Compound
1 tablet includes:
- Cartilago suisD4 – 300 mcg;
- Funiculus umbilicalis suisD4 – 300 mcg;
- Embryo totalis suisD4 – 300 mcg;
- Placenta totalis suisD4 – 300 mcg;
- Toxicodendron quercifoliumD2 – 540 mcg;
- Arniсa montanaD1 – 600 mcg;
- Solanum dulcamaraD2 – 150 mcg;
- Symphytum officinaleD8 – 150 mcg;
- Sanguinaria canadensisD6 – 540 mcg;
- NadidumD6 – 30 mcg;
- Coenzym AD6 – 30 mcg;
- Natrium diethyloxalaceticumD6 – 30 mcg;
- Acidum silicicumD6 – 3 mg;
- Acidum DL-α-liponicumD6 – 30 mcg.
Additional ingredients: magnesium stearate, lactose.
1 ampoule includes:
- Cartilago suisD6 – 2.2 mg;
- Funiculus umbilicalis suisD6 – 2.2 mg;
- Embryo totalis suisD6 – 2.2 mg;
- Placenta totalis suisD6 – 2.2 mg;
- Solanum dulcamaraD3 – 11 mg;
- Symphytum officinaleD6 – 11 mg;
- NadidumD8 – 2.2 mg;
- Coenzym AD8 – 2.2 mg;
- Sanguinaria canadensisD4 – 3.3 mg;
- Natrium diethyloxalaceticumD8 – 2.2 mg;
- Acidum DL-α-liponicumD8 – 2.2 mg;
- Toxicodendron quercifoliumD2 – 11 mg;
- Arniсa montanaD4 – 220 mg;
- Sulfur D6 – 3.96 mg.
Additional ingredients: water for injection, sodium chloride.
100 grams of ointment include:
- Cartilago suisD2 – 1 mg;
- Funiculus umbilicalis suisD2 – 1 mg;
- Embryo totalis suisD2 – 1 mg;
- Placenta totalis suisD2 – 1 mg;
- Rhus toxicodendronD2 – 270 mg;
- Arniсa montanaD2 – 300 mg;
- Solanum dulcamaraD2 – 75 mg;
- Symphytum officinaleD8 – 750 mg;
- Sanguinaria canadensisD6 – 270 mg;
- NadidumD6 – 10 mg;
- Coenzym AD6 – 10 mg;
- Acidum DL-α-liponicumD6 – 10 mg;
- Natrium diethyloxalaceticumD6 – 10 mg;
- Acidum silicicumD6 – 1 g.
Additional base ingredients: emulsifying cetyl stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, liquid paraffin, purified water, 96% ethanol.
Tsel T solution d/in 2.2 ml No. 5
Compound
Active substance:
- Cartilago suis D6 2.2 mg
- Funiculus umbilicalis suis (funiculus umbilicalis suis) D6 2.2 mg
- Embryo totalis suis (embryo totalis suis) D6 2.2 mg
- Placenta totalis suis (placenta totalis suis) D6 2.2 mg
- Solanum dulcamara (Dulcamara) (solanum dulcamara (dulcamara)) D3 11 mg
- Symphytum officinale (Symphytum) (symphytum officinale (symphytum)) D6 11 mg
- Nadidum (nadidum) D8 2.2 mg
- Coenzym A (coenzyme A) D8 2.2 mg
- Sanguinaria canadensis (Sanguinaria) (sanguinaria canadensis (sanguinaria)) D4 3.3 mg
- Natrium diethyloxalaceticum (Natriumdiethyloxalacetat) (sodium diethyloxalacetate) D8 2.2 mg
- Acidum DL-α-liponicum (Acidum alpha-liponicum) (acidum DL-α-liponicum (acidum α-liponicum)) D8 2.2 mg
- Toxicodendron quercifolium (Rhus toxicodendron) (toxicodendron quercifolium (Rus toxicodendron)) D2 11 mg
- Arnica montana (Arnica) (arnica montana (arnica)) D4 220 mg
- Sulfur D6 3.96 mg
Excipients: water, sodium chloride.
Indications for use
In the complex therapy of arthrosis of various etiologies, spondyloarthrosis and glenohumeral periarthritis.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active ingredients and/or to any of the excipients listed in the “Composition” section.
- Known hypersensitivity to Rhus toxicodendron or other plants of the Asteraceae family.
- Age up to 18 years due to insufficient clinical data.
Directions for use and doses
Unless otherwise prescribed, administer 2.2 ml intramuscularly (contents of 1 ampoule) 2 times a week. The dose, frequency of administration and duration of treatment are prescribed by the doctor. The average course of treatment is 4-5 weeks. A repeat course is possible after consultation with a doctor.
Storage conditions
Store in a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of the reach of children!
Best before date
5 years. Do not use after the expiration date.
special instructions
With caution:
Liver diseases, with simultaneous intake of hepatotoxic substances. When taking homeopathic medicines, existing symptoms may temporarily worsen (primary worsening). In this case, you should stop taking the drug and consult your doctor.
If side effects not described in the instructions for medical use occur, you should stop taking the drug and inform your doctor.
Description
Homeopathic medicine used for pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Dosage form
Colorless, transparent, odorless liquid.
Use in children
Contraindicated for people under 18 years of age.
Action
A multicomponent homeopathic medicine, the effect of which is determined by the components included in its composition.
Side effects
Allergic reactions are possible.
In cases of intolerance to Rhus toxicodendron and plants of the asteraceae family (for example, arnica), a reaction accompanied by fever, redness, and pain at the injection site can extremely rarely develop.
For medicines and formulations containing sanguinaria, isolated cases of increased blood activity of “liver” enzymes (transaminases) and bilirubin values are described in the literature. In very rare cases, gastrointestinal disorders. If side effects are detected, you should stop taking the drug and consult your doctor.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The use of the drug is possible if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus and child. A doctor's consultation is required.
Interaction
Prescribing complex homeopathic medicines does not exclude treatment with other medicines.
Overdose
Cases of overdose have not been reported to date.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The drug does not affect the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions (including driving vehicles, working with moving mechanisms).
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Goal T belongs to the group of homeopathic remedies with complex action, which is determined by the effects of all its constituent ingredients of mineral and biological origin.
The drug is characterized by chondroprotective, anti-inflammatory, regenerative and analgesic effectiveness, based on the normalization of the functionality of intra-articular processes, as well as the activation and development of the protective forces and reserves of the human body.
The ingredients of the drug actively participate in the regenerative processes occurring in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system , relieve pain , help reduce swelling around the damaged joint, improve its mobility and enhance the production of chondrocytes , stimulating their mitosis .
Indications for use
All dosage forms of Target T are indicated for use, both in monotherapy and in combination with other drugs, in the treatment of:
- arthrosis of various origins ( gonarthrosis , spondyloarthrosis , polyarthrosis );
- consequences of fractures and injuries ;
- glenohumeral periarthritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- metabolic osteopathies;
- tendinopathy and chondropathy ;
- cervical migraine;
- heel spurs;
- rheumatic pathologies ( Reiter's syndrome , rheumatoid polyarthritis );
- lumbosacral disorders.
An integrated approach to the treatment of osteoarthritis: in focus Goal T
The incidence of diseases increases with age. The most common joint disease is deforming OA, observed in 97% of cases, especially in people over 65 years of age. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the prevalence of arthritis and chronic joint diseases in different age groups is as follows: 18-44 years old - 19%, 45-64 years old - 42%, over 65 years old - 59% . Thus, after 50 years, arthrosis occurs in 27.1%, and after 70 years – in 90% of the population. In recent years, there has been a pronounced “rejuvenation” of the disease [1]. A survey of 3660 respondents aged 40–49 years showed that more than half of them (71%) suffer from joint pain, 52.3% report joint pain, and even among 20-year-olds they occur in 4% of cases [2]. Today, the leading pathological mechanism causing the destruction of cartilage is considered to be a violation of the metabolism of proteoglycans - proteins that make up the main substance (matrix) of cartilage. Articular cartilage consists of an intercellular matrix (collagen and proteoglycans) and a cellular component represented by chondrocytes [3]. Matrix preservation is important for chondrocytes, since it is the matrix that forms the biophysical “layer” through which articular structures are nourished. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a) are pro-inflammatory cytokines and, if their activity is not balanced, they are capable of inducing the formation of other substances such as nitric oxide radicals or prostaglandin E2, which are factors development of inflammation. If this happens, the degree of cartilage degradation becomes higher than the repair activity [4].
Of particular importance for the normal functioning of cartilage is the ratio of collagen, proteoglycans, non-collagenous glycoproteins and water in the tissue. 90% of cartilage proteoglycan is aggrecan, the molecule of which consists of a protein core with chains of chondroitin sulfate (CS), keratin sulfate and hyaluronic acid attached to it. This structure of aggrecan provides high hydrophobicity, which, combined with low viscosity, helps counteract the load on the joint [4]. During the degenerative-dystrophic process, the amount of cholesterol sharply decreases, which leads to cartilage degradation [3]. CS is a substance that is normally part of articular cartilage and plays an important role in maintaining the necessary osmotic pressure, due to which the matrix and collagen threads stretch, and has a chondroprotective, chondrostimulating pharmacological effect that stimulates regeneration [5]. CS is involved in the construction of the basic substance of cartilage and bone tissue and thus improves phosphorus-calcium metabolism in cartilage tissue. By inhibiting enzymes that disrupt the structure and function of articular cartilage, it inhibits the processes of degeneration of cartilage tissue. Having a stimulating effect on the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, it normalizes the metabolism of hyaline tissue, promotes the regeneration of cartilage surfaces and the joint capsule. Prevents compression of connective tissue, increases the production of intra-articular fluid and mobility of affected joints, slows down bone resorption, reduces calcium loss and accelerates bone tissue repair processes, inhibits the progression of OA [5].
The condition of cartilage depends on the balance of anabolic and catabolic processes. The intensity of catabolic processes is enhanced by cytokines (IL-1, TNF-α, cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, metalloproteinases (collagenase, stromelysin) produced by both chondrocytes and cells of the synovial membrane and subchondral bone. Constant renewal of the matrix is carried out through the secretion of cytokines or chemical messengers such as IL-1 and TNF-a, which activate various metalloproteinases (matrix metalloproteinases). Proteinases (collagenase and hyaluronidase) dissolve collagen fibers and proteoglycans. This process is balanced by the activity of transforming growth factor (TGF-β), which is secreted by Th3 -cells. TGF-β, on the contrary, stimulates chondrocytes to synthesize proteoglycans and collagen and to secrete metalloproteinase inhibitors. Thus, constant renewal of cartilage occurs [4].
With OA, the matrix loses the constituent parts of proteoglycans - glycosaminoglycans from various zones of cartilage. This leads to disintegration and splitting of the matrix, changes in the processes of diffusion of metabolites in it, dehydration, disorganization and rupture of collagen fibers. The key role in this case is given to chondrocytes - highly differentiated cells of cartilage tissue, which, for reasons that are not fully understood, in OA begin to produce “incomplete” low-molecular-weight proteins of the matrix (intermediate tissue of cartilage), which reduces its shock-absorbing properties [4].
OA therapy should be complex, differentiated, long-term and systematic. It is necessary to take into account the variety of factors that caused the disease, its stage, features of the clinical course, and the degree of dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system. The optimal combination is considered to be a combination of non-drug, including physical rehabilitation (limiting the load, using additional support, reducing body weight, increasing the strength of the muscles stabilizing the affected joint, orthopedic disorders), and medicinal treatment methods. The main goals of OA therapy are: reducing pain; improving the function of the affected joint, reducing the degree and frequency of disability; preventing or slowing the progression of the disease and its complications; improving the quality of life (QoL) of patients [3]. The goal of therapy for OA is primarily to relieve pain. At the same time, attempts are being made to stop or at least slow down the progression of damage to the cartilage tissue of the joint. In some cases, patients with chronic arthritis need to constantly take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the main mechanism of action of which is to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes and block the COX enzyme of arachidonic acid metabolism [2]. Unfortunately, this group of drugs is characterized by pronounced side effects, which manifest themselves primarily in the digestive tract. The highest prevalence of OA is observed in elderly people with concomitant diseases that require drug therapy. This creates additional difficulties in patient management. Side effects are also typical for a new class of NSAIDs - COX-2 inhibitors. Frequency of gastrointestinal symptoms when using NSAIDs: dyspepsia - up to 50% of cases, stomach ulcer - 15% of cases, duodenal ulcer - 11%, severe damage to the digestive tract - more than 2%. 25% of all bleeding cases in patients over 60 years of age are caused by taking NSAIDs. The search for a new alternative to NSAIDs for the treatment of arthrosis still remains relevant [1].
According to the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR), 2003, the use of NSAIDs and chondroprotectors in the treatment of OA is the most effective (evidence class 1A) [3]. Chondroprotectors are structural elements (glycosaminoglycans) of natural cartilage tissue, necessary for the construction and renewal of articular cartilage, and can have a modifying effect on the course of the disease, inhibiting inflammation in the joint tissues. They act very slowly and are used for a long time. To obtain a real therapeutic effect, it takes at least 4–6 months. treatment, 2–3 courses throughout the year. These studies were confirmed by studies on experimental models. L. Chen et al. (2011) conducted a comparative study to evaluate the chondroprotective effect of injectable forms of cholesterol on an experimental model of OA in 28 rabbits [6]. During the study, a positive response to the treatment of OA was obtained, realized through 3 main mechanisms: 1) stimulation of the production of the outer cellular matrix (protein glycan, cholesterol, hyaluron); 2) suppression of inflammatory mediators (myeloperoxidase, N-acetyl-glucosaminidase, collagenase, hyaluronidase, elastase) and 3) inhibition of cartilage degeneration. There are short reports (clinical case), the results of clinical and multicenter studies, indicating the effectiveness of the homeopathic drug Cel T in the treatment of OA. Goal T is a multicomponent preparation that includes minerals, plant and biological ingredients. It has chondroprotective and chondrostimulating, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, restorative and immunostimulating effects [7, 8]. The composition of the drug Tsel T includes sulfur, which takes part in the synthesis of the structural elements of cartilage tissue; the drug also promotes the production of synovial fluid, thereby improving the functional characteristics of the joint and metabolic processes in the cartilage.
It has been experimentally proven that Target T contains flavonoids known for their antioxidant properties. The components of the drug influence the release of IL-6 by macrophages, which play a leading role in the development of chronic inflammation and angiogenesis [1]. An animal experiment showed that treatment with Cel T for induced arthrosis led to less cartilage erosion than in the control group. At the same time, the level of vascularization of the deep layers of cartilage was many times lower than in the comparison group. It is emphasized that Target T has the ability to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor. The effectiveness of motor therapy with Tzel T tablets has been confirmed by numerous studies: the drug was prescribed in a dose of 1 to 3 tablets/day, depending on the clinical manifestations of OA. The duration of treatment ranged from 6 to 10 weeks. and more; the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect increased with the duration of treatment. The best results were obtained in the treatment of grade 1–2 OA [1]. In practical recommendations G.N. Bagirova et al. (2003) showed the effectiveness of using Goal T in the treatment of gonarthrosis based on an analysis of comparative studies [9]: group 1 of patients received diclofenac 75 mg/day, nicotinic acid, and physiotherapeutic treatment; Group 2 – diclofenac 75 mg/day, nicotinic acid, physiotherapeutic treatment + Goal T, 1 tablet 3 times/day for 4 weeks. Efficiency assessment indicators: reduction in joint pain, palpation pain in the joint, stiffness, joint volume, increase in range of motion, reduction in the time the patient travels a straight distance, the time of going up and down stairs. The effectiveness of treatment in group 1 was 60%, the time of onset of exacerbation after a course of treatment was 3 months; in group 2 – 90%, time of onset of exacerbation after a course of treatment – 6–12 months. Thus, this study demonstrated an increase in the degree of effectiveness of therapy for gonarthrosis with the introduction of the drug Cel T into complex therapy.
The drug Cel T has been studied for its effect on COX-1 and COX-2 and has shown both high efficacy and excellent tolerability in arthritis. The action of Goal T is not limited to a regulatory decrease in the activity of COX-1 and COX-2, leading to a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, but due to the presence of catalysts, organ extracts and mineral components, it covers all aspects of the process of cartilage destruction (Fig. 1) [8]. In biochemical studies M. Stancikova (1999) [10] assessed the antihomotoxic properties of the drugs Tsel T and Tsel compositum in vitro, which showed the effect of these drugs on the activity (reduction by up to 70%) of the most aggressive enzyme of inflammation - leukocytelastase, which belongs to lysosomal proteinases synthesized during inflammation by leukocytes, in particular neutrophils. In addition to the ability to destroy elastin, elastase cleaves polysaccharide chains from the protein residue of the proteoglycan. The negative effects of elastase are most pronounced in rheumatoid arthritis and OA, since it poses a threat to articular cartilage, which is rich in proteoglycans. Based on the results of the study, the author concluded that since elastase plays a large role in the inflammatory process (in particular, in rheumatoid arthritis) and there are no clinically applicable specific inhibitors for it, in some cases the therapeutic use of the drug Cel T can be recommended.
In a clinical cohort study conducted by R. Gottwald et al. (2000), the effectiveness of the injectable form of Cel T in the treatment of arthritis was assessed [11]. The study included 100 patients with painful knee joints. Characteristics of the group: 78% were women, 68% were over 60 years old, 58% of patients had concomitant diseases (hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, cardiomyopathy), in 69% of cases the duration of the disease was more than 2 years, 12% of patients had bilateral damage to the knee joints; in 91% of cases, treatment was carried out before the study (NSAIDs, chondroprotective and corticosteroid drugs, electro- and balneotherapy). All patients received Cel T injections periarticularly 2 times/week. 1 ampoule. In the majority of patients (58%), the duration of therapy was 4–6 weeks; in 72%, Tzel T was prescribed as monotherapy; in the remaining cases, combination therapy (physiotherapy, etc.) was prescribed. The effectiveness of therapy was assessed by the intensity of symptoms (stiffness, pain with movement and at rest) on a 4-point scale (no pain, mild, moderate and severe) and on a 5-point scale for assessing patient therapy. During the period of 10 injections, the intensity of symptoms significantly decreased in 89% of cases, 67% of patients reported that the first symptoms of improvement were noted in the 2-5th week. Clinical improvement was noted in 84% of cases; patients assessed the effectiveness of therapy as “very good” in 24%, “good” in 37%, and “average” in 24%. 96% of patients completed the full course of therapy. The authors concluded that therapy for OA of the knee joints by administering Cel T periarticularly in the vast majority of patients (92%) leads to a significant clinical reduction in the severity of symptoms after the 2-5th injection and has a good safety profile.
In a clinical study by A. Lesiak et al. (2001) assessed the effectiveness of the injection form of the drug Cel T in the treatment of arthritis [12]. The study involved 523 patients (71% women, 29% men) with arthritis of different locations: knee joint (53%), spine (30%), hip (29%), shoulder (13%), fingers ( 7%), ankle (6%), others (5%). The duration of the disease was 1–10 years (38% – more than 5 years). All patients received injections of Cel T intra-articularly, periarticularly or intramuscularly. Efficiency assessment was carried out after the 6th injection (significant improvement in clinical manifestations was noted in 66%) and after the 10th injection (94%). The authors came to the conclusion that intra-articular, periarticular or intramuscular administration of Cel T in 94% significantly improves the condition of patients with arthritis of various localizations after the 10th injection; in 2/3 of the patients in the study group, improvement occurred after the 6th injection.
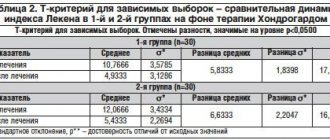
U. Maronna et al. (2002) conducted a randomized, double-blind, controlled, multicenter clinical trial of 121 patients with arthritis of the knee joints (mild and moderate) [13]. Patients were prescribed Cel T tablets and diclofenac at a daily dose of 25 mg 3 times a day. The duration of therapy was 10 weeks. The effectiveness was assessed using the WOMAC index. During the study, equal therapeutic efficacy of the studied drugs was noted, while no side effects (cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, etc.) were observed with the drug Cel T. H. Birnesser et al. (2003) conducted a prospective controlled multicenter cohort study involving 592 patients suffering from knee OA in stages I and II of activity [14]. Patients were prescribed the homeopathic chondroprotector Cel T 3–5 tablets/day (n=323) and a COX-2 inhibitor (celecoxib 100–200 mg or rofecoxib 12.5–25 mg/day) (n=269). The duration of the study was 6–10 weeks. The effectiveness of therapy was assessed using the WOMAC index (0 – no restrictions, 100 – severe restrictions) (Fig. 2). The study found that the drugs used had similar efficacy rates against knee OA. Both groups are comparable in the severity of clinical manifestations. After 4 weeks in both groups there was a significant decrease in symptoms. The improvement in the control group was somewhat more pronounced, which is explained by the rapid effect of COX-2 inhibitors, after another 2 weeks. The treatment results in both groups were absolutely identical. The results on the WOMAC scale coincided with this. After 4 weeks. COX-2 inhibitors had a greater effect on pain, but after 6 weeks. treatment results in both groups were similar. Significant differences were noted regarding drug tolerability. In 90.5% of cases of treatment with Target T, tolerability was assessed as “excellent”. When treated with COX-2 inhibitors, tolerability was “excellent” in 74% of patients. There were no undesirable effects of treatment with Target T. During the use of COX-2 inhibitors, they were noted in 3 cases (diarrhea with vomiting, dizziness and nonspecific manifestations of the gastrointestinal tract).
In the observation of CW Engelbert (2006), who described the condition of a 39-year-old patient who suffered from severe right-sided coxarthrosis [2], taking painkillers and NSAIDs (diclofenac at a dosage of up to 150 mg/day, paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid) did not have the desired effect. The patient was offered endoprosthetics, which the patient refused. In search of an alternative, the patient was prescribed periarticular injections of the complex homeopathic drug Cel T (2 times per week, 2 ampoules for 6 weeks). Additionally within 2 weeks. the patient received Cel T tablets orally (2 tablets 3 times a day) and 5 sessions of auriculopuncture. During the course of treatment, the drug was also injected into trigger points (mm. gluteus maximus, gluteus medium, piriformis) and acupuncture points. After 2 weeks from the start of treatment there was a marked decrease in pain; in 4 weeks gait became normal, pain disappeared; after 6 weeks Only Purpose T was prescribed, 1 tablet 3 times a day. Despite the fact that the acute manifestations of the pathology were stopped, the intake of Cel T tablets was continued. Every year a series of periarticular injections and acupuncture courses were carried out. When observed for 10 years, the patient remains physically active, goes in for sports, and no pain syndrome is noted. The author concluded that, despite the diagnosis and recommendations for endoprosthetics, alternative therapy with the homeopathic drug Tsel T helped to avoid surgery.
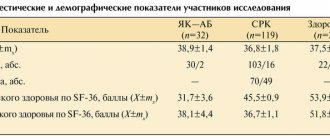
At the Department of General Medical Practice of the Orenburg State Medical Academy O.Yu. Maiko et al. (2009) conducted a study in which 281 patients with OA of the knee and hip joints in the acute stage were observed for 2 years [15]. The purpose of the study was to assess the quality of life of patients with OA during therapy with NSAIDs (group 1) and in combination of NSAIDs with a chondroprotector: chondroitin sulfate or Tsel T (comparison groups). The age of patients in the group as a whole was 41–65 years, 71% were women, Kellgren stages of OA were I, II and III. The study showed a significant improvement in clinical parameters (VAS scores at rest and during movement, Lequesne indices, WOMAC, QoL) from the 3rd month. from the start of treatment in groups where chondroprotectors were used in combination with NSAIDs. There was also significant clinical improvement in most of the studied parameters after 12 and 24 months. from the start of treatment, only 2–3 clinical parameters and 3 quality of life indicators did not differ significantly from the baseline. Thus, the authors came to the conclusion that with NSAID monotherapy, all studied indicators were significantly worse than in groups with the addition of a chondroprotector.
A number of comparative studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of different forms of the drug Tsel T [9]: − R. Vodic et al. (1995) showed that the effectiveness of using Cel T ointment for OA is 75.1%; − G. Nahler et al. (1996), M. Weiser et al. (1996) demonstrated that the use of Target T 2 injections/week. within 4–5 weeks. intra-articularly for gonarthrosis helps reduce pain and morning stiffness; efficiency is 80%; − M. Weiser (2001) showed that when prescribing Zel T, 1 tablet 3 times a day (compared to diclofenac 75 mg/day) for 10 weeks. A progressive decrease in pain was noted, the results were equivalent. Very often, injections of Tzel T are combined with the drug Traumeel S. At the same time, their actions are not opposed, but, on the contrary, it is noted that Traumeel S is recommended to be prescribed for injuries and acute inflammation, and Tzel T – for degenerative changes, when it is especially effective. In a study involving 900 patients, Cel T was administered together with the drug Traumeel S in a 1:1 ratio intra-articularly or periarticularly, the full course was 10 injections over 2 weeks. (5 injections/week) [16]. In patients with initial manifestations of OA (stage 1), after 2–3 injections, in 80% of cases the pain significantly decreased or disappeared altogether. The duration of remission in 73% of patients was 1 year. In 27% of cases due to the appearance of pain after 6 months. The drug was administered intramuscularly 2 times/week. (10 injections in total), a positive effect was achieved. In the studies of I.S. Roller (1996), A.E. Radzevich (1998) showed that the combined use of Cel T and Traumeel S intra-articularly in patients with OA complicated by synovitis or periarthritis has anti-inflammatory, anti-exudative, analgesic effects without side effects (unlike glucocorticoids) [9].
Conclusion. Based on a number of studies, we can conclude: the main significance of Goal T is that it has a chondroprotective and chondrostimulating effect, activates the synthesis of chondrocytes, increases the hydrophilicity of cartilage and the nucleus pulposus, thereby ensuring their resistance to stress [17]. The drug Tsel T, both in monotherapy and in combination with other drugs, is effective for OA of any etiology and location. Target T can be used as a drug of choice in the treatment of OA due to its complex action. Its effectiveness has been confirmed in numerous clinical studies, and it can either act as an alternative to existing NSAIDs or complement complex treatment regimens (including glucosamine, cholesterol, etc.). The excellent safety profile of the drug allows it to be prescribed to elderly patients with multiple organ damage if it is impossible to prescribe NSAIDs.
References 1. Kavalersky G.M., Silin L.L. Application of Goal T in orthopedics for the treatment of degenerative diseases (analytical review) // Biological Medicine. 2011. T. 17. No. 2. P. 38–47. 2. Engelbert K. A safe alternative to NSAIDs // Biological medicine. 2006. No. 2. P. 62. 3. Lygina E.V. Chondroprotectors in the treatment of osteoarthritis // Modern rheumatology. 2012. No. 2. P. 59–64. 4. Bagirova G.G., Maiko O.Yu. Osteoarthritis: epidemiology, clinic, diagnosis, treatment. M.: Arnebia, 2005. 224 p. 5. Shavlovskaya O.A. Review of foreign literature on the use of chondroitin sulfate // RMJ. 2012. T. 20. No. 34. P. 1678–1682. 6. Chen L., Ling PX, Jin Y., Zhang TM Hyaluronic acid in combination with chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid improved the degeneration of synovium and cartilage equally in rabbits with osteoarthritis // Drug Discov Ther. 2011. Vol. 5. No. 4. R. 190–194. 7. Purpose T: instructions for use. URL: https://www.rlsnet.ru/tn_index_id_3517.htm. 8. Purpose T: instructions for use. URL: https://www.arnebia.ru/cgi-bin/index.cgi. 9. Bagirova G.G., Maiko O.Yu., Popova O.V. Osteoarthrosis: a modern view of the problem: A textbook for sixth-year students of the Faculty of Medicine, general practitioners, and interns. M., 2003. 10. Stancikova M. Hemmung der Leukozytenelastase-Aktivit in vitro mit Zeel T, Zeel comp. und ihren verschiedenen potenzierten Bestandteilen // Biologische Medizin. 1999. Vol. 28(2). R. 83–84. 11. Gottwald R., Weiser M. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee with Zeel T // Medicina Biologica. 2000. Vol. 13(4). R. 109–113. 12. Lesiak A., Gottwald R., Weiser M. Skutecznosc kuracji preparatem Zeel T w iniekcjach dostawowych okolostawowych i domiesniowych w chorobie zwyrodnieniowej stawow // Medycyna Biologiczna;kwiecień czerwiec zeszyt. 2001. Vol. 2. R. 30–36. 13. Maronna U. et al. Oral treatment of arthritis of the knee with Zeel® comp. – The results of a double-blind equivalence study versus diclofenac // Biological Therapy Fall. 2002. R. 10–11. 14. Birnesser H., Klein P., Weiser M. Modernes Homöopathikum ist COX 2-Hemmern ebenbürtig // Der Allgemeinarzt. 2003. Vol. 25. No. 4. R. 261–264. 15. Maiko O.Yu., Bagirova G.G. The influence of a course of treatment with the use of chondroprotectors and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the quality of life of patients with osteoarthritis // Clinical Medicine. 2009. T. 87. No. 4. pp. 47–54. 16. Stepanova L.V. Practical experience of antihomotoxic therapy of joint diseases in a sanatorium // Biological Medicine. 2000. No. 1. P. 49–50. 17. Zeel T. Effective, safe and natural therapy for osteoarthritis and rheumatic joint diseases // Product Monograph. 2013. 36 rub. Biologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH. Baden-Baden, Germany. First Edition: February. 2013.079216.
Contraindications
All pharmacological forms
- hypersensitivity to the ingredients of the drug (especially to the aster family and Rhus toxicodendron).
Tablets Purpose T
- diseases associated with sugar intolerance ;
- age up to 18 years.
Target T injections
- age under 18 years;
- liver pathologies , parallel use of hepatotoxic drugs (with extreme caution).
Ointment Purpose T
- skin diseases;
- age up to 6 years;
- damage to the skin in the area of application.
Side effects
Zeel T tablets
- allergic manifestations (if symptoms are detected, treatment should be interrupted and the doctor should be informed).
Ampoules Zeel T
- with hypersensitivity to the aster family and Rhus toxicodendron - redness, increased temperature;
- with sensitivity to sanguinaria - an increase in bilirubin values and transaminase activity;
- pain at the injection site;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- allergic manifestations (if symptoms are detected, treatment should be interrupted and the doctor should be informed).
Zeel T ointment
- allergic manifestations on the skin (if symptoms are detected, you should interrupt treatment and inform your doctor).
special instructions
For all dosage forms
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. Does not affect.
For solution for intramuscular administration and homeopathic lozenges
When taking homeopathic medicines, existing symptoms may temporarily worsen (primary deterioration). In this case, you should stop taking the drug and consult your doctor. If side effects not described in the instructions for medical use occur, you should stop taking the drug and inform your doctor.
For lozenges and ointments for external use homeopathic
Depending on the severity of the disease, in agreement with the doctor, it is possible to include other dosage forms of the drug in the treatment regimen, as well as the drug Traumeel S®.
Additionally for homeopathic lozenges
Information for patients with diabetes: carbohydrate content in 1 table. of the drug corresponds to 0.025 XE. Tablets should be protected from moisture. Close the pencil case immediately after using the drug.
Additionally for ointment for external use homeopathic
Protect from overheating. The tube should be closed immediately after using the drug. Avoid contact of the ointment with the eyes and mucous membranes.
Instructions for use Purpose T
Tablets Purpose T, instructions for use
Tablets (granules) are intended for use sublingually (under the tongue) until completely dissolved, regardless of food. As a rule, taking 1 granule three times every 24 hours is indicated. Duration of treatment for gonarthrosis and arthrosis is 5-10 weeks; for glenohumeral periarthritis and spondyloarthrosis – 1 month; in other cases - as prescribed by a doctor.
Target T injections, instructions for use
The injection solution is used for intradermal, intraarticular, intramuscular, subcutaneous, paravertebral, periarticular, intraosseous administration. Basically, intramuscular or intra-articular injections are carried out in a dose of 2.2 ml (1 ampoule) twice every 7 days, for 4-5 weeks. In other cases - as prescribed by a doctor.
Ointment Purpose T, instructions for use
The instructions for Zeel T ointment suggest the use of the medicine in this pharmacological form only for local (external) use. A little ointment should be applied to the skin in the area of the problem joint (can be under a bandage), rubbing in slightly, at intervals of 2-3 times every 24 hours.
For gonarthrosis and arthrosis , the duration of applications is 5-10 weeks; for glenohumeral periarthritis and spondyloarthrosis – approximately 1 month; in other cases - as prescribed by a doctor.
Directions for use and doses
Homeopathic solution for intramuscular administration: i/m. Unless otherwise prescribed - 2.2 ml (contents of 1 amp.) IM 2 times a week. The dose, frequency of administration and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor. The average course of treatment is 4–5 weeks. A repeat course is possible after consultation with a doctor.
Opening the ampoule. The contents in the ampoule head should be shaken off by lightly tapping (the colored dot should be at the top). After this, the upper part of the ampoule is broken off by pressing on the colored dot.
Homeopathic lozenges: orally, keep in mouth until completely dissolved - 1 tablet. 3 times a day.
Course of treatment: for arthrosis and gonarthrosis - 5–10 weeks; for spondyloarthrosis and glenohumeral periarthritis - about 4 weeks.
Ointment for external use, homeopathic: externally, unless otherwise prescribed, for adults and children over 12 years of age, apply 4–5 cm of ointment to the skin in the area of painful joints and rub in with light movements 2–3 times a day. It is possible to apply a gauze bandage.
Course of treatment: for arthrosis - 5–10 weeks, for spondyloarthrosis and glenohumeral periatritis - about 4 weeks.
Analogs
Level 4 ATX code matches:
CONDROnova
Gialgan Fidia
Bishofite
Movex Comfort
Traumeel S
Artra
Incena
Alflutop
Piascledine 300
Chondroitin Complex
Glucosamine-Chondroitin
Rumalon
For tablets
- Arthrofoon;
- Artra;
- Traumeel S;
- Kondronova;
- Chondroflex;
- Tazan;
- Chondroxide;
- Structum;
- Artron , etc.
For injection solution
- Alflutop;
- Discus compositum;
- Biartrin;
- Traumeel S;
- Rumalon;
- Sinoart , etc.
For ointment
- Artrin;
- Traumeel S;
- Viprosal;
- Capsicam;
- Chondroitin;
- Nayatoks;
- Espaul;
- Chondroxide;
- Finalgon;
- Chondroflex , etc.
Reviews about Target T
The most popular forms of Zeel T are ointment and injection solution. Reviews of Target T ointment, as well as reviews of Target T injections, are overwhelmingly positive.
Many patients note a significant improvement in the condition of their joints and other problem areas of the musculoskeletal system, especially when using the ointment and solution in combination.
Among the negative aspects of treatment, the most discussed is the injection procedure, which, when the solution is administered intra-articularly, paravertebrally or periarticularly, is actually somewhat painful. Reviews about the tablets are not so numerous, but in 90% of cases they are also positive.
Let us remember that homeopathic medicines require a continuous course of therapy, and visible improvement in the condition is not observed as quickly as when using traditional medicines. But due to the virtual absence of side effects and a fairly long-lasting effect, these drugs have recently become increasingly popular.
Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the joints and spine rank first in prevalence among all diseases of the musculoskeletal system [16]. Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the joints, characterized by primary damage to the articular cartilage and further involvement in the process of the subchondral bone and surrounding soft tissues (joint capsule, ligaments, synovium). OA (arthrosis) accounts for 60–70% of all joint diseases; 10–12% of the population suffers from arthrosis. The incidence of diseases increases with age. Thus, after 50 years, arthrosis occurs in 27.1%, and after 70 years – in 90% of the population. In recent years, there has been a pronounced “rejuvenation” of the disease. A survey of 3660 respondents over 40 years of age showed that more than half of them (71%) suffer from joint pain at the age of 40–49 years, 52.3% report joint pain, and even in 20-year-olds they occur in 4% of cases [29 ].
Despite the huge number of studies devoted to the treatment of arthrosis, according to a number of authors, for the majority (up to 75%) of patients, treatment does not bring significant relief and their quality of life remains unsatisfactory [6]. In everyday practice, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are most widely used for the relief of pain and inflammation. When treating OA with drugs, it is necessary to take into account that we are talking mainly about long-term use of drugs, more often in older patients of age groups. In addition, simultaneous use of several drugs increases the risk of side effects by 3.5 times [35].
The side effects of NSAIDs are well known. They are most common with long-term use and are most often associated with damage to the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and impaired renal function. The following symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract are noted when using NSAIDs: dyspepsia - up to 50% of cases, stomach ulcer - 15%, duodenal ulcer - 11%, severe damage to the digestive tract - more than 2%; 25% of all bleeding cases in patients over 60 years of age are caused by taking NSAIDs [35]. According to other data, with long-term use of these drugs, 70% of patients develop damage to the gastric mucosa, 15–30% develop gastric ulcers, 5% experience bleeding and perforation, and 0.17% of patients die from complications. 11 thousand hospitalizations per year are associated with the use of NVPS [35]. Despite preventive measures, the frequency of hospitalizations per year due to complications of therapy (bleeding, ulcers, perforation) is 10.7 thousand in Germany, 12 thousand in the UK, and 70 thousand cases in the USA. Every year, 1100–2200 people die from NVPS in Germany, 4000 in the UK, and 16 thousand patients in the USA. Similar effects are also characteristic of a new class of NSAIDs—cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors [29]. It is believed that the safety of COX-2 inhibitors from the digestive tract is exaggerated [35], so the search for an alternative to NSAIDs remains one of the urgent tasks in the treatment of OA.
Goal T is a multicomponent preparation that includes minerals, plant and biological ingredients. It has chondroprotective and chondrostimulating, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, restorative and immunostimulating effects. The drug promotes the production of synovial fluid, thereby improving the functional characteristics of the joint and metabolic processes in the cartilage. Purpose T is available (Baden-Baden, Germany) in the form of injection solution, sublingual tablets and ointment. The company recommends simultaneous or sequential use of all three dosage forms of the drug.
Treatment with the drug Tzel T refers to pathogenetic therapy, because not only has an anti-inflammatory effect, but is also aimed at correcting the mechanisms of pathology. Thus, organ components ensure the restoration of cartilage tissue, plant ingredients have a complex anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, sulfur and silica hydride are involved in the metabolism of cartilage, and biocatalysts activate cellular respiration and redox processes in tissues, thereby improving their regeneration and normalizing metabolism.
It has been experimentally proven that Cel T contains flavonoids known for their antioxidant properties [37]. The components of the drug influence the release of interleukin-6 (IL-6) by macrophages, which plays a leading role in the development of chronic inflammation and angiogenesis. In an animal experiment, it was shown that treatment with Cel T for induced arthrosis resulted in less cartilage erosion than in the control group [42]. At the same time, the level of vascularization of the deep layers of cartilage was many times lower than in the comparison group. It has been emphasized that Cel T has the ability to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor [30, 31].
One of the most important issues in the treatment of OA is the effect of drugs on the morphofunctional state of articular cartilage. To assess the condition of joint cartilage, X-ray diffraction and birefringence methods are used [33, 38]. With their help, the morphofunctional state of articular cartilage is assessed in the treatment of stage 1–4 gonarthrosis using intra-articular administration of the drug Tzel T 1–2 times a week (treatment duration is up to 3 months). When examining biopsy material (articular cartilage) taken before and after the end of the course of treatment with Cel T, a reduction in erosion and a decrease in the degree of mineralization are clearly visible; calcium phosphate tubercles and stalked bodies were reduced or absent altogether. The peaks indicating sclerosis of the cartilage also disappeared, which indicated revitalization of the articular cartilage.
The conducted studies revealed a positive effect of therapy on the morphofunctional state of articular cartilage. This was especially noticeable in the reduction of erosion, extensive new formation of integumentary cartilage, and the presence of interference inherent in cartilage in the stage of active regeneration [3].
Intra-articular administration of the drug Cel T is widespread and has been well reflected in the scientific literature [34, 41]. At the same time, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effects, improvement of the metabolism of the synovial membrane and the composition of the synovial fluid have been proven, which has a beneficial effect on cartilage regeneration [41].
In a study involving 900 patients, the drug Cel T was administered together with the drug Traumeel S in a 1:1 ratio intra- or periarticularly, the full course was 10 injections over 2 weeks (5 injections per week) [23]. It should be noted that Tzel T is indicated for degenerative changes, and Traumeel S for inflammation. In patients with initial manifestations of OA (stage 1), after 2-3 injections in 80% of cases, pain significantly decreased or disappeared altogether. The duration of remission in 73% of patients was a year. In 27% of cases, due to the appearance of pain after 6 months, the drug was administered intramuscularly 2 times a week (10 injections in total), as a result of which a positive effect was achieved.
In patients with grade 2 OA, after 4–5 injections, a sharp exacerbation of the pain syndrome was noted. After the 7–8th injection, the pain disappeared, the distance traveled increased 5–6 times. All patients with arthrosis of the 2nd degree received a repeat course after 6 months with additional rubbing of Cel T ointment and subsequent preventive treatment annually.
In case of OA of the 3rd degree, it was only possible to reduce pain to some extent and increase mobility; in all cases, injection therapy was combined with physical methods of treatment. Thus, the high effectiveness of injection therapy with Cel T and Traumeel S for OA of the 1st and 2nd degrees has been proven.
O.I. comes to the same opinion. Rybachuk, S.I. Gerasimenko et al. Tzel T was administered 2 times a week for grade 1-2 OA intra-articularly or periarticularly for gonarthrosis, intraarticularly for coxarthrosis and periarticularly for arthrosis of the subtalar joint. The duration of treatment was 6–8 weeks.
By the end of the first week there was a significant improvement, and by the end of the course there was clinical remission, which lasted more than six months.
In 5 cases, the course of treatment was repeated after 6 months due to exacerbation of the disease.
The authors came to the conclusion that intra-articular or periarticular administration of Tzel T in the early stages of degenerative-dystrophic joint lesions significantly improves the condition of patients, helps restore the disturbed functional balance in cartilage by activating anabolic and suppressing catabolic processes.
The dosage of the drug Tzel T for intra-articular injections ranges from 1 ampoule for arthrosis of the 1st degree to 2 for arthrosis of the 2nd and 3rd degrees, 1-2 times a week. However, some authors recommend up to 5 injections per week [23]. Vast clinical material has proven the high efficiency and safety of intra-articular injections Goal T. Nevertheless, the desire to get away from intra-articular injections prompted the authors to develop methods for periarticular administration of the drug.
Thus, B. Potrafki [18] presents the results of observation of 350 patients with gonarthrosis of varying degrees of severity, who were prescribed periarticular injections for 12 weeks. Injections were made into painful points of the periarticular bursa and into the places of attachment of ligaments. Dosages were 1 ampoule for mild arthrosis, 2 ampoules 2 times a week for moderate and severe arthrosis.
The patients' condition was assessed based on clinical testing of joint function and pain. No side effects were noted. All patients tolerated periarticular injections well, treatment results were assessed as very good, and drug tolerability was excellent. The author came to the conclusion that periarticular injections of Cel T are comparable in effectiveness to intra-articular injections, and there is no risk of joint infection. Other authors provide similar data on the effectiveness of periarticular injections [8, 13, 23, 49].
Very often, injections of Cel T are combined with Traumeel S [10, 22, 23, 39]. At the same time, the authors do not contrast the effect of these drugs, noting that Traumeel S is recommended to be prescribed for injuries and acute inflammation, and Target T is recommended for degenerative changes, when it is especially effective [27].
Researchers note that due to the different types of effects on the mechanisms of acute and chronic inflammation inherent in degenerative diseases, the combined use of Tzel T and Traumeel S is considered quite justified: Tzel T - for long-term treatment, Traumeel S - at the onset of the disease and during its exacerbation [40] . At the same time, it is emphasized again and again that both drugs have an excellent tolerability profile.
The effectiveness of motor therapy with Tzel T tablets is confirmed by the results of numerous studies: the drug is prescribed in a dose of 1 to 3 per day, depending on the clinical manifestations of OA. The duration of treatment ranges from 6 to 10 weeks or more [32]. With the duration of treatment, the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects increase. The best results were obtained in the treatment of grade 1–2 OA [39].
Of particular interest are the results of a multicenter examination of 498 patients with degenerative joint diseases with the inclusion of Cel T ointment in therapy [4]. The most common indication for the use of the ointment was monoarthrosis; in addition, it was prescribed for poly-, spondyloarthrosis and other degenerative diseases of the joints. Depending on the manifestations of a specific pathology, additional drug and non-drug therapy was prescribed. Most often, ointments were used without a bandage, sometimes with a bandage. In some cases it was used in combination with iontophoresis. The frequency of rubbing the ointment ranged from 1 to 5 times a day, more often – 3, less often – 5 times. In the vast majority (75.9%) of cases, the ointment was used in the form of motor therapy, in 12.1% it was combined with Cel T injections, in 8.8% with taking Cel T tablets. All three forms of the drug were used simultaneously in 3.2% cases. All patients received non-drug therapy: exercise therapy (physical therapy), cryo-, electrotherapy, massage, etc. In some cases, drug therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs, local analgesics, corticosteroids, etc. was additionally prescribed.
Already by the 3rd day of treatment, the total pain index decreased noticeably; from days 3–10, a gradual decrease in the total pain index was observed, which persisted until the end of the observation period (more than a month). During therapy, a significant improvement in the patients' condition was noted: cessation of pain at night and when moving. The best results were obtained in the treatment of monoarthrosis. But in other degenerative diseases, a decrease in the pain index was noted already in the first days of using the ointment, and subsequently the pain gradually decreased until the end of the study.
Analysis of observations showed that the effectiveness of therapy with ointment and ointment in combination with other forms of Cel T or other options for drug therapy did not differ from each other. At the same time, the reduction in pain intensity in patients who additionally received physiotherapeutic treatment (PTT) occurred faster. Moreover, the effect of FTL manifested itself only from the second week of treatment. The therapeutic effect of Cel T ointment was observed in 92.6% of cases, incl. 75.1% were rated “good” or “very good.”
Another study compares the effectiveness of using Cel T ointment using iontophoresis and intra-articular administration of the drug. Based on the data obtained, the authors come to the conclusion that both routes of administration of the drug are highly effective, noting a long-lasting analgesic effect [6]. Tolerability of the ointment is “good” in 95.6% of cases [4].
As already noted, one of the most important areas of conservative therapy for degenerative diseases remains the search for an alternative to the use of NSAIDs. Numerous studies have been conducted on the comparative effectiveness of treatment of rheumatic joint diseases with Zel T and NSAIDs [35]. In all studies, the WOMAC index was used as a comparison criterion, with the help of which the advantages of Zel T were confirmed. This applies to comparisons with both diclofenac and COX-2 inhibitors. No side effects from the Cel T drug were noted in any case.
Let us present the results of one of these numerous studies [32]. 592 patients with grade 1–2 gonarthrosis were observed, 323 of them received Cel T for 6 to 10 weeks in an amount of 1 to 3 tablets per day. In the comparison group, 269 patients received COX-2 inhibitors celecoxib 100–200 mg or rofecoxib 12.5–25.0 mg. Both groups were comparable in the severity of clinical manifestations.
After 4 weeks, a significant decrease in symptoms was noted in both groups. The improvement in the condition of patients in the control group was somewhat more pronounced, which is explained by the rapid effect of COX-2 inhibitors; after another 2 weeks, the treatment results in both groups were absolutely identical.
The results on the WOMAC scale coincided with this. After 4 weeks, COX-2 inhibitors had a greater effect on pain, but after 6 weeks of treatment, the results were similar in both groups.
Significant differences were noted regarding drug tolerability. In 90.5% of cases, the tolerability of Target T was assessed as “excellent”. When treated with COX-2 inhibitors, tolerability was “excellent” on the part of 74% of patients. There were no side effects during treatment with Cel T. During the use of COX-2 inhibitors, they were noted in 3 cases and were characterized by diarrhea with vomiting, dizziness and nonspecific manifestations of the gastrointestinal tract.
One of the advantages of Goal T is the following: it can be successfully used in combination with traditional treatment of OA [14]. A comparative assessment of the effectiveness of treatment of gonarthrosis using the traditional method was carried out, namely: with the use of NSAIDs (diclofenac 25 mg 3 times a day); Nikoshpana, 1 tablet 3 times a day; vitamins, compresses with dimexide, FTL (in the comparison group) with the main group, which was added to the treatment with Target T, 1 tablet 3 times a day. The total duration of treatment in groups was 4–5 weeks. Initially, the pain syndrome was approximately the same in both groups (65.3 VAS in the control group and 63.3 VAS in the main group). By the end of treatment in the Cel T group, pain was almost 2 times less than in the comparison group (24.0 and 41.4, respectively). A year after treatment in the control group, pain increased to 56, while after combining traditional treatment with Target T, the pain syndrome changed virtually little [5, 27].
When traditional complex treatment was combined with the drug Cel T, there was a significantly more pronounced decrease in the severity of synovitis than in the control group, and the clinical effect persisted throughout the entire observation period. According to ultrasound examination (ultrasound), in contrast to the control group, there was a significant increase in the number of joints with a normal synovial membrane and a decrease in tendivitis of all muscle tendons.
The use of the drug Cel T did not lead to an increase in the side effects of treatment [14, 15]. Using the drug Tzel T together with NSAIDs allows you to reduce the dose of the latter and reduce their negative impact on the body.
The study of economic costs in the treatment of NSAIDs with complications from their use, on the one hand, and Goal T, on the other, showed that the transition to therapy with the latter can contribute to significant savings in financial resources. From a medical point of view, such a change is completely justified for mild to moderate severity of arthrosis, especially taking into account the duration of therapy, when the absence of side effects comes to the fore [35].
Another study compared chondroprotective therapy for OA using chondroitin sulfate and Cel T in combination with NSAIDs if necessary [15]. Treatment results in all groups were approximately the same. At the same time, the costs of treatment with chondroprotectors significantly exceeded the cost of therapy with the drug Tzel T. The author came to the conclusion that from a clinical and economic point of view, a combination of a course of treatment, including nimesulide and Tzel T, is advisable.
Thus, the drug Tsel T, either in the form of motor therapy or in combination with other drugs, appears to be effective for OA of any etiology and any location. The predominance of publications on the treatment of arthrosis of the knee and hip joints is explained primarily by the frequency of damage to these joints and the particular severity of clinical manifestations. It is the knee and hip joints that are the most disabling localization of OA. Due to gonarthrosis, 10% of people over 55 years of age lose their ability to work [39]. The drug is effective for both primary and secondary arthrosis, regardless of the number of affected joints. The best results were obtained with OA of 1–2 degrees. The best effect of using ointments is achieved in the treatment of monoarthrosis.
Among degenerative lesions, periarthropathic shoulder syndrome occupies a significant place. The process is most often associated with spinal osteochondrosis. Target T is usually used in chronic cases [17, 27]. In the study, the drug was administered 2 times a week, 1-2 ampoules, perifocally and into trigger zones; to enhance the effect, Cel T was additionally prescribed in the form of tablets and ointments. FTL and exercise therapy were also used. Efficacy was assessed 2–4–6 weeks after the start of treatment. The tolerability of Target T was assessed as good, and the high therapeutic efficacy of the drug in the treatment of periarthropathic shoulder syndrome was proven [9, 17].
Thus, the drug Cel T is widely used for the treatment of degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system. All authors noted its high tolerability. Not a single case of a side effect of the drug has been described.
Target T has good anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, which allows us to recommend it as a complete alternative to NSAIDs. This is especially important with long-term use of the drug, when taking NSAIDs causes significant side effects. If necessary, Purpose T can be used in conjunction with COX-2 inhibitors, which reduces the likelihood of the latter having a negative effect on the body. However, the main significance of Goal T is that it additionally has chondroprotective and chondrostimulating effects, activates chondrocytes, increases the hydrophilicity of cartilage and nucleus pulposus, thereby ensuring their resistance to stress. The drug promotes the production of normal synovial fluid, thereby improving friction characteristics in the joint and metabolic processes in cartilage, and has an immunostimulating effect. The drug affects the pathogenesis of the disease and is basic in the treatment of degenerative lesions. The drug is used in the form of intramuscular, intraarticular, periarticular, paravertebral injections, homeosiniatry (introduction into biologically active points), mesoinfiltration (subdermal injections into painful points), in the form of tablets and ointments.
The advantages of Goal T treatment include the following: it can be carried out both in a hospital and on an outpatient basis. Depending on the objectives, Target T can be combined with other antihomotoxic agents and other drugs.
Goal T can be successfully used in the practice of not only an orthopedic traumatologist, but also a surgeon, neurologist, therapist, arthrologist and rheumatologist.
Price Target T, where to buy
Today you can buy this medicine in Moscow in the following price range:
- the average price of Target T ointment is 600 rubles;
- the average price of Target T injections is 1000 rubles (the price of 1 ampoule is 250 rubles);
- The average price of Target T tablets is 400 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Aim T tablets sublingual.
50 pcs. Biologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH RUR 519 order - Purpose T solution for intramuscular injection. 2.2ml 5 pcs Biologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH
RUB 1,094 order
- Goal T ointment 50gBiologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH
RUR 751 order
- Purpose T ointment d/nar. approx. homeopathic 100gBiologische Heilmittel Heel
RUB 1,092 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Goal T ointment 50g Biologische Heilmittel Hell
RUR 707 order
- Purpose T ampoules 2.2 ml No. 5Biologische Heilmittel Hell
RUB 813 order
- Target T tablets No. 50Biologische Heilmittel Hell
481 rub. order
- Purpose T ampoules No. 100Biologische Heilmittel Hell
RUB 16,907 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Goal T 50 g ointment Biologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH, Nimetchina
292 UAH.order - Goal T N50 tablets Biologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH, Nimecchina
186 UAH order
- Goal T 2 ml N10 solution for injection Biologische Heilmittel Heel GmbH, Nimecchina
960 UAH. order
Release form
Homeopathic solution for intramuscular administration. 2.2 ml in ampoules of colorless glass of hydrolytic class I. Each ampoule is marked with a notch and a colored dot. 5 amp. placed in an open plastic blister pack. 1 or 20 open plastic blister packs (5 or 100 amps each) are placed in a cardboard pack.
Homeopathic lozenges. 50 tablets each in a white polypropylene case with a polypropylene lid. A label is glued to each pencil case and placed in a cardboard box.
Homeopathic ointment for external use. 50 g in an aluminum tube with a screw cap made of propylene. Each tube is placed in a cardboard pack.