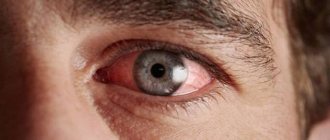
Donovanosis (granuloma inguinale, granuloma venereum) is a classic, chronic sexually transmitted disease. It is caused by the bacterium Klebsiella granulomatis (formerly called Calymmatobacterium granulomatis). It is found endemically in underdeveloped countries in tropical and subtropical regions. In the United States, blacks are seven times more likely to be infected than whites. People living in poor socio-economic conditions are most often affected.
Klebsiella granulomatis is a gram-negative bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Penetrating through the skin, it causes an inflammatory reaction that can lead to the destruction of infected tissue. As part of the inflammatory focus, bacteria are localized inside tissue macrophage cells (Donovan bodies). Donovan Taurus is named after Charles Donovan. He was the first to discover them.
The bacteria are an integral part of the physiological intestinal flora and can very easily be transmitted to the genital area through autoinoculation or sexual intercourse.
The first known name for this condition was "serpiginous ulcer", dating back to 1882. The correct clinical term used today for donovanosis is granuloma inguinale. Granuloma is a type of inflammatory reaction that occurs as a result of injury or infection.
Incubation and symptoms of donovanosis
The content of the article
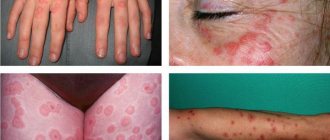
The incubation period - the time from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms - is long and lasts from 10 to 40 days. It manifests itself by the appearance of small painless nodules in the area of the external genitalia (vulva, penis).
Subsequently, the skin over the change ruptures and ulceration of the granulomatous bottom occurs. It spreads by autoinoculation and affects the perineal area, anal area and groin. The ulcers are usually painless and relatively clean. Inguinal lymphadenopathy, an enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes, is also often present.
Treatment of donovanosis
Antibiotic treatment is very effective. This is why the incidence of this classic sexually transmitted disease is very low in developed countries (about a hundred cases per year are reported in the United States), in contrast to underdeveloped regions where the availability of antibiotics is limited.
Treatment is usually with the following antibiotics:
- sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim (Sinersul) orally for 14 days;
- doxycycline (vibramycin, chiramycin) per os for 14 days;
- azithromycin (Sumamed) orally for 7 days;
Although improvements in the condition appear after the first week of taking antibiotics, treatment should be completed completely to reduce the number of relapses.
Effective preventive measures include:
- avoiding sexual contact with people at risk, especially in endemic areas;
- preventive testing for sexually transmitted diseases.
Causes and timing of appearance
The formation of chancre most often occurs 3 to 5 weeks after infection with syphilis. The beginning of this process indicates the transition of the disease from the incubation to the primary stage. Syphiloma is where the causative agent of the disease, Treponema pallidum, entered the body of an infected person. Here it begins to actively reproduce, because for this it requires an ambient temperature of 37 degrees.
If you do not take countermeasures, the disease will progress, and there will be much more treponemes. The secondary and tertiary periods are syphilis without chancre. However, other characteristic external symptoms appear, and the carrier of the disease becomes dangerous to others.
For the formation of a chancre, it is necessary that the causative agent of syphilis penetrate into the tissues of a healthy person. This is possible under the following circumstances:
- unprotected sexual contact;
- use of non-sterile medical and cosmetic instruments;
- the presence of damage to the skin and mucous membranes upon contact with the patient;
- kiss;
- using other people's things;
- blood transfusion and surgical procedures.
Promiscuous sexual intercourse most often leads to infection with sexually transmitted diseases, including syphilis.
If syphiloma is in the oral cavity of a sick person, then you can get infected from him even through a kiss.
Unsafe sex remains the main route of transmission. Also at risk are representatives of medical professions and drug addicts.
Ulcus molle (chancroid, soft chancroid)
Ulcus molle is a classic sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi. Usually found in the tropics - Africa, Asia, Central and South America. The disease occurs 20 times more often in men than in women. Chancroid is particularly important in the context of HIV (AIDS), given the high incidence of both diseases in Africa.
Haemophilus ducreyi is a rod-shaped gram-negative bacterium. In cell culture it takes the form of multirow chains.
Diagnostics
To carry out successful treatment, it is important to detect syphilis chancre in time and begin treatment of the disease. Before prescribing drug therapy, it is necessary to verify the correctness of the diagnosis, since the possibility of false suspicions cannot be excluded.
The following types of studies can be used for diagnosis:
- ELISA;
- Wasserman reaction;
- microprecipitation reaction;
- RIBT;
- REEF;
- passive hemagglutination reaction;
- serological tests.
Syphilis is confirmed by the presence of treponema pallidum in tissue scrapings, as well as antibodies to it in blood samples. Based on the results of tests and physical examination, one can judge the extent of the infection.
It is also necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of the following diseases (depending on the location of the chancre and the presence of accompanying symptoms):
- angina;
- herpes;
- candidiasis;
- tuberculosis;
- traumatic erosions.
Clinical picture of chancroid
Incubation (time from infection to onset of symptoms) is usually 3-5 days. A small spot appears at the site of penetration. The next day a pustule (purulent vesicle) forms on it; after a few hours it ruptures, and small ulcers with a bottom filled with pus are formed. The sores are painful to the touch, and the surrounding skin is often erythematous and edematous (red and swollen). New ulcers around the primary ulcer may result from manual transmission of infection (autoinoculation). The so-called kissing ulcers located opposite each other. In more than 50% of patients, regional lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes) occurs within 7 days.
Areas prone to ulceration
For men:
- the inner part of the foreskin;
- glans penis;
- external urethral opening;
- coronary sulcus;
- bridle.
For women:
- labia majora;
- entrance to the vagina.
Patients who simultaneously suffer from scabies or genital herpes may experience 50 to 60 ulcers at the same time.
Treatment of chancroid
When prescribing therapy, it should be taken into account that the sensitivity of Haemophilus ducreyi to antibiotics varies in different geographical regions.
Ceftriaxone is considered the most effective. It is administered once intramuscularly.
Alternative drugs are azithromycin per os, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole per os, erythromycin per os for 7 days.
Hospitalization is recommended for patients, as rest prevents the occurrence of lymphadenopathy.
Sexual partners should be treated simultaneously with one of the mentioned therapeutic methods.
Lymphogranuloma venereum - symptoms
Lymphogranuloma venereum occurs in men five times more often than in women. The disease is characterized by a relatively long incubation period (the time from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms), amounting to two weeks or more.
A primary, often very small, ulcerative lesion appears on the external genitalia. Accompanied by regional enlargement of lymph nodes. Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area often merge and can form fistulas (a fistula is an unnatural narrow channel connecting a pathological lesion or organ to the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, or two or more organs together).
Prices for services
Initial appointment with a urologist FOR MEN + ultrasound of the prostate gland (assessment of complaints, medical history, if necessary, rectal digital examination, ultrasound of the prostate gland in men)
Primary appointment – visiting a doctor of a specific specialty for the first time. Includes a conversation with the patient, an initial examination, anamnesis, if necessary, a digital rectal examination, and an ultrasound of the prostate gland. The price is valid from 02/01/2021 The price is not valid for appointments at the branches of Bolshevikov Ave. and Prosveshcheniya Ave. Make an appointment
900 ₽
Repeated appointment with the urologist
Make an appointment
700 ₽
Lymphogranuloma venereum - complications
Late complications can occur several years after the initial lesion:
- Elephantiasis is a syndrome characterized by elastic, hard swelling of the legs (ivory) or external genitalia. This occurs with chronic stagnation of lymph due to inflammatory (filariasis, lymphogranuloma venereum) or non-inflammatory factors. It is important to treat the underlying disease; conservative (compression bandages, massage) and surgical (lymphatic drainage) treatment is also used.
- Genital strictures are cicatricial narrowings that occur as a result of injury or inflammation.
- “Identification reaction” on the skin is an allergic reaction to an inflammatory focus.
- Erythema multiforme is an increased change in the skin, usually the size of a smaller or larger coin. Color varies from light red to brownish red. The central part quickly recedes and becomes pale in color, while the edges of the change persist, retaining a reddish hue.
- Erythema nodosum - manifests itself as painful nodules on the legs. It is more common in young people, especially women. This is an allergic reaction to various microorganisms and medications. During treatment, it is important to eliminate the predisposing factor. The prognosis is very good.
Types of formations and their features
A typical chancre makes it quite easy to diagnose the disease.
In this case, syphilomas can be classified according to a number of criteria:
| Classification category and photo | Main types |
| According to quantitative characteristics, chancre can be single or multiple. |
|
| According to the degree of penetration into the tissue structure
|
|
| To size
|
|
| of various shapes. |
|
| Depending on the nature of its location, chancre can be located in different parts of the body. |
|
Atypical forms
It is much more difficult to diagnose syphilis if the chancre manifests itself in an atypical form. That is why the final diagnosis can only be made by a qualified doctor.
The most common variants of atypical syphilomas are:
| Title and photo | Short description |
| chancre-herpes
| The manifestations are similar to balanoposthitis; the foreskin and head of the penis are affected, as well as sometimes the lips (can also be observed in the oral cavity). |
| Syphiloma felon
| It is located on the fingers, closer to the nail plate, which can provoke its rejection. There is a pronounced inflammatory process. |
| Amygdalite
| One of the pharyngeal tonsils is affected, there are no erosive changes in the mucous membrane, no pain. All this allows us to differentiate the problem from a sore throat. |
| Indurative syphiloma
| Tissue swelling occurs, affecting areas near the chancre. When pressing on the neoplasm, no visible marks remain. |
Such chancrees not only complicate the diagnostic process, but are also accompanied by various complications. In addition, they are characterized by the presence of pain, although with syphilis this symptom is extremely rare.
Chancroid
A special form of skin formation is chancroid - soft chancre. It appears under the influence of streptobacilli, it does not contain the causative agent of syphilis, Treponema pallidum.
Characteristic signs of such a neoplasm are:
- soft edges of the ulcer, lack of a hard base;
- the presence of a pain symptom;
- erosion color – bright red;
- there is copious purulent discharge;
- peeling of the skin;
- the appearance of small ulcers independent of the chancroid, which can merge with it into a single focus of inflammation.
Due to the active reproduction of streptobacilli and their spread through the bloodstream, the patient exhibits signs of general intoxication of the body: nausea, headaches and dizziness, malaise. The inflammatory process increases body temperature.
Unlike hard chancre, soft chancre is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact. In addition, after healing it leaves noticeable scars, which is associated with severe inflammation of the superficial lymph nodes and the formation of bubonic ulcers, as well as their opening. Syphiloma disappears almost without a trace.