve root diseases, and after brain surgery. The route of administration is exclusively intramuscular.
Cerebrolysin is a studied Austrian drug for developmental delays in children and dementia, after a stroke. This means that as a result of clinical trials, indications, contraindications, side effects, and dosage regimens were determined. The medication is used intramuscularly, intravenously and as part of droppers. The only drawback is the high cost.
When choosing between analogues, one should take into account financial capabilities, efficiency and sufficient research.
Discuss the choice of analogues cheaper than Cerebrolysin with your doctor due to possible contraindications, side effects and nuances of prescription. Many drugs with similar effects are not sold freely in pharmacies. Before use, read the instructions for use.
Features of interaction and manufacturer's instructions
Cerebrolysin should not be combined with drugs containing lipids or agents that can change its pH. The medicine must not be mixed in one dropper, but can be used in complex therapy:
- with solutions of amino acids, vitamins;
- drugs against cardiovascular pathologies.
The abstract focuses on the following nuances:
- special care is needed when performing procedures on patients with allergies;
- the medicine is not suitable for patients with kidney failure;
- Cerebrolysin does not affect the speed of reactions, does not interfere with driving or working with complex moving mechanisms, but during therapy it is better to refrain from such tasks due to the risk of developing side effects that affect the nervous system.
After opening the ampoule, the solution must be used immediately. If there is a foreign sediment or color change in the liquid, then the medication is not suitable for use.
Answers on questions
- Cerebrolysin - prescription or not?
Yes, the drug is a prescription and is used as prescribed by a doctor. The dosage and course of treatment are also determined by a specialist.
- How is Cerebrolysin administered - intravenously or intramuscularly?
The method of administration is determined by the doctor based on the patient’s condition, severity of the disease, and age. Medicine up to 5 ml is administered intramuscularly, up to 10 ml intravenously, over 10 ml is prescribed in the form of droppers with other approved solutions.
- Does Cerebrolysin increase or decrease blood pressure?
Among the side effects when using the medicine and exceeding the dosage are arrhythmia, increased heart rate, increased or decreased blood pressure.
Adverse reactions
In exceptional cases, the drug causes non-standard symptoms. Common side effects include:
- loss of appetite;
- depression;
- state of general weakness;
- high or low blood pressure;
- pulmonary hyperventilation syndrome;
- shortness of breath;
- painful sensations in the chest;
- flu-like symptoms.
In some cases, severe emotional arousal, confusion, aggressive behavior, and sleep disturbances may occur.
Violation of the requirements for the administration of an injection solution causes:
- drowsiness, hot flashes;
- muscle tremors, increased sweating;
- cephalgia, itching, skin rashes, redness of the dermis.
Quincke's edema, anaphylaxis, and fever were occasionally recorded. The drug can cause epileptic attacks, convulsive activity, arrhythmia, tachycardia, and dyspeptic disorders.