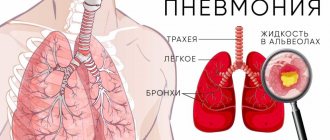
Pulmonary sclerosis is a disease in which lung tissue is replaced by connective tissue. Pulmonologists at the Yusupov Hospital, based on a comprehensive examination, identify the cause of sclerosis of the lung tissue and carry out effective therapy for the disease that caused it.
Pulmonary sclerosis can be local or diffuse. Pathological changes often form in the following diseases or accompany them:
- chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases;
- infectious, viral and fungal diseases of the lungs;
- pneumoconiosis;
- genetically determined lung diseases;
- injuries and consequences of penetrating chest wounds.
If their treatment is ineffective, prerequisites for the development of sclerosis arise in the lung tissue. Among the provoking factors of the disease, heart failure, pulmonary thrombosis, the influence of ionizing radiation, and dysfunction of the immune system should be noted.
With incomplete resolution of the inflammatory process in the lungs, connective tissue grows, which leads to pneumosclerosis. Similar changes in lung tissue are observed after pulmonary tuberculosis. Diffuse sclerosis develops in patients suffering from Hamman-Rich syndrome. In this case, the lung resembles a honeycomb. With mitral valve stenosis and cardiac left ventricular failure, fluid leaks from the blood vessels, which leads to cardiogenic pulmonary sclerosis.
Description
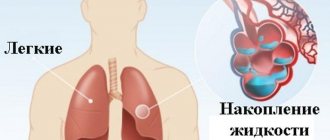
Pneumosclerosis is a pathological process characterized by the replacement of pulmonary connective tissue, which is accompanied by impaired elasticity and gas exchange in the affected areas.
The process is irreversible; the condition gradually worsens due to the proliferation of connective tissue, which is unable to perform the functions assigned to the lung tissue. Such a progressive process requires medical attention, because without treatment there is a threat of disability and even death from complications. Pneumosclerosis develops as an outcome of inflammatory or dystrophic lung diseases, and is more common in men aged 50 years and above.
There are limited and diffuse pneumosclerosis, which differ in the prevalence of the pathological process in the lungs. Diffuse pneumosclerosis is much more severe due to the large volume of damage to the lung tissue.
Based on the severity of replacement of pulmonary connective tissue, the following are distinguished:
- pneumofibrosis – precedes pneumosclerosis, characterized by alternation of airy lung tissue and altered areas;
- pneumosclerosis - compaction and replacement of the lung parenchyma with connective tissue;
- pneumocirrhosis – develops as an outcome of pneumosclerosis, characterized by complete replacement of the lung tissue, vessels, bronchi with connective tissue, compaction of the pleura, as a result of which the lungs decrease in size, which leads to a displacement of the mediastinal organs towards the lesion.
Pneumosclerosis can be the outcome of the following diseases:
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), chronic bronchitis;
- past infectious lung diseases;
- injuries and wounds of the chest, including the lungs;
- pulmonary sarcoidosis;
- prolonged course of pleurisy;
- foreign bodies in the bronchi;
- hereditary lung diseases.
Despite the various causes of pneumosclerosis, the mechanism of the disease remains the same for everyone. It consists of a violation of the ventilation function of the lungs and the drainage function of the bronchi, and is also accompanied by impaired lymph and blood circulation. Such changes can lead to the development of chronic respiratory failure, so it is important not to ignore the symptoms of respiratory diseases, but to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Pathogenesis
During the inflammatory process, the lung tissue does not receive oxygen. Reactions are triggered in the body, as a result of which connective tissue consisting of collagen fibers appears in place of the affected lung parenchyma. It is important to monitor the level of saturation in the blood and its normality in order to understand how well the lungs are working.
It is dense, inelastic, and unable to properly expand and fill with air. The condition is aggravated by sclerotic changes that affect the bronchi and blood vessels. The replaced areas become dense and airless.
Healthy tissue also suffers, trying to ensure respiratory function at the proper level, the alveoli expand and increase in volume. Diffuse pneumosclerosis provokes the development of emphysema (overfilling with air).
Symptoms
Photo: ceemax.in
The severity of the symptoms of the disease depends on the severity of the process, which, in turn, depends on the volume of affected lung tissue. Focal (local) pneumosclerosis usually does not manifest itself in any way, and for quite a long time a person does not suspect its presence. Sometimes patients with focal pneumosclerosis complain of a slight cough with scanty sputum. Diffuse pneumosclerosis is more severe, since the pathological process covers a large volume of lung tissue. The first symptom that a person notices is shortness of breath. Initially, it appears only after intense physical exertion. In this case, a person does not immediately suspect the possibility of illness and does not consult a doctor, since even healthy people may experience shortness of breath after prolonged exercise. However, the condition gradually worsens, shortness of breath begins to bother you when lightly running, walking, and even at rest. In addition, people with diffuse pneumosclerosis are bothered by a cough. At first it is rare, then it becomes intrusive with the release of mucous or mucopurulent sputum.
Against the background of these specific symptoms, general symptoms are observed in the form of weakness and increased fatigue, leading to decreased ability to work, and the disease is often accompanied by a decrease in body weight.
Due to a decrease in the volume of functioning lung tissue, chronic respiratory failure gradually occurs. Externally, this condition manifests itself as cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin). Depending on the stage of chronic respiratory failure, the localization of cyanosis varies. For example, at the subcompensated stage, blueness of the lips and fingers and toes is observed. During the decompensation stage, cyanosis spreads to large areas of the body.
Diagnostics
Photo: likar.info
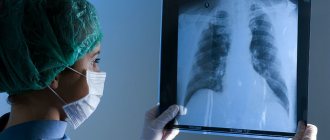
At each appointment, the doctor performs a general examination of the patient, with the help of which the person’s condition is preliminarily assessed. With pneumocirrhosis, you can detect a deformation of the chest, which will be noticed not only by the doctor, but also by the patient himself. By auscultating the lungs, the doctor listens for weakened breathing, wet and dry rales. It should be noted that such an auscultation picture is characteristic of diffuse pneumosclerosis; with focal pneumosclerosis, the results of auscultation of the lungs differ little from the norm. Next, the doctor writes out a referral for an X-ray examination of the lungs. With the help of this study, it is possible to detect changes in the lung tissue, assess their prevalence and severity. An x-ray reveals an increase in the pulmonary pattern; with cirrhosis, a decrease in the size of the affected part or the whole lung is determined, due to which the mediastinal organs shift to the affected side. The lower parts of the lungs can take on the appearance of a porous sponge, in which case the lung is called “honeycomb”. A more detailed assessment of the structure of the lung tissue is provided by CT and MRI.
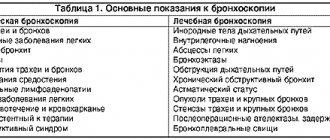
With pneumosclerosis, the volume of normally functioning lung tissue decreases, as a result of which the lungs do not cope 100% with their immediate functions. To establish this, an assessment of external respiratory function is prescribed. This research method helps to assess the ventilation function of the lungs using graphical recording and subsequent processing of the obtained data on a computer. Using a test with bronchodilators (dilators that dilate the lumen of the bronchi), it is possible to identify reversible or irreversible bronchial obstruction. Bronchoscopy can also detect this phenomenon. This endoscopic technique aims to visualize the tracheobronchial tree.
Disease prognosis
A prognosis for complete recovery cannot be given. Changes in lung tissue are irreversible. Therapy is aimed only at stopping or slowing down the pathological process as much as possible and achieving a normal quality of life for the patient and maintaining his ability to work. It is important at what stage the disease was detected and how much lung volume is affected.
With timely treatment, normal life and ability to work can be extended by 10-15 years. With pneumocirrhosis, the prognosis is unfavorable, the patient faces disability.
A complete cure is impossible, but with proper treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, you can live a full life for many years, maintaining your ability to work.
- NCBI. Lung texture on serial chest computed tomography: correlation with radiologist-determined severity of acute changes after radiation therapy. / [url] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Chronic lung diseases. Federal program. RMJ, 2001
- Gasteva Z. A., Neshel E. V., Uspenskaya V. G. Pneumofibrosis and pulmonary emphysema. — 1965.
- Vasilenko V.Kh. Propaedeutics of internal diseases. — 2001.
Author: Shirokhova Natalya Pulmonologist, immunologist, allergist
Treatment
Photo: sanatoriy-kirova.ru
To prevent the development of pneumosclerosis, you should promptly treat respiratory diseases, take precautions when interacting with pneumotoxic substances, and do not delay going to the doctor if characteristic symptoms occur. When working in hazardous industries, it is important to use respirators that prevent dust and chemicals from entering the respiratory tract. In addition, the immediate production management must take care of the proper operation of exhaust ventilation.
When diagnosing pneumosclerosis, treatment begins with lifestyle changes. First of all, it is recommended to stop smoking, as cigarettes can aggravate bronchial obstruction. All family members must understand that there is a concept of passive smoking, so it is important not only for the patient himself to forget about cigarettes, but also for the people living in the same living area. Meals should be fractional, complete, sufficiently filled with vitamins and microelements. Despite the fact that pneumosclerosis is accompanied by shortness of breath, especially when playing sports, you should not completely give up physical exercise. It is necessary to arrange long distance walks and perform therapeutic exercises.
Considering that with pneumosclerosis, the lungs cannot fully provide the body with the necessary amount of oxygen, oxygen therapy is used. This treatment helps saturate the blood plasma with oxygen, which leads to a decrease in the severity of shortness of breath. However, safety rules should be observed, since frequent or excessive use of pure oxygen or inhalation mixtures with high oxygen concentrations can lead to oxygen intoxication.
For the symptomatic treatment of cough, expectorants are used to promote the separation of sputum. For the same purpose, mucolytic agents are prescribed, which dilute sputum, thereby facilitating its removal.
Disease prevention
There are several methods of prevention: primary preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of pneumosclerosis, and secondary ones are aimed at preventing the worsening of the disease and the development of relapses when the disease is put into stable remission.
Preventive methods are mainly aimed at the formation of nonspecific immunity. It is recommended to consume sufficient amounts of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, think through your diet, provide walks in the fresh air and other ways to strengthen the immune system.
It is equally important to undergo an annual fluorographic or x-ray examination in a timely manner. These techniques make it possible to suspect the development of pneumosclerosis in the early stages, as well as monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
To prevent the spread of this lung pathology, it is important to strictly adhere to the regimen of taking medications prescribed by a pulmonologist for treatment.
Medicines
Photo: proizjogu.ru
Medicines are not able to relieve the patient of pneumosclerosis; they only alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Cough with pneumosclerosis is unproductive; to correct this, expectorants and mucolytics are prescribed. Ambroxol is the most common drug due to its low cost and sufficient effectiveness. The drug achieves its effect by stimulating the glands of the bronchial mucosa. This increases the content of the mucous component of sputum, which facilitates its release. The drug is well tolerated, side effects are extremely rare. For example, in case of individual intolerance to the components of the drug, an allergic reaction develops, which can manifest itself as urticaria or angioedema. Other side effects observed less frequently are: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headaches, general weakness.
Bromhexine is another drug that is used to thin phlegm. Not for use in children under 3 years of age and pregnant women (1st trimester). In all other cases, there are no strict contraindications to the use of the drug. People who have an allergic reaction to the active substance, bromhexine hydrochloride, should be treated with caution. Such people should notify their doctor in advance about the presence of an allergy to a previous drug intake, so that the doctor can select another drug with the desired effect.
Folk remedies
Photo: s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws
It should be understood that pneumosclerosis is an irreversible process, therefore it is impossible to completely cure it, but you can improve your overall well-being. To improve the function of external respiration and strengthen the body, physical therapy exercises are recommended. Classes should be conducted in the morning, duration is 20 – 40 minutes. Particular attention should be paid to breathing exercises that train the inhalation and exhalation phases. General strengthening exercises are performed with the involvement of various muscle groups participating in the exercises alternately. The pace of classes should be slow with a gradual increase to medium; a fast pace is contraindicated. Physical therapy begins with a minimum load and gradually increases to the maximum tolerated. Patients with pneumosclerosis get tired faster than healthy people, so they independently indicate the maximum tolerated load, referring to subjective sensations.
To reduce the severity of shortness of breath and cough, there are various traditional medicine recipes. In the fight against shortness of breath, tea made from reeds (brooms) has proven itself well. To prepare it you will need 1 glass of crushed raw materials, which is poured with 1 liter of boiling water. After steeping, the tea is ready to drink. It is recommended to take 1 glass three times a day. The course is at least 3 weeks.
There is a recipe for a tincture based on honey, lemon and garlic. To prepare, you will need 1 liter of liquid honey, 10 lemons and 10 heads of garlic. Honey should be mixed with peeled and minced garlic, add lemon juice. This mixture must be thoroughly mixed, closed in a jar and allowed to brew in a dark place for 1 week. Take 4 teaspoons per day once. A special feature of the application is the fact that the mixture should not be swallowed immediately, it should be kept in the mouth, slowly dissolving. The full course of use is 2 months; after a break, you can repeat the dose if necessary.
The most popular folk recipe for cough is a glass of warm milk with honey. You can drink this drink during the day at any time convenient for you; it is especially recommended to take it at night so that coughing attacks do not disturb your sleep.
There is another assistant that alleviates the general condition and eliminates cough. To prepare it, you need to boil 1 lemon for 10 minutes, after which it should be cut in half, squeeze out the juice and combine with 2 tablespoons of glycerin. Next, honey is added in such an amount that the glass is filled almost to the top. The resulting syrup is used 1 teaspoon several times a day.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.